- Current Issue
- Adopt Most Downloaded Most Read Archive
-
LI Rongrong, SUN Xin, HUANG Kai, ZHAO Zhimin, PENG Yuan, LIU Chenghai
2023,31(12):1519-1529, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 001
Abstract:
Objective To observe the characteristics of C57BL/6N-Tg (1. 28HBV) / Vst transgenic hepatitis B virus (HBV-Tg) model mice and analyze their transcriptomic characteristics. Methods Twenty male HBV-Tg mice were divided into an experimental group and a wild-type ( control) group ( n= 10 mice per group). The virological characteristics of the model mice were evaluated according to serum levels of HBV DNA, HBsAg, and HBeAg, and expression levels of HBsAg and HBcAg in liver tissue. Serum levels of alanine transaminase ( ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and Sirius red staining, and hydroxyproline(Hyp) in liver tissue were detected to evaluate the degree of liver inflammation and fibrosis. Liver tissue samples were randomly selected from three mice in each group for RNA extraction for high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. Significantly differentially expressed genes were identified using R software. Functional enrichment of differential genes was determined by Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses, and genes with significant differences were verified by real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Results ALT and AST levels were increased in the model group compared with the normal group, with the result for ALT being more significant (P< 0. 05). HE staining of liver tissue showed enlargement of the liver nucleus and swelling of some hepatocytes in the model group, while Sirius red staining showed a small amount of collagen deposition in the sink area and interlobule in the HBV transgenic group, in the shape of thin lines. A total of 1352 differential genes were obtained by screening ( | logFC | > 2 and P.adj < 0. 05), including 703 up-regulated and 649 down-regulated genes. KEGG analysis suggested that differential genes were mainly enriched in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ( PPAR) signaling pathway, retinol metabolism, fatty acid degradation, and other pathways (P.adj < 0. 05). The main significantly up-regulated genes included Cyp4a10, Cyp4a14, Acot1, Acot3, and Ehhadh, and the significantly down-regulated genes included Scn5a、Apol10b、Igddc4、Cxcl1、9530077C05Rik. The trend was consistent after RT-qPCR detection (P< 0. 05). Conclusions HBV-Tg mice have a tendency to develop spontaneous fibrosis. Transcriptomic analysis showed that chronic hepatitis B mainly involves PPAR signaling, retinol metabolism, fatty acid degradation, drug metabolism, and other pathways.
-
KANG Jing, YANG Lili, WANG Ziyan, YOU Yue, SHI Yue, MA Yanlei, MENG Hongxu, LI Lei
2023,31(12):1530-1538, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 002
Abstract:
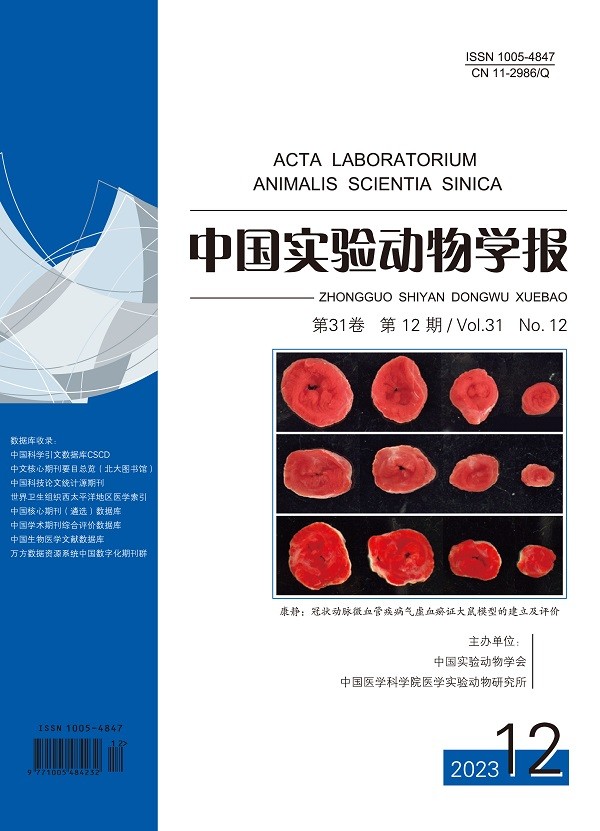
Objective The incidence of coronary microvascular disease ( CMVD) is increasing annually. According to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), CMVD belongs to the category of “collaterals”, and qi deficiency and blood stasis are the main syndrome type of CMVD. Notably however, no studies have reported on the use of animal models of CMVD with qi deficiency and blood stasis. The current study therefore aimed to establish and evaluate a rat model of CMVD with qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome. Methods Forty-five male SD rats were divided randomly into sham group, CMVD group, and CMVD + QXXY group (n= 15 rats per group). Rats in the CMVD + QXXY group were randomly deprived of sleep for 14 ~ 16 h/ day for 6 weeks, and the model of qi deficiency syndrome was established. Animals in the sham group and the CMVD group were fed normally for 6 weeks. After 6 weeks, rats in the CMVD and CMVD + QXXY groups were anesthetized, their chests were opened, and embolic microspheres (40 ~ 120 μm) were injected into the left ventricle. Rats in the sham group underwent thoracotomy without injection of embolic microspheres. On day 7 after operation, relevant detection indicators were measured in each group. Results Compared with the sham group, the CMVD group showed a significant decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction and left ventricular shortening rate, while the activities of creatine kinase MB isoenzyme ( CK-MB) and lactate dehydrogenase ( LDH) were significantly increased. Heart function, hemorheology, myocardial enzyme index, and the degree of myocardial cell damage differed significantly between the CMVD + QXXY group compared with the sham group. Conclusions A rat model of CMVD + qi deficiency + blood stasis syndrome can be successfully established by sleep deprivation combined with intraventricular injection of embolic microspheres. This model will be suitable for the study of the pathogenesis of CMVD and the mechanisms of TCM.
-
WANG Shumin, HAO Shulan, FENG Mali, JIANG Meng, WANG Yonghui, GAO Zhenfei, WANG Xixing, JI Haijie
2023,31(12):1539-1544, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 003
Abstract:
ObjectiveTo establish and evaluate chemotherapeutic phlebitis model rats induced by vinorelbine via the dorsalis pedis vein. Methods Rats were divided randomly into control and 4 different concentration of vinorelbine-induced model groups. Control rats were injected with 0. 1 mL normal saline via the dorsalis pedis vein of the hind limb, while other rats were injected with different concentrations of vinorelbine (2, 3, 4, 5 mg/ mL), as above. General observations were performed and the hind limb volume was measured daily for 7 consecutive days to calculate the swelling rate. The rats were then killed and histological changes in the dorsalis pedis vein were observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Microstructural changes on the surface of the vascular endometrium were observed by scanning electron microscopy. Results Injection of 2, 3, 4, 5 mg/ mL vinorelbine via the dorsalis pedis vein significantly induced hind limb swelling in a concentration-dependent manner, peaking on day 3 in each group. The phlebitis rates on day 7 were 50% in the 2 mg/ mL group and 83. 3% in the 3 mg/ mL group. Phlebitis was also induced in the 4 mg/ mL and 5 mg/ mL groups, including grade Ⅲ in 66. 6% and grade Ⅳ in 83. 3%. Histopathology showed inflammatory cell infiltration, wall thickening, lumen stenosis, and thrombosis in the tissues surrounding the veins. Scanning electron microscopy showed destruction of tight junctions of venous endothelial cells, and a rough surface of the vascular lining, resultsing in blood cell adhesion. Conclusions Injection of 0. 1 mL of 3 ~ 5 mg/ mL vinorelbine via the dorsalis pedis vein could induce red, swollen, and cord-like veins, as well as infiltration of inflammatory cells around the vein, thickened vein walls, lumen stenosis, and thrombosis. In addition, the surface of the venous intima was rough and adhered to numerous blood cells. All these features are consistent with those of clinical chemotherapeutic phlebitis in terms of the symptoms and pathological structure.
-
XIE Haina, PAN Zhiqiang, CAO Linna
2023,31(12):1545-1554, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 004
Abstract:
Objective To explore the animal model of syndrome used in the study of hot flash phenomenon in women. Methods Twenty-four female SD rats were divided randomly into three groups: Con group, Ovx group, and tamoxifen group (n= 8 rats per group). Hot flashes were induced by bilateral oophorectomy and intragastric tamoxifen 10 mg/ (kg·d), respectively. Open-field activity, anal temperature, and body surface infrared thermograms were detected on model days 14 and 28. The rats were then killed on day 29 and their uteruses were removed, weighed, and sectioned. Blood estradiol and catecholamine levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Gene expression levels of adrenal sex hormone synthetases (Star, Cyp11a1, Cyp17a1, Cyp19a1, Por, Hsd3b2, Hsd17b1) and catecholamine synthetases (Th, Ddc, Dbh, Pnmt) in the adrenal medulla were detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Results Rat body weight was significantly higher in the Ovx group compared with Con group (P< 0. 01), while body weight increased slowly in the tamoxifen group. The maximum body surface temperature was significantly decreased on day 28 in the Ovx group (P< 0. 01), the difference between the maximum and minimum abdominal temperatures was significantly increased on day 14 (P< 0. 05), the difference between the maximum and minimum temperatures on the back was significantly increased on day 28 (P< 0. 01), and the open-field activity was decreased (P< 0. 01). Compared with the sham operation group, the maximum body surface temperature in the tamoxifen group was significantly decreased (P< 0. 01) but the open-field activity was increased (P< 0. 01). The uterine index was significantly decreased in both models (P< 0. 01). Estradiol levels were significantly decreased (P< 0. 01) and NE and epinephrine were also significantly decreased in the Ovx group compared with Con group (P< 0. 05), and β-EP was also significantly decreased in Ovx group (P< 0. 05). Adrenal Cyp11a1 gene expression was significantly increased (P< 0. 05) while Cyp17a1 and Hsd17b1 gene expression levels were significantly decreased (P< 0. 05) in bilateral ovariectomized rats compared with Con group. Compared with Con group,gene expression levels of Star and Por were significantly increased (P< 0. 01) while Cyp17a1 gene expression was significantly decreased (P< 0. 01) in the tamoxifen group, and Pnmt gene expression was significantly down-regulated in Ovx group (P< 0. 01). Conclusions Bilateral ovariectomized rats can be used for the study of perimenopausal hot flashes, which resemble kidney Yang and Yin deficiency in traditional Chinese medicine.
-
HE Jiahui, HE Jieying, ZHANG Bairong, ZHANG Shuidi, WEI Yuanjun, YANG Chaoyan, CHEN Yanfen
2023,31(12):1555-1563, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 005
Abstract:
Objective To prepare rat models of liver stagnation syndrome constipation-type irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C) using single and multi-factor modeling method with different indicators, to provide ideal experimental animal models of IBS-C. Methods Forty-two SD rats were divided randomly into blank (Normal), cold-water gavage (Cold), restraint (Restrain), tail-clamping (Tail), cold-water gavage + restraint (C + R), and cold-water gavage + tailclamping groups (C + T). Body weight, food intake, water intake, and survival status, as well as open-field behavior, fecal Bristol score, visceral sensitivity, and small intestine propulsion were observed in each group during the modeling period. Pathological changes in the rat colon were observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining, and the serum and colon contents of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and vasoactive intestinal peptide ( VIP) were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results The body weight in each group decreased after modeling (P< 0. 05, P< 0. 01), the food and water intakes decreased, and serum 5-HT levels increased. The number of fecal particles and Bristol score decreased while the colon 5-HT content increased in the Cold group (P< 0. 05, P< 0. 01); the total distance and average speed of the restraint group in the open field decreased (P< 0. 01); the preference for sugar water in the Tail group decreased (P<0. 01); the preference for sugar water, total open-field distance, small intestine propulsion rate, defecation particles, and Bristol score all decreased, while the colon 5-HT content increased and the VIP content decreased in the C + T group (P<0. 05, P< 0. 01); and the total distance, average speed, and VIP content in the colon decreased in the C + R group (P<0. 05). Except for the Tail group, all the model groups showed visceral hypersensitivity (P< 0. 05, P< 0. 01) compared to the blank group at various pressure values on days 7 and 14 of modeling. Pathological observations showed no significant inflammatory cell infiltration or pathological changes in any of the model groups. Conclusions The combination of icewater gastric lavage and tail clamping can be used to establish a rat model of liver depression syndrome in IBS-C. This may be the best of the five tested method, and the resulting model may lay the foundation for further systematic and in-depth research into the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in preventing and treating IBS-C.
-
ZHANG Shuling, WANG Junwei, ZUO Luyu, HU Shiliang, SUN Junzhi, WANG Chun
2023,31(12):1564-1572, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 006
Abstract:
ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of oral probiotics on gut microbiota diversity, colony structure, and intergroup differences in mice with subcutaneous colon cancer tumors, based on 16S rRNA sequencing technology. Methods Twenty-four 6-week-old male BALB/ c mice were divided randomly into normal control group (NC group, n= 8), model group (M group, n= 8), and probiotic + model group (PM group, n= 8) after adaptive feeding for 1 week. Mice in the PM group were given 200 μL probiotic mixed solution (Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus mixed lyophilized powder, 2 × 108 colony-forming units) by gavage three times/ week for 7 weeks, while the M group and PM group received 200 μL normal saline. At 10 weeks old, 0. 2 mL CT26.WT cell suspension (1 × 107 / mL) was inoculated subcutaneously into the left hind limbs of M group and PM group, while NC group were inoculated with 0. 2 mL normal saline. The general state of mice was observed, the growth of subcutaneous tumor was monitored, and the changes of intestinal flora structure were detected by 16S rRNA sequencing. Results The subcutaneous tumors of the M group were prominent, and the subcutaneous tumor volume and weight of the PM group were significantly reduced (P<0. 05). Compared with NC group, Alpha diversity index was lower in the M group, and a significant difference of Beta diversity inter groups (P< 0. 01). And supplementation of probiotics had a certain effect on gut microbiota diversity in the M group. Compared with M group, the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Muribaculaceae,Bacteroides were higher in the PM group, while the relative abundance of Firmicutes, Desulfobacterota, Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_ group, Alistipes were lower in the PM group. LEfSe analysis showed that Muribaculaceae and Bacteroides in the PM group were different species with high abundance (LDA values > 4). Conclusions Oral probiotics may improve the gut microbiota by increasing the relative abundance of beneficial Muribaculaceae and Bacteroides in subcutaneous tumors in mice with colon cancer.
-
YE Zhichao, CHEN Guoyu, PAN Ruolang, SHI Yuhua, GU Liqiang, XIA Lijuan, LIN Xiaobo, ZHANG Qiang, XU Shasha, SHAO Jinjin, ZHANG Lijiang
2023,31(12):1573-1580, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 007
Abstract:
Objective To establish a quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for the analysis of human-derived SRY DNA in mouse tissues, and to study the tissue distribution of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMSCs) in immunodeficient NOG mice after a single intravenous injection. Methods We established a quantitative PCR method for the analysis of human SRY DNA in mouse tissues, and validated the standard curve, linear range, accuracy, precision, and stability. Thirty-six NOG mice (18 male, 18 female) were administered 3. 5 × 107 HUCMSCs/ kg by single intravenous injection. Six mice were then anesthetized and dissected after blood collection (EDTA anticoagulation) at 6, 12, 24, and 72 h, and at 1 and 2 weeks, respectively. DNA was extracted from lung, kidney, heart, liver, brain, spinal cord, stomach, small intestine, fat, skin, spleen, testis, uterus, and ovary tissues, and the distribution of HUCMSCs in each tissue was determined by the validated quantitative PCR method for detecting the humanderived SRY gene in mouse tissues. In addition, 18 NOG mice (9 male, 9 female) were divided into control (n= 6) and treatment groups (n= 12) injected intravenously with 0. 9% sodium chloride and 3. 5 × 107 cells/ kg, respectively. Acute toxic reactions were observed during the administration period, and four animals were dissected at 72 h and at 2 and 4 weeks after administration to observe the gross organs. Mitochondrial protein expression was detected in paraffin sections of lung tissues by immunohistochemistry to analyze the colonization of HUCMSCs in lung tissues. Results The established RT-qPCR method for human-derived SRY DNA in mouse tissues met the validation criteria for each index. After a single intravenous injection in NOG mice, HUCMSCs were mainly distributed in the lungs and blood within 1 week after administration, with higher concentrations in lung tissues than in blood. The concentrations of HUCMSCs in lung tissue and blood remained relatively stable within 6 ~ 24 h and 6 ~ 72 h, respectively, and then decreased over time. The distribution of HUCMSCs in other tissues was not measured at all sampling points. The colonization result showed that HUCMSCs were detected in lungs 72 h after intravenous injection, but not at 2 and 4 weeks. No obvious acute toxicity was observed in NOG mice after single intravenous administration of HUCMSCs. Conclusions The above method for analyzing the distribution of HUCMSCs in mouse tissue is reliable and feasible. HUCMSCs were mainly distributed in lung and blood in NOG mice within 1 week after a single intravenous injection, and mainly colonized lung tissue at 72 h. A single intravenous administration of HUCMSCs has a good safety profile.
-
LIU Yuqian, YANG Wenqian, WANG Haitao
2023,31(12):1581-1587, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 008
Abstract:
Objective To elucidate the role of the glutathione (GSH) / glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4)-mediated ferroptosis pathway in preventing age-related hepatocyte peroxidation injury following aerobic exercise in mice, and to provide a new target for improving liver aging and metabolism disorders. Methods Twenty specific-pathogen-free C57BL/6 male mice aged 52 weeks were divided randomly into an elderly control group (EC group) and elderly exercise group (EE group) (n= 10 per group). The mice performed moderate-intensity exercise with incremental loads (1 ~ 2 weeks 14 m/ min, 3 ~ 4 weeks 15 m/ min, 5 ~ 10 weeks 16 m/ min, 11 ~ 16 weeks 17 m/ min, 60 min/ day, slope 0°) for 16 weeks. After perfusion of the ascending aorta, the lateral liver lobes were harvested and sectioned for hematoxylin and eosin staining and ultrathin sections were used for transmission electron microscopy. Levels of 8-hydroxy-2 deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) in the liver and serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Hepatic glycogen, triglycerides (TG), malondialdehyde (MDA), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), and GSH were determined by colorimetry. Hepatic GPx4, glucose transporter (GLUT2), NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), and solute carrier protein 7 family member 11 (SLC7A11) were detected by Western Blot. Results (1)Oxidative damage to hepatocytes was effectively delayed, normal mitochondrial structure and glycogen storage in hepatocytes were maintained. (2) Hepatic GSH and NADPH contents were significantly increased in EE mice compared with EC mice (P< 0. 01). (3)In addition, liver levels of 8-OHdG, 4-HNE, MDA, and non-heme iron were significantly decreased in the EE group compared with the EC group (P< 0. 01). (4)Expression levels of GPx4, NQO1, and SLC7A11 in the liver were increased (P< 0. 01) while NOX2 expression was decreased (P< 0. 01) in the EE group compared with the EC group. Conclusions GSH synthesis was increased in aged mice following aerobic exercise, providing reaction substrates for GPx4 and activating the GSH/ GPx4 pathway. Ferroptosis was inhibited, thus improving hepatocyte peroxidation damage caused by aging, and maintaining the normal structure and physiological function of hepatocytes.
-
GUO Yaxi, LIU Ruixue, DU Xiaopeng, ZHU Hua
2023,31(12):1588-1597, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 009
Abstract:
ObjectiveUsing different sterilization method to sterilize pig specific formula milk powder, exploring the sterilization method and conditions that minimize the loss of nutritional components in formula milk powder. Methods Pig-specific formula milk powder was divided into high-pressure sterilization and irradiation sterilization groups. Formula milk powder in the high-pressure group was sterilized using different sterilization conditions and that in the irradiation group was sterilized using different 60Co γ-radiation doses. The sterility and the nutritional contents of the sterilized formula milk powders were determined according to national standards. Results The sterility tests for both groups of formula milk powder were negative. Compared to control group, the crude protein contents were significantly lower in formula in the highpressure group sterilized at 121℃ for 30 min and in the irradiation liquid group sterilized at 50 kGy (P< 0. 01). The water, crude protein, and calcium contents were significantly lower (P< 0. 001) in the irradiation group sterilized at 50 kGy. There was no significant difference in the valine, isoleucine, or leucine content under 50 kGy sterilization conditions in the irradiation sterilized group, but all amino acid contents were decreased in the high-pressure sterilization and irradiation sterilized liquid groups (P< 0. 001). Analysis of trace elements showed an increased iron content (P< 0. 001) in formula sterilized at 121℃ for 30 min in the high-pressure sterilization group, increased iron and potassium contents (P< 0. 001) under 25 kGy sterilization conditions in the irradiation sterilization liquid group, and increased magnesium content (P< 0. 01). The magnesium (P< 0. 05) and sodium contents (P< 0. 01) differed significantly in formula treated under 50 kGy sterilization conditions in the irradiation sterilized powder group. VE and VB2 contents were increased in formula sterilized at 121℃ for 30 min in the high-pressure sterilization group (P< 0. 001), the VE content was increased (P< 0. 05) and the VB2 content was decreased (P< 0. 001) in formula sterilized under 50 kGy conditions in the irradiation sterilization liquid group, and the VE and VA contents were decreased in formula sterilized at 25 kGy in the irradiation sterilized powder group (P< 0. 001). Conclusions Sterilization at 121℃ for 30 min result ed in the least loss of nutritional components in the high-pressure sterilization group, while irradiation sterilization result ed in the least loss of nutrients at a dose of 50 kGy. Comparing the two sterilization method, irradiation of milk powder at 50 kGy result ed in the least loss of nutrient content.
-
CHEN Hanmu, LI Hui, ZHAO Jumei, SHI Changhong
2023,31(12):1598-1604, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 010
Abstract:
Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative deamination of monoamine neurotransmitters and dietary amines. It plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis, progress, and treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. Recent studies have revealed that elevated expression of MAOA in prostate cancer (PCa) is closely associated with tumor progression and drives the heterogeneity of PCa. In this review, we summarize the role of MAOA in the development of PCa in different disease stages, including oncogenesis, development, invasion, metastasis, and drug resistance. We also discuss the involvement of MAOA in the tumor microenvironment and explore the potential utility of MAOA inhibitors. We further propose therapeutic strategies based on targeting MAOA in preclinical models to promote relevant clinical trials. This review aims to provide new potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of PCa.
-
LI Xuechan, HAN Le, WANG Xuewen, LIU Lijun, WU Jianjun, WANG Jing
2023,31(12):1605-1609, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 011
Abstract:
Aging is a process of degenerative change that occurs as a result of time-related accumulation, associated with age-related diseases. Understanding the causes and mechanisms of aging and finding drugs that can effectively delay aging and prevent and cure age-related diseases currently present a great challenge for humans. Aging animal models thus represent an important tool in aging research, and various aging animal models have been created using different aging mechanisms. These different models having specific advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different research purposes. This review considers aging rodent models to provide information for aging research.
-
LI Mengyao, GAO Feng, ZHENG Fanfan, HE Mengze, HE Zhao, LI Youlei
2023,31(12):1610-1616, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 012
Abstract:
Depression is a complex mental disease with polygenic inheritance and a high incidence. Our understanding of the clinical manifestations and pathogenesis of depression has recently improved. Continuous progress in gene-editing technologies has increased the construction efficiency and reduced the cost of gene-knockout animals, leading to their increasing use in the fields of basic research and drug development for depression and providing a powerful tool for revealing the pathogenesis of depression. In this review, we summarize recent progress in understanding the roles and mechanisms of candidate genes in depression using knockout model mice.
-
WANG Bo, SONG Qinghua, TANG Huimeng, LIU Yang, XIE Yang, TIAN Yange
2023,31(12):1617-1628, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 013
Abstract:
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a progressive, interstitial fibrotic lung disease characterized by persistent scar formation in the lung parenchyma, and a reduced quality of life and poor prognosis for patients. The pathogenesis of PF is unknown and there is a lack of effective therapeutic agents; however, animal models are currently the main tool used to explore the pathogenesis of the disease and to find effective therapeutic agents. PF can be induced by various factors and to different degrees according to known etiologies. Among these, bleomycin-induced models are widely used because of their reproducibility and the similarity between the fibrosis pathology and clinical conditions. The main induction method include intratracheal drip, intratracheal nebulization, tail vein injection, intraperitoneal injection, and transnasal inhalation, and these can be classified into single and multiple doses, according to the frequency of induction. Based on the relevant literature, the current review summarizes the characteristics of the bleomycin-induced PF model using different induction frequencies and method, to provide a basis for the application of this model.
-
ZHANG Min, ZHANG Jingjing, NING Guozhu
2023,31(12):1629-1635, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 014
Abstract:
The zebrafish xenograft model plays an important role in cancer modelling, especially breast cancer xenografts. This model facilitates the real-time observation of tumor cell growth, metastasis, and interactions with the immune system, thus providing novel insights and experimental foundations for breast cancer treatment. Furthermore, the zebrafish xenograft model offers a valuable tool for high-throughput drug screening. This review provides an overview of the contributions of the zebrafish xenograft model to elucidating the mechanisms underlying breast cancer development, and its use in screening anti-tumor drugs and conducting therapeutic research.
-
WANG Yan, CAO Yongchun, XING Kai
2023,31(12):1636-1645, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2023. 12. 015
Abstract:
Animal models of human diseases include experimental animals and related materials established during biomedical research, which in turn play a vital role in medical research. Pigs and humans are similar in terms of their anatomy, physiology, immunology, and genetics. Pigs are thus suitable model animals for biomedical research and have various advantages compared with other model animals. Recent advances in biotechnology, such as genetic engineering, have contributed to a rapid increase in the use of pig models for human disease research. In addition to serving as xenotransplant organ donors and as tools in drug-design studies, pigs can also be used as model animals to study human developmental processes, congenital diseases, and disease-response mechanisms, thus making important contributions to improving human health. This review considers the current status and future applications of pigs as research models for studies of human cardiovascular diseases, cancer, ophthalmology, craniofacial, musculoskeletal, and skin research, reproductive and fetal development, nutrition, microbiome research, brain and neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, infectious diseases, and vaccine design, as well as for xenotransplantation.
Volume 31,2023 Issue 12
Volume 31,2023 Issue 12
-
Advances in the study of neural mechanisms in animal models of anger
ZHANG Chunpeng, GAN JIA HONG, ZHANG Yonghua
Abstract:
The negative emotion of anger can have many effects on the body. The brain regions associated with the production of anger are mainly related to the central gray matter, amygdala, and hypothalamus. Animal models are an important tool for understanding diseases and mechanisms, and in recent years there has been a gradual increase in research on animal models of anger and the mechanisms of anger. Most studies on anger models have focused on the mid-suture dorsal nucleus, hypothalamus, and hippocampal regions, and related neurotransmitter studies have mainly been related to GABA expression and monoamine neurotransmitter content. The aim of this paper is to summarize the intracerebral neural mechanisms of anger onset by retrieving anger-related animal models, hoping to provide useful references for the study of angry emotions.
-
Exploration of establishing the dynamic time model of acute lung injury in mice based on the NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD signal pyroptosis pathway
Abstract:
Objective: Based on the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD pyroptosis pathway, a mouse model of LPS-induced acute lung injury was established over time, and the lung injury of mice was observed at different time points. According to the changes in injury at different time points and the expression of pyroptosis pathway-related proteins, the best time point for modeling was screened comprehensively, which laid the foundation for animal models for subsequent experiments. Methods: 54 six to eight weeks of SPF male BAL b/c mice were divided into nine groups randomly, which including control group and building time group (1, 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 48 and 72 h group), body weight, lung tissue was detected in general and pathological observation and semi-quantitative score, lung index, lung water content of wet and dry weight ratio; The white blood cell count and the concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-18 and BCA protein in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were detected. Using western blot method to detect the lung tissue of classic coke death pathways related NLRP3, pro - Caspase 1, Caspase 1, GSDMD protein expression. Results: According to the body weight statistics, the body weight of each group decreased, and the 24h and 48h groups showed the most significant weight loss. The results of gross observation and pathological examination of lung tissue showed that the injury of lung tissue in 24h to 72h was severe, and the difference between each group and Con group was statistically significant. Lung index, lung water content and wet/dry weight ratio were significantly increased at 24-72 hours. Alveolar lavage fluid white blood cells from 6 h after building began to rise, 48 h can reach a peak, 72 h all keep increasing; IL-18 in lavage fluid began to increase at 24 hours and continued to increase at 72 hours. TNF alpha, beta, IL - 6, IL - 1 inflammatory factors were keep the highest level at the time of 6 h, 48 h significantly reduced; A lavage in protein concentrations within 24 h, 48 h and 72 h compared with Con group were significantly increased; Found by western blot method and ALI model each time series jiao wu pathway proteins NLRP3, pro - Caspase 1, Caspase 1 and GSDMD protein expression were raised, 24 h - 72 - h group of channel protein expression enhanced significantly compared with control subjects. Conclusions: Comprehensive analysis of the experimental indicators, inflammatory factors and the expression of pathway proteins in WB in different time groups showed that the mechanism of pyroptosis was closely related to the occurrence and progression of ALI, and it moved with time. From the experimental results, it was found that the expression of pyroptosis pathway was the most obvious and the lung injury was the most serious in 24h-48h. This study provides a model reference and experimental basis for the subsequent study of the specific mechanism and intervention targets of ALI.
-
Effects of cultured Mycelium Cordyceps Sinensis on carbon tetrachloride induced liver fibrosis mice by regulating AMPK/SirT1 signaling pathway
Yang Zhao, Yan Ruanyu, Wu Hongyu, Huang Kai, Shen Li, Tao Yanyan, Liu Chenghai, Peng Yuan
Abstract:
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate the effects of cultured Mycelium Cordyceps Sinensis (CMCS) on AMPK/SirT1 signaling pathway in carbon tetrachloride(CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Methods Forty male C57BL/6 mice of SPF grade were randomly divided into normal control group, CMCS control group (3.0g/kg/d), Model control group, CMCS1.5g/kg group(1.5g/kg/d) and CMCS 3.0g/kg group (3.0g/kg/d). Mice were intraperitoneally injected with 10% CCl4 (2ml/kg) to induce liver fibrosis. 2 weeks later, serum levels of ALT, AST and TBil were measured. Inflammation and collagen deposition in liver tissue were observed by H&E and Sirius red stainings, respectively. The content of Hyp in liver tissue was detected by Jamall's hydrochloric acid hydrolysis method. The levels of IL-6, MCP-1, IFN-γ, TNF, IL-10 and IL-12p70 in liver tissue were detected by CBA analysis system. Immunohistochemistry was used to observe the expression of Collagen I and SirT1 in liver tissue. Real-time fluorescent quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to observe the levels of Prkaa1, Prkaa2, Lkb1 and p53 in liver tissue. Results Compared with the normal control group, the serum levels of ALT, AST and TBil in the model control group were significantly increased(P<0.05). HE and Sirius red staining showed a large number of inflammatory cell infiltration and collagen deposition in the liver, respectively. The levels of Hyp content and the expressions of IL-6, MCP-1, and TNF in the liver tissues exhibited a significantly higher level (P<0.05). Conversely, the expressions of IL-10 and IL-12p70 displayed a decrease in significance (P<0.05). Immunohistochemical staining revealed an increase in the expression of Collagen I. And the staining of SirT1 was decreased in the hepatic sinusoidal space, while it was increased in the collagen deposition. RT-qPCR presented that the expression of Prkaa1, Prkaa2, and Lkb1 in liver tissue decreased, and the expression of p53 increased(P<0.05), respectively. CMCS could significantly reduce serum ALT and AST levels, decrease the expression of IL-6, MCP-1 and TNF in liver tissue(P<0.05), up-regulate the levels of IL-10 and IL-12p70(P<0.05), alleviate liver inflammation, collagen deposition and Hyp content, up-regulate the expression of SirT1 in the hepatic sinusoidal space, enhance the levels of Prkaa1, Prkaa2 and Lkb1(P<0.05), down-regulate collagen I and p53(P<0.05) in liver, respectively. In comparison with the CMCS 1.5g/kg group, the CMCS 3.0g/kg group exhibited a significant inhibitory effect on liver inflammation, collagen deposition and up-regulate AMPK/SirT1 expression(P<0.05). Conclusion CMCS could improve CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, and its mechanism was associated with the up-regulation of AMPK/SirT1 signaling pathway.
-
Establishment of inhibition model of bone formation induced by lipid toxicity in zebrafish induced by palmitic acid
Wang Xiaoyi, LI Miao, WANG Linxia, YU Bin, HUA Yongqing
Abstract:
Objective To establish a palmitic acid-induced bone formation inhibition model of zebrafish lipotoxic injury. Methods The embryos of AB strain zebrafish were randomly divided into blank Control group (Control group), palmitic acid group (PA group) and simvastatin group (SIM group). From 3 dpf (days post fertilization), PA and SIM groups were given PA . From 5 dpf, the SIM group was administered continuously for 4 days. Calcein staining, Nile red staining, triglyceride and total cholesterol content determination and q-PCR to determine whether the model was successfully established on the 9 dpf. Results PA significantly decreased the number of vertebrae, promoted lipid accumulation, increased triglyceride triglyceride and total cholesterol content, promoted lipid-related genes and inhibited the expression of osteogenic genes. SIM can improve the inhibitory effect of PA on bone formation in zebrafish. Conclusion PA can successfully create the inhibition model of lipotoxic injury bone formation similar to the pathological process of OP, and the method is simple, sensitive and controllable, which can be used for drug screening of OP and related diseases.
-
Establishment and Evaluation of a Canine Vertebral Augmentation Puncture Model under Fluoroscopic Guidance
wanghaotian, liujia, huangjian, qijunqiang, xuguohua
Abstract:
Objective: To establish a fluoroscopic percutaneous vertebral augmentation model in dogs through measurement and analysis of canine spinal anatomy. Furthermore, the effectiveness and safety of this modeling method are assessed through post-operative radiological analysis. Methods: Morphological measurements and their parameters of the lumbar vertebrae of six dogs aged around 12 months were taken: height of the L1-L7 vertebrae, width of the vertebral base, distance from the upper edge of the intervertebral disc to the narrowest part of the vertebra, distance from the vertical line of the spinous process to the upper edge of the intervertebral disc, and the vertical distance from the midpoint of the transverse process to the lower edge of the intervertebral disc. This was done to clarify the anatomical characteristics of the canine vertebrae and to determine the optimal location, direction, and depth for bone cement injection. Subsequently, a percutaneous vertebral augmentation model was established in the L4, L5, and L6 vertebrae of six healthy Beagle dogs weighing between 20-25kg. Four weeks post-surgery, the subjects were euthanized and radiologically examined. Primary observations included: surgical duration, post-operative distribution of the implanted bone cement, and the integrity of the vertebral canal and anterior edge of the vertebrae. Results: Anatomical observation of the canine vertebrae revealed that the vertebral height gradually increased from L1 to L5 and then decreased from L5 to L7. The width of the vertebral base consistently increased from L1 to L7. The distance from the vertical line of the spinous process to the upper edge of the intervertebral disc showed an increasing trend from L1 to L7 (1.9 to 4.0 mm). The distance between the midpoint of the base of the transverse process and the lower edge of the intervertebral disc gradually increased from L1 to L5 (4.7 to 6.9 mm). There was no significant statistical difference in the distance between the midpoint of the base of the transverse process and the lower edge of the intervertebral disc in the L4, L5, and L6 segments among the dogs (P=0.925). The midpoint of the root of the transverse process of the spine was taken as the puncture point, and the insertion direction and horizontal plane were at an Angle of 20° - 30 °, with a head tilt of 5° - 15° and a puncture depth of 1.2 cm to 1.5 cm. If the puncture was directed towards the caudal side of the vertebra, the angle of the needle tail was 30° to 35°, with a penetration depth of 1.5 cm to 1.8 cm. This technique allowed for the successful construction of a canine vertebral puncture surgical model. A total of 15 canine vertebral puncture surgical models were successfully created, with an average surgery time of 22.7 ± 4.6 minutes (ranging from 15 to 30 minutes) per vertebral segment. During surgery, one vertebral segment experienced spinal cord injury resulting in paralysis of the hind limbs and incontinence of both bowel and bladder. Two vertebral cortical bones fractured, but there were no deaths due to anesthesia or infection. Four weeks post-surgery, Micro-CT three-dimensional reconstructions consistently showed bone cement distributed within the trabecular bone of the canine vertebrae, with newly formed bone tissue enveloping the implanted material. There was no leakage, and no complications such as damage to the vertebral canal or the anterior wall of the vertebrae were observed. Conclusions: Based on the anatomy of the canine lumbar vertebrae (L4 to L6), using the midpoint of the base of the transverse process as a bony landmark, a safe and reliable canine vertebral augmentation puncture model can be successfully established.
-
Differential expression analysis of mRNAs in the pneumoconiosis based on transcriptome sequencing
liang xiaoqiao, yang ying, he zhouyang, ning li
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective Utilizing transcriptomic sequencing, this study aimed to monitor the expression alterations of GIMAP8 and SEC14L5 throughout the progression of pulmonary fibrosis, thereby providing insights into the underlying mechanisms of its pathogenesis and evolution. Methods C57BL/6 male mice were assigned in a randomized manner to either the experimental or control cohorts. The model group underwent non-exposed endotracheal intubation on days 0 and 14 with 50 μL 100 mg/mL silica suspension, while the control group received 50 μL phosphate-buffered saline solution. On day 28, lung function was detected and the mice were sacrificed, and lung morphology, fibrosis, and mRNA levels were observed. Results The pneumoconiosis group was found to have a total of 2,988 mRNAs compared with the control group, of which 626 mRNAs showed large expression differences, including 242 up-regulated and 384 down-regulated genes. The enrichment analysis indicated that the primarily affected mRNAs with altered expression were associated with pathways such as p53, nuclear factor-κB, tumor necrosis factor, AMP-activated protein kinase, and other signaling pathways. In the model mice, the alveolar structures were compromised, characterized by the presence of collagen fiber accumulation and the formation of fibrous masses. In contrast, the control mice maintained a normal pulmonary architecture. GIMAP8 expression was up-regulated whereas SEC14L5 expression was down-regulated in lung tissues in the model mice, and mice in the model group had poorer lung function. Conclusions The onset and progression of pulmonary fibrosis may be significantly influenced by GIMAP8 and SEC14L5 expression in the blood in patients with pneumoconiosis and in silicosis animal models.
-
Analysis of gut microbiota in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome induced by letrozole
YANG Hong, ZHANG Zhen, FU Xufeng
Abstract:
Objective: To investigate whether letrozole (an estrogen synthesis inhibitor) can affect the composition, diversity and abundance of intestinal microbiota in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Methods: The PCOS rat model was induced and constructed by letrozole, an estrogen synthesis inhibitor. The gut microbiota structure of normal and PCOS rats was analyzed by 16S rRNA sequencing. Results: At the phylum level, the PCOS group had a lower abundance of Firmicutes (77.2% vs. 73.3%) and a higher abundance of Bacteroidetes (17.2% vs. 23.9%) than the normal group. At the genus level, the abundance of Rochella (16.1% vs. 5.6%) and Zurichella (10.0% vs. 1.8%) in PCOS group was lower than that in the normal group. However, the abundance of Lactobacillus (15.9% vs. 18.8%)、 Prevotella (0.5% vs. 4.6%) and Ruminococcus (1.2% vs. 3.0%) increased. The KEGG signaling pathways of the two groups of differentially expressed bacteria were further analyzed. The results showed that the signaling pathways related to bile acid biosynthesis in the intestine were changed in the PCOS rat model. Conclusion: These results provide a basis for further in-depth study of microbial structure and function and regulatory mechanisms in PCOS patients.
-
Study on the Micro-CT based animal model of lung adenoma in BALB/c mice
jian qin, xiang sirui, wang chuchu, chen wu, fu xi, you fengming, zheng chuan, lin junzhi
Abstract:
Objective To establish an animal model of lung adenoma in BALB/c mice based on dynamic characterization by micro-computed tomography (CT). Methods Eighty female SPF-grade BALB/c mice were divided randomly into four groups: model low-dose group (1 mg/g urethane, intraperitoneal [ip], once), model medium-dose group (1 mg/g urethane, ip, once a week, followed by 2 weeks), model high-dose group (1 mg/g urethane, ip, once a week, followed by 4 weeks), and blank group (equal volume of saline). Growth of lung nodules in the mice was monitored regularly using micro-CT. Three-dimensional images of the lungs were drawn using the Analyze 12.0 system, and lung tissues were taken for histopathological examination (hematoxylin and eosin). Results Lung nodules with round high-density shadows were observed at week 11 in all model groups compared with the findings in the blank group. The rate of nodule formation increased with increasing modeling weeks, with rates of nodule formation in the model high-, medium-, and low-dose groups of 93.8%, 93.8%, and 87.5%, respectively, at week 21. Most mice had two to four, followed by one, and one to two nodules, respectively. The average maximum diameter of the lung nodules in the low-dose group was significantly higher than the diameters in the medium- and high-dose groups (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in lung nodule volume among the three groups. Regarding pathological type, hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed that the tumors in all the model groups were lung adenomas. Conclusions Lung adenomas were successfully induced in all urethane-dose groups of mice and growth of the lung nodules could be characterized by micro-CT. The rate of nodule formation was highest in the medium-dose group, which developed a moderate number of lung adenomas and provided a stable model, and was thus considered the most suitable model for the study of lung adenomas in mice.
-
Mechanism of Jianpi Huatan Fang in Intervention of Lipid Metabolism in PCOS-IR Rats by Regulating FOXO1/PDK4 Signal Pathway
Abstract:
Objective: To investigate the effects of Jianpi Huatan recipe on lipid metabolism and expression of FOXO1 and PDK4 in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and insulin resistance (IR) . Methods: Fifty female rats were randomly divided into a blank control group of 10 and a model group of 40. A PCOS-IR rat model was established using a high-fat diet (8 weeks) combined with letrozole (added at weeks 4-8), and the model was evaluated through HOMA-IR and ovarian tissue pathology observation. Thirty successfully modeled rats were randomly divided into a model control group, a Jianpi Huatan Fang group (11.07g/kg), and a Metformin group (0.2g/kg), with 10 rats in each group. Drug intervention was given for 4 weeks. Hematoxylin eosin (HE) staining was used to observe the histopathology changes of the ovary; Fasting blood glucose (FBG) and blood lipids (triglyceride TG, cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) were measured by blood biochemical analyzer; Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the levels of sex hormones follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), testosterone (T) and insulin (FINS); Immunoblotting (WB) and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR were used to detect changes in the expression of FOXO1 and PDK4 in the ovaries. Results: Compared with the blank control group, the model control group showed significant weight gain, significant polycystic ovarian changes, and dysregulation of glucose and lipid metabolism (P<0.01). Compared with the model control group, the weight growth rate of rats in the Jianpi Huatan Fang group slowed down, and the development of follicles improved. Serum LH, T, LH/FSH, FBG, FINS, HOMA-IR, TC, TG, LDL-C decreased, E2 and FSH increased, while ovarian FOXO1, PDK4 mRNA and protein expression were down regulated (P<0.05, P<0.01); It can increase the serum HDL-C content, but there is no statistically significant difference between groups (P>0.05). Conclusion:Jianpi Huatan recipe can effectively regulate the secretion of sex hormones, improve the ovarian reproductive function and regulate glucose and lipid metabolism in obese PCOS-IR rats, which may play a role by inhibiting FOXO1/PDK4 pathway.
-
Development of Microsatellite Markers and Analysis of Genetic Characteristics in Closed Colony of Apodemus peninsulaeDevelopment of Microsatellite Markers and Genetic Diversity Analysis of Apodemus peninsulae
ZHANG Qing, ZHANG Xiwen, HE Song, YUAN Bao, CHEN Jian, REN Wenzhi, QUAN Fushi, HU Jinping, DING Yu
Abstract:
Objective The development of polymorphic microsatellite markers of A.peninsulae can enrich the genetic data of A.peninsulae and lay a foundation for genetic quality control and gene mapping of A.peninsulae.Based on genomic data, microsatellite loci of A.peninsulae were developed for genetic quality analysis of A.peninsulae and enriched the genetic data of A.peninsulae. Methods Microsatellite loci were screened based on the genome sequence of Apodemus peninsulae, and microsatellite primers were mined. The genetic diversity of the population were analyzed by multiplex PCR. Results Thirty microsatellite markers were successfully developed, and 30 microsatellite loci were evaluated using 60 samples of Apodemus peninsulae. A total of 152 alleles were detected, with an average number of observed alleles of 5.067. The average observed heterozygosity was 0.592. The average Shannon index was 1.2645 ; the average polymorphism information content ( PIC ) was 0.598. Conclusions Based on the microsatellite loci developed in this study, the genetic diversity of A.peninsulae population can be effectively analyzed, which lays a foundation for the establishment of genetic quality standards and genetic quality detection methods of A.peninsulae.
-
Analysis of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Nephritis Animal Model Based on Data Mining
Abstract:
Objective: To investigate the modeling of Henoch-Sch?nlein purpura nephritis based on data mining, and to provide a reference for the preparation of a standardized Henoch-Sch?nlein purpura nephritis animal model. Methods: We searched the China HowNet, Wanfang, Weipu, China Biomedical Literature Database, and PubMed Chinese–English Database by computer to obtain studies of animal experiments relating to Henoch-Sch?nlein purpura nephritis in the past 20 years. The species, modeling methods, dosage, dosing cycle, modeling standards, and detection indexes were screened manually, and a database was established by using Microsoft Excel 2021 software for statistical analysis. The association rules of high-frequency indicators were analyzed using SPSS Modeler 18.0, and Cytoscape 3.6.1 was used to visually upgrade the association network diagram. Results: A total of 106 articles that met the inclusion criteria were summarized. Sprague Dawley rats and Kunming mice were the mostly commonly used animal models of Henoch-Sch?nlein purpura nephritis and most studies used drug-induced models. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) + lipopolysaccharide + carbon tetrachloride + castor oil, ovalbumin + Freund’s complete adjuvant, gliadin + Indian ink, and BSA + staphylococcal enterotoxin B were used to produce the animal models, generally with cycles of 5–14 weeks. The standard of modeling was skin purpura and increased numbers of urine red blood cells. Proteinuria, glomerular mesangial hyperplasia in kidney tissue, and immune complex mainly composed of immunoglobulin A (IgA) deposited in small blood vessels indicated successful modeling. There were 36 medical indexes, including 23 indexes related to the kidney and urine and nine indexes related to blood. Among these, 10 indexes, such as 24-h urine protein quantification, interleukin, renal pathology, urine red blood cell count, IgA, circulating immune complex and creatinine were used in ≥ 10% of cases. Cluster analysis of high-frequency indicators showed that the comprehensive evaluation model of 24-h urinary protein quantification + interleukin + renal pathology + urinary red blood cell count + IgA was mostly used. Conclusion: Most existing animal models of Henoch-Sch?nlein purpura nephritis have used male Sprague Dawley rats or female Kunming mice, and most models were induced by drugs. Among these, the method of stasis-heat syndrome combined with IgA nephropathy (disease-syndrome combination method) has the advantages of good repeatability and a high modeling rate, and may thus provide a reference for the selection of animal experimental models of Henoch-Sch?nlein purpura nephritis.
-
To explore the protective effect of EGCG on acute kidney injury induced by cisplatin in rats based on Network Pharmacology
YANG CHUNXUE, XU ENSHUANG, ZHANG FENG, ZHENG JIASAN
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the protective effect of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on acute kidney injury induced by cisplatin (CIS) in rats based on network pharmacology. Methods 32 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups as follows: control group (CON group),EGCG group, CIS group (cisplatin group) and CIS+EGCG group. CON group and CIS group were given normal saline every day, EGCG and CIS+EGCG group were given EGCG (40 mg/kg) every day for 28 days. On the 26th day, CIS group and CIS+EGCG group were intraperitoneally injected with cisplatin (7 mg/kg).On the 29th day, blood and tissue were taken from each group. The levels of serum urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (SCr) were detected, renal pathological changes were observed by HE staining, TUNEL was used to detect apoptosis in renal tissue. Drugs and disease targets were screened by TCMSP, Gene Cards and OMIM websites, protein-protein interaction network (PPI) was constructed after intersection, gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genome (KEGG) enrichment analysis were carried out, and the results were verified by Western Blot 、RT-QPCR and immunohistochemistry. Results The results showed that EGCG preconditioning significantly decreased the levels of BUN and SCr in serum of AKI rats and improved the nephropathy of AKI rats, and relieved the renal tissue apoptosis of AKI rats. 87 EGCG and AKI intersection genes and 25 core targets were screened by network pharmacology, which affected the development of AKI through PI3K/AKT and other signal pathways and a variety of biological processes. Conclusions EGCG alleviates CIS-induced acute kidney injury in rats through PI3K-AKT signaling pathway.
-
The models of adenoviral transfection and hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in AMCMs
LI Xiaoru, YAO Xinye, LIU Jia, ZHANG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Yiman, LAI Baochang, MA Qiang, WANG Yidong, TIAN Hongyan, YIN Qian
Abstract:
Objective To build the models of viral transfection and hypoxia-reoxygenation induced cellular injury in AMCMs which are isolated by a non-Langendorff method. Methods AMCMs were isolated, extracted, sedimented and wall-plated by a non-Langendorff method. The morphology and survival rate of isolated cells was evaluated at 2 h, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h after wall-plating. The isolated AMCMs were infected with adenoviruses carrying RFP-expressing vector. Fluorescence photographs were taken at 36 h and 48 h post infection and used for calculation of transfection efficiency. The cells were cultured under hypoxic for 45 min and reoxygenated for 24 h. The cells were then stained with propidium iodide (PI) to verify the establishment of hypoxia-reoxygenation injury model. Results the survival rate of AMCMs at 2 h, 24 h and 48 h after plating were comparable, whereas this number at 72 h was significantly reduced. More than 80% of cells were transfected with adenovirus at 48 h. The hypoxia-reoxygenation treatment induced 42% of cells stained by PI, suggesting successful establishment of AMCMs injury model. Conclusions In this study, we developed a non-Langendorff method for quickly and easily isolating AMCMs with high cell viability. The isolated cells can be efficiently infected with adenovirus and are response to hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Our findings provide a systematic method for isolating AMCMs as well as gene modification and hypoxia-reoxygenation injury in these cells.
-
Regulation of tryptophanmetabolism instress-relatedgastrointestinaldisorders
chenjingqing, zhengjianhua, dongqiaoyan, zhangwensheng, maliansu, qiuyefeng
Abstract:
Exposure to different types of stressors has been known to increase susceptibility to diseases and disrupting the body homoeostasis. It is necessary for healthy animals and humans to maintain the physiological functions under stressful conditions. Intestine, the largest immune and metabolicsite, is important for animal health. The integrity of mucosal barrier and function are fundamental to protect the health of the intestine. It is reported that stress has profound effects on the gastrointestinal tract including alterations in gut permeability,intestinal barrier and homeostasis. Tryptophan, a functional essential amino acid,that alters the gut microbiota, regulates intestine structural and functional changes,thus contributing to host physiology and metabolism. Tryptophan metabolism perturbations and its metabolites alterations in brain and intestinal tissues during stress suggest that tryptophan may play an important role in stress response. We therefore review the literature on the underlying mechanisms of stress with diseases, and the role of tryptophan metabolic pathway in the regulation of gut homeostasis, with particular focus on functional bowel disorders and their relationship to stress, and laid a theoretical foundation for the treatment of tryptophan in stress-related intestine diseases.
-
Construction of macrophage-specific KLF2 gene knockout mice
MENG Xue, WANG Xinzhong, GAO Shuibo, WU Hong
Abstract:
Objective To establish a macrophage-specific KLF2 gene knockout mouse model, and explore the regulatory effect of KLF2 on macrophage inflammatory response. Methods The KLF2flox/+mice were constructed using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology. By breeding with Lyz2-Cre+/+ mice and screening genotypes through PCR, the target genotype mice were obtained, and the KLF2 knockout efficiency was verified using genotyping, qPCR and western blotting. BMDMs were Separated and cultivated, and the mRNA levels of inflammation-related factors in LPS-induced BMDMs were detected. Results A KLF2flox/flox/ Lyz2-Cre+ mouse model was established. The levels of KLF2 mRNA and protein in mouse bone marrow and BMDMs were significantly lower than those in the control group, while the expression of KLF2 in heart, liver, and kidney showed no significant changes compared to the control group. No significant differences in body weight, diet, drinking water and appearance were found between the two groups. Under the stimulation of LPS, the expression level of IL-6 mRNA in KLF2 deficient BMDMs was significantly lower than those in the control group, IL-1, iNOS, and CD86 mRNA were significantly higher than those in the control group. Conclusions The macrophage-specific knockout KLF2 mouse model was constructed, laying the foundation for further research on the regulatory effect and mechanism of macrophage KLF2 on clinical inflammatory-related diseases.
-
Study on establishment of mouse model of medial temporal lobe epilepsy with kainic acid
YE Zuliang, MIAO Yujing, LIU Quanlei, ZHU Quan, WEI Penghu
Abstract:
Objective An ideal animal model of epilepsy can be used to study the pathogenesis of epilepsy and evaluate novel antiepileptic drugs. To optimize the simulation of the pathological characteristics and seizure behavior of medial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE), we aimed to establish a chronic epilepsy model of MTLE by unilateral, single hippocampal injection of kainic acid (KA) via stereotactic surgery, and to validate this epilepsy model in terms of behavior, electrophysiology, and pathology. Methods A total of 22 healthy C57BL/6 wild-type male mice were divided randomly into a control group (n = 6) and an experimental group, which received KA injections (n = 16). Both groups underwent microinjection of equal doses of saline or KA in the hippocampal CA3 area via stereotactic surgery. One week later, all mice were implanted with electrodes in the hippocampal CA3 area to facilitate electroencephalogram (EEG) recording. Seizure frequency and duration were analyzed statistically. The chronic epilepsy model was assessed in terms of behavior, electrophysiology, and pathology. Results No mice in the control group experienced seizures, while all surviving mice in the experimental group developed seizures. Adult model mice exhibited chronic spontaneous seizure behaviors, such as staring, chewing, head and facial muscle twitching, and limb spasms. Two mice died as a result of the surgery, four mice died during the acute seizure phase, and 10 model mice were successfully established. EEG recordings showed epileptiform changes consistent with MTLE. Immunofluorescence staining revealed neuronal loss in the CA3 area and astrocytic changes, consistent with characteristic pathological changes of hippocampal sclerosis. Conclusions We successfully established a chronic epilepsy model of MTLE by unilateral, single intracranial injection of KA and confirmed the validity of the model in terms of behavior, electrophysiology, and pathology. This KA model possesses several advantages, including being time-efficient, easy to perform, cost-effective in terms of drug usage, easily replicated, and being KA-dose-dependent. This epilepsy model exhibits similarities to human MTLE in terms of EEG, behavior, and neuropathological changes, and can thus be used to study effective drugs for treating temporal lobe epilepsy and as an ideal animal model for predicting the outcome of epilepsy surgery.
-
Establishment and Optimization of Rapid Model of Osteoporosis in zebrafish
MAO Hongyun, LIU Yutong, ZHAO Xinyue, JIANG Deli, Wang Xiaoyi, ZHAO Kexuan, HUA Yongqing, Xu Huiqin
Abstract:
Objective In this paper, a fast, stable and sensitive model of zebrafish osteoporosis (OP) was established by comparing different methods of establishing common zebrafish osteoporosis models. Methods The OP model was induced by iron overload and prednisolone (Pred). The bone formation and animal mortality were observed. Ammonium ferric citrate (FAC) was used as the model drug in iron overload induction method. The Pred induction method was Pred-3 dpf (day post fertilization) method, the modeling time was 3 ~ 9 dpf; Pred- 5 dpf method, the modeling time was 5 ~ 10 dpf; Pred withdrawal method, 3 dpf began to make the model, and 7 ~ 9 dpf was removed every day. Results The significant effect of FAC on bone formation was not observed at the dose of 500 μg/mL. Compared with the control group, the number of bone and the length of the first vertebra in the model group induced by Pred-3dpf decreased significantly (P < 0.01, P < 0.05), but the mortality of zebrafish was higher. There was no significant difference between Pred-5 dpf method (P > 0.05) Pred withdrawal method model group were significantly reduced (P < 0.01), and no death. AC, CA and AL all had anti-OP effect, and CA had more sensitive and stable anti-OP effect. The optimization results of dyeing parameters of alizarin red (ARS) showed that the dyeing concentration was 0.02%, and the washing conditions of 0.5% KOH and glycerol for 2 hours were the best. The results of chemical staining showed that calcein was more sensitive to the staining of bone nodes and ARS was more sensitive to the staining of the first vertebra. Conclusions The zebrafish OP model induced by Pred withdrawal method is more rapid, stable and sensitive, and it is a stable and reliable model for OP study.
-
Establishment of an orthotopic implantation model of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice
pan rui, yu kun, zhang hailiang, zheng yongren, zhao xiaoyu, tang junze, wu jianming, cheng xin
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To explore the advantages and disadvantages of orthotopic injection of cell suspensions and transplantation of tumor tissue blocks to establish an orthotopic implantation model, and to provide technical reference for the establishment of an orthotopic implantation model. Methods A total of healthy Kunming mice were divided into four groups. Direct injection H22 cells was used in group A. Direct injection H22 ascitic cells was used in group B. Transplantation of tissues was used in group C. Direct injection was saline used in group D. The activity and weight change of each group were observed regularly. The survival time of the four groups of mice was recorded. Liver tumor formation, tumor size, abdominal organ adhesion degree and metastasis of the mice were observed. B-ultrasound imaging was performed to detect the concentration of alpha fetoprotein (AFP), abnormal prothrombin (DCP) and HE staining to observe liver histopathological changes. Results The mice in groups A, B and C were (3.36±0.44) min, (3.30±0.41) min and (5.68±0.65) min, respectively. After 25 d of modeling, the rate of mice in groups A, B and C was 100.0%, the severe abdominal adhesion in group A was 40.0%, 60.0% in group B, and neither group C or D. The rates of ascites in groups A, B and C were 40.0%, 100.0% and 0.0%, respectively; the rates of abdominal wall tumors were 30.0%, 60.0% and 0.0%, respectively. Mice in group B also had liver metastasis 40.0%). B ultrasound imaging, detection of serum AFP and DCP levels, histopathological results showed that mice in group A, B, C had smooth liver margins, uneven echo and slightly lower echo mass, maintaining AFP and DCP high secretion; large number of inflammatory cells and tumor cells. Conclusion H22 cells and H22 ascitic cells have the advantages of simple operation and high survival rate. transplantation of tissues has the advantages of less metastasis and light abdominal adhesion. All three methods can establish an orthotopic transplantation model of HCC, which can be an ideal model to evaluate the effect of drugs against HCC.
-
The impact of embryonic uveitis exposure on the offspring mice response to IRBP-induced experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU)
Xufei, Liu Jianping, Dong Shifang, Huanghui, Gong xinyi, Hu kaijiao, Chen feilan
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of embryonic inflammatory exposure on the offspring response to IRBP-induced experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU). Methods RNA transcriptome sequencing data from eyeball in the C57BL/6J offspring gestated from active parental EAU were used to screen immune-associated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the eyes of exposed offspring. Gene fragments overlapping in the two datasets were screened using gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses to identify biological pathways associated with gene fragments. Hub genes were identified from these intersecting genes by protein-protein interaction networks (PPI) analysis. EAU models of offspring affected by maternal uveitis were established by immunization with IRBP651-670, and the expression levels of the pivotal genes in the offspring exposed to inflammation by maternal uveitis were examined by fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (q-PCR). The EAU severity, T lymphocytes proliferation and serum cytokines were detected to investigate the immune effect of offspring gestated from materinal active inflammation response to 150 μg IRBP induction. Results Microarray analysis identified 72 immune-related genes in ocular tissue DEGs compared with control samples. These genes were mainly enriched in pathways involved in Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, and B cell receptor signaling pathway. Further PPI network interaction analysis screen out four hub genes, namely, Psmc5, Psmc3, Psmd4, and Psmd8. Meanwhile the adult offspring gestation from materinal active uveitis expressed increased mRNA level in those four hub genes compared with those healthy offspring. In addition, under 150 μg IRBP induction, an increase in the severity of EAU in the offspring during the inflammatory activity period was observed, with significant differences in clinical and pathological aspects compared with the control group. Meanwhile, the proliferation of T cells in the offspring during the inflammatory activity stage was enhanced, and the secretion of inflammatory cytokines IL-17 and IL-6 was increased. Conclusions Psmc5, Psmc3, Psmd4, and Psmd8 may be the important genes exacerbating offspring uveitis associated with the increased T cell proliferation and production of IL-17 and IL-6.
-
Three Tiao-Bu Fei-Shen therapies can improve airway mucus hypersecretion in COPD rats by inhibiting ERK1/2 signaling pathway
LI Gaofeng, LIU Shujuan, LI Ya, LI Suyun, FAN Zhengyuan, SHEN Tingting
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the three Tiao-Bu Fei-Shen therapies in improving airway mucus hypersecretion in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) rats. Methods 90 rats were randomly divided into nine groups: control group, COPD group, Bu-Fei Jian-Pi (BJF) group, Bu-Fei Yi-Shen (BYF) group, Yi-Qi Zi-Shen (YZF) group, ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD98059) group, BJF + PD98059 group, BYF + PD98059 group and YZF + PD98059 group. The rat model of COPD was established by exposing them to cigarette smoke and repeated bacterial infection from the first to the eighth week. From the ninth to the sixteenth week, the Control group and the COPD group were given normal saline 2 ml, the TCM treatment group was given three Tiao-Bu Fei-Shen formulas by gavage, and the inhibitor group and the combination group were given PD98059 by intraperitoneal injection for 7 days. Lung function tests were conducted at the end of 16 weeks along with assessments on lung tissue morphology, lung water content,inflammatory cell count in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and level of inflammatory factors in serum. AB-PAS staining was used to determine goblet cell proportion while immunohistochemistry was employed to measure Muc5AC and Muc5B expression levels. PCR analysis was performed to detect ERK1/2 mRNA expression as well as ENaC, CFTR, AQP5 mRNA expressions. Western Blot analysis measured protein expression levels of ERK1/2and P-ERK1/2 in lung tissue. Results Compared with the Control Group, TV, MV, FVC, FEV0.1, FEV0.1/FVC significantly decreased (P<0.01) in COPD Group.Lung pathology revealed alveolar disorder, massive fracture of alveolar wall, and severe shrinkage/thickening of airway wall accompanied by extensive infiltration of inflammatory cells. Water content in lung tissue increased significantly (P<0.01). The proportion of macrophages in BALF was significantly reduced (P<0.01), whereas the proportions of neutrophils and lymphocytes were significantly increased (P<0.01). The level of TNF-α and IL-1β in serum were significantly increased (P<0.01). The percentage of goblet cells and expression levels of Muc5AC and Muc5B in airway epithelial cells exhibited a significant increase (P<0.01). Expression levels of ERK1, ERK2, and ENaC mRNA in lung tissue were significantly elevated (P<0.01), while expression levels of CFTR and AQP5 mRNA were significantly decreased (P<0.01). Compared to the COPD group, the treatment groups demonstrated improvements in the aforementioned indicators (P<0.05), with the three Tiao-Bu Fei-Shen formulas combined PD98059 group showing superior efficacy compared to single treatment groups (P<0.05). Conclusions Three Tiao-Bu Fei-Shen therapies can ameliorate airway mucus hypersecretion in COPD rats by inhibiting the ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
-
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of small intestine Ski-overexpressing on acetic acid-induced writhing mice
Abstract:
Objective: To study the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Ski protein overexpression on mice induced by acetic acid.? Methods: Eight-week-old male ICR mice were selected and given 0.7% acetic acid solution (0.1ml/10g body weight) to induce writhing reaction.Experimental mice were divided into Sham group, acetic acid group, acetic acid + ibuprofen group, acetic acid +Ad-EGFP group, acetic acid +Ad-ski-1 group and acetic acid +Ad-ski-2 group, with 10 mice in each group. Observe and record the incubation period for the first appearance of twisting, while also recording the number of twisting times within 15 minutes. Obtain small intestine tissue, identify adenovirus transfection effect, detect protein expression levels of pro-inflammatory factors and pain biomarkers, and further analyze the protein expression of NF-kB p65 and its binding with Ski protein. Results:Ski protein was successfully overexpressed in small intestine after intraperitoneal injection of Ad-ski adenovirus. Overexpressed Ski protein prolonged the incubation period of writhing and decreased the frequency of writhing reaction, which was comparable to ibuprofen (P > 0.05). Compared with acetic acid group, overexpressed Ski protein significantly inhibited the protein expression of pro-inflammatory factors and pain biomarkers (*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01). Moreover, NF-kB p65 forms complexes with Ski. Conclusion: Overexpression of Ski protein has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects on acetic acid induced inflammatory pain by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors and pain biomarkers, and is related to Ski regulation of the NF-kB signaling pathway.
-
Exploration of the Establishment of an Experimental Animal Platform for Intelligent Acupuncture Robotic Acupuncture Feasibility and Safety Evaluation
MA Weigang, PAN Xingfang, QIU Jiwen, GAO Weifang, ZHANG Yonglong, DONG Yuge, TANG Yuzi, REN Haiyan, LI Zhongzheng
Abstract:
Objective:The development of intelligent acupuncture robots is in the early exploratory stage and lacks a reliable experimental research platform. This study aims to explore the experimental animal platform for the acupuncture feasibility and safety evaluation of intelligent acupuncture robots, and to lay the foundation for further research.Methods: Six 2-month-old Guangxi Bama miniature pigs were used as experimental subjects for acupuncture verification after anaesthesia. Firstly, manual acupuncture verification was carried out, and 6 acupoints were selected for each experimental animal, and the needles were left for 20 min after the lifting, inserting and twisting manipulation, and before and after control was carried out. The experiment was carried out for 28 days, and the experiment was conducted once every two days for a total of 10 times. After the verification of manual acupuncture, a point was taken 10 mm beside each of the 6 selected acupoints, and a total of 12 points were taken, and the intelligent acupuncture module of the acupuncture robot was used to carry out acupuncture operations on the experimental animals at different frequencies and angles to further verify the stability and feasibility of the animal platform. Results: The safety-related indicators in the blood routine were not abnormal, and were stable compared with the before and after comparisons of themselves. Blood biochemistry indicators were not abnormal, and were stable compared with the before and after comparisons. The average heart rate of the animals was 126 beats/min, and the average blood pressure was 87/36 mmHg. The average blood pressure of the animals was 87/36 mmHg, and the average body temperature of Bama miniture pigs was 36℃ at room temperature of 25℃. There was no significant change in body temperature during and after the experiment. On the basis of the experimental platform, the pre-test of acupuncture manipulation with the intelligent acupuncture module of the acupuncture robot was successfully completed, and there were no abnormalities related to acupuncture such as bending, breaking, or stagnation of needles during the experimental process, and the experimental animals did not show any obvious abnormality.Conclusion:In this study, a stable experimental animal platform for the evaluation of acupuncture feasibility and safety of intelligent acupuncture robots was initially established by drawing on the existing experimental method of miniature pigs, laying a foundation for further research related to intelligent acupuncture robots to be carried out.
-
Establishment of Liver-specific RBP4 Transgenic Mice and Analysis of Glucose Metabolism Characteristics
LU Wanxian, MA Qi, WANG Li, LIU Mengdi, GUO Baoping
Abstract:
Objective To construct a liver-specific Rbp4 knockout mouse model and to explore the effect of liver RBP4 on glucose metabolism. Methods Homozygous liver-specific Rbp4 knockout (Rbp4flox/flox:Cre+) mouse model was obtained by multiple breeding hybridization between LoxP-labeled Rbp4flox/+ mice and Alb-Cre tool mice. The genotype of mice was identified by agarose gel electrophoresis. Eighteen-week-old male mice were selected and divided into liver-specific Rbp4 knockout mice group (Rbp4flox/flox:Cre+, n=10), littermate control mice group ( Rbp4flox/flox, n=10) and wild-type mice group (WT, n=10). Western blot and qRT-PCR were used to detect the expression levels of Rbp4 protein and mRNA in liver and the expression levels of Rbp4 mRNA in other tissues to verify the specific knockout results. HE staining was used to observe the morphological changes of liver tissue in mice. Glucose tolerance and insulin tolerance were measured at the end of the 18 th week. The expression of liver glucose metabolism genes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase ( Pepck ) and glucose-6-phosphatase ( G6pase ) was detected by qRT-PCR. Results Western blot and qRT-PCR results showed that the expression of Rbp4 in the liver of Rbp4flox/flox:Cre+ group was decreased (P< 0.05 ). HE staining, glucose tolerance and insulin tolerance results showed that liver-specific Rbp4 knockout had no significant effect on liver morphology, glucose tolerance and insulin tolerance. Compared with WT group, the relative expression of Pepck mRNA in Rbp4flox/flox group was increased, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Compared with WT group, there was no significant difference in the relative expression of Pepck mRNA in the liver of Rbp4flox/flox:Cre+ group (P> 0.05 ).Compared with the Rbp4flox/flox group, the relative expression of Pepck mRNA in the liver of the Rbp4flox/flox:Cre+ group was decreased, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the expression of G6pase mRNA in the liver of the three groups (P> 0.05 ). Conclusion A liver-specific Rbp4 knockout mouse model was successfully constructed. Under physiological conditions, liver-specific Rbp4 knockout had no significant effect on liver tissue morphology, glucose tolerance and insulin tolerance in mice, and reduced the expression of liver glucose metabolism gene Pepck, suggesting that RBP4 plays a role in liver glucose metabolism.
-
The creation and translational relevance of abdominal aortic aneurysm animal models
Xia Congcong, Liu Haole, Hou Haiwen, Liu Enqi, zhao sihai
Abstract:
With the population aging in our country, the incidence of abdominal aortic aneurysm(AAA), an aged disease, has gradually increased. Because of the high mortality of ruptured AAA, which became one of the most severe life-threaten diseases. In histopathology, main AAA pathological features include elastin degradation, smooth muscle cells (SMCs) depletion, extracellular matrix digestion, and mural leukocytes accumulation. In clinics, open/endovascular repair remains the effective strategy for AAA management, and the drug therapy is still lacking. The detailed molecular mechanism of AAA is still unclear, which is one of the important bottlenecks affecting the development of potential drug targets. Animal models are the most powerful tools to clarify the pathogenesis of AAA. Though some medium to large laboratory animal models (such as rabbits, guinea pigs, dogs and pigs) are established for AAA study, rodent models (mice and rats) still take the first place in this field. At present, the methods to induce AAA include intra-infrarenal aortic infusion of elastase, subcutaneous infusion of angiotensin II (Ang II), periaortic calcium chloride painting, decellularized aortic xenograft and so on. For the cease of pre-induced stimulation (medical or surgical), AAA tends to stabilize in most models. Therefore, the development of ideal animal models, which maintains the continuous aortic dilation and even rupture, remains a problem. AAA animal models are helpful in elucidating the pathogenesis, screening new drug targets and promoting its clinical translation. This review aims to discuss the application of current AAA modeling methods and their translational relevance.
-
Progress in the study of animal models of hemophilic arthritis
Abstract:
Hemophilia Arthritis (HA) is caused by recurrent bleeding, which seriously affects the life of patients and consumes a lot of social and medical resources. Limited by ethical requirements, it is necessary to establish an animal model of HA for research. In order to summarize the research progress of animal models of hemophiliac arthritis, this paper reviewed the literature on animal HA models at home and abroad in recent years, from the aspects of species selection, modeling methods, histopathology, imaging evaluation methods, etc.
-
The metabolic profiles of serum lysophosphatidylcholine and amino acid in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
ZHAO Mei-yu, SHI Xin-yue, ZHOU Shu-ling, LI Hai-jun, FAN Shu-ting, XIONG Yin-hua
Abstract:
Objective: Using metabolomics methods to study the metabolic profiles of amino acids and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) in serum of rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD), and to identify biomarkers that can characterize NAFLD and speculate on the possible mechanism of its occurrence. Methods: NAFLD rats were prepared by feeding high-fat diet feed and intraperitoneal injection of carbon tetrachloride. The levels of 15 LPCs and 18 amino acids in the serum of the control and NAFLD groups were determined using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.SPrincipal component analysis and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis were used to analyze the changes in serum LPC and amino acid metabolic profiles in NAFLD rats. Pearson correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between biomarkers and NAFLD.SResults: The metabolic profiles of serum LPC and amino acid in the NAFLD group significantly deviated from the control group and could be completely distinguished.SLPC (20:1), arginine and glutamic acid had significant contributions to NAFLD, and these species were identified as biomarkers. Furthermore, LPC (20:1) and arginine were significantly correlated with serum biochemical indicators such as AST, ALT, LDL, and TBIL.SConclusions: The metabolic profiles of serum LPC and amino acid were closely related to NALFD.
-
The effect and mechanism of olaparib on the senescence of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
Wang Dawei, Guo Jing, Bian Jichun, Wang Shasha, Lu Meichao, Zhang Daizhou, Jia Yuping
Abstract:
Objective To study the performance and related molecular mechanism of Olaparib-induced senescence in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Methods Real-time cell analysis (RTCA) was used to dynamically detect anti-proliferation and anti-migration activities in real time. Senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) staining was used to observe the senescence-inducing activity of cells. The effects of olaparib on the expression of senescence-associated genes p16INK4a, p21, C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) , interleukin (IL) -6, IL-8, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) , phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) , p27, retinoblastoma protein (RB1) , Ki67 and E2F1 were analyzed by qPCR. The effects of olaparib on the expression of senescence-associated proteins p21, γH2AX, pRB, cyclin D1, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) and Ki67 were analyzed by Western blot. Results Olaparib could inhibit the proliferation and migration of MCF-7 breast cancer cells and induce the senescence of MCF-7 cells. The gene expression levels of p16INK4a, p21, p27, CHOP, IL-6, IL-8, PAI-1, PTEN and RB1 in MCF-7 cells treated with olaparib for 96 h were significantly up-regulated (P < 0.01) , and the gene expression levels of Ki67 and E2F1 were significantly down-regulated (P < 0.01) . The expression levels of p21, γH2AX and IGFBP3 proteins in MCF-7 cells were significantly increased (P < 0.01, P < 0.01, P < 0.05) , and the expression levels of cyclin D1, pRB and Ki67 proteins were significantly decreased (P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.05) . Conclusion Olaparib can produce anti-MCF-7 breast cancer cells by anti-proliferation, migration and induction of cell senescence.
-
The Protective Effect and Mechanism of BBD on Doxorubicin-induced Myocardial Injury in Zebrafish model
LI Xianmei, ZENG Laifeng, HUANG Bin, YU Lanxin, LIN Jiumao
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the protective effect and mechanism of BBD on Doxorubicin (Dox) induced myocardial injury in zebrafish. Method A zebrafish model of myocardial injury induced by chemotherapy drug Dox was established. The effects of BBD at different concentrations on pericardial edema ratio and heart rate were observed under a stereo microscope. Transgenic zebrafish Tg(mpx:EGFP) was used to observe the inhibitory effect of BBD on neutrophil infiltration in the heart in situ., and observe the effect of BBD on SOD, CAT and MDA. Real-time qPCR was used to detect the expression of ferroptosis related factors gpx4a, ptgs2, alox5a, acsl4. The accumulation of ferrous ion in zebrafish heart was detected using a ferrous ion fluorescent probe. Results BBD significantly improved Dox induced pericardial edema, heart rate and neutrophil infiltration in zebrafish (P<0.05), significantly increased the reduction of SOD and CAT activity (P<0.05), and decreased the concentration of MDA (P<0.05). Compared with the Dox group, the Dox group showed significantly increased expression of gpx4a (P<0.05) and decreased expression of ptgs2, alox5a, and acsl4 (P<0.05), and significantly inhibited Dox induced ferroptosis in zebrafish hearts. Conclusion BBD can attenuate Dox induced myocardial injury in zebrafish by inhibiting the occurrence of lipid peroxidation and regulating ferroptosis.
-
A review of studies on the construction of experimental animal models and evaluation methods of spleen deficiency syndrome
ZHANG Yonglong, MA Weigang, QIAN Xingyu, ZHAO Suhong, LI Shanshan, GUO Yi, GUO Yongming, XU Zhifang, PAN Xingfang, QIU Jiwen, LI Zhongzheng
Abstract:
The construction of experimental animal models of Chinese medicine syndromes plays an important platform support role in the research of the mechanism of action of Chinese medicine. In recent years, there are more and more reports in the literature on the construction and evaluation of the animal model of spleen deficiency evidence, but there are different standards of the construction method and insufficient objectification of the evaluation indexes. In this paper, we will summarize the construction and evaluation methods of the animal model of spleen deficiency from the aspects of animal selection, model establishment, macroscopic characterization, behavioral experiments, and objective indexes of spleen deficiency. evaluation methods, with a view to providing theoretical guidance for the construction of experimental animal models of spleen deficiency and literature reference for the selection of animal model platforms for spleen deficiency.
-
Research Progress in Mouse Model of Sarcopenia
Abstract:
Through the study of literature retrieval related to sarcopenia, the modeling method and model evaluation scheme of sarcopenia mice were summarized. The operation methods, advantages and disadvantages, and application scope of the four modeling methods of drug injection, aging, muscle atrophy, and transgenic were reviewed. The evaluation methods of muscle function, muscle strength, and muscle endurance were summarized, and their advantages and disadvantages were compared to provide reference for the later research of sarcopenia.
-
Therapeutic effects of Isaria feline combined with cyclophosphamide in hepatoma H22 tumor-bearing mice
SHI Xiaowei, CHEN Jingjing, YU Guoyan, ZHANG Yiyin, CHEN Lixia, ZHAO Lili, YANG Yongming, WANG Jing, YAN Lei, YANG Xihua
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To investigate the therapeutic effects of Isaria felina originated from cordyceps sinensis combined with cyclophosphamide in hepatoma H22 tumor-bearing mice. Methods The model of H22 tumor-bearing mice was established and twenty-five Kunming mice were randomly divided into one blank control(NC)and four H22 tumor-bearing groups including tumor model control(MC), positive control(CTX), Isaria felina group(IF)and combined administration group(IF + CTX). The mice in the blank control group and the model control group received distilled water by oral gavage, the mice in the positive control group were intra-abdominally injected with CTX olution(25 mg/kg body weight every day), the mice in the IF group were orally administered Isaria felina(dispersed in distilled water) at 400 mg/kg body weight, and mice in the combined administration group were administerd the above two medications per day. The adminisation cycle was 10 d. At the end of the experiment, the mean tumor volume and weight, tumor inhibition rate, q value and immune organ index were calculated, and the levels of blood routine and cytokines were determined. The pathomorphological changes of tumor tissues were observed by HE staining. Results the tumor volume and mass of mice in each treatment group were significantly lower than those in MC group(P < 0.05). The tumor inhibition rates of CTX, IF and IF + CTX groups were 49.3%, 34.2% and 72.8%, respectively and the q value was 1.09. The number of WBC, Lymph and PLT in IF + CTX group was significantly higher than that in CTX group(P < 0.05). The spleen index of MC group was significantly higher than that of NC group, and the spleen index of IF + CTX group was significantly lower than that of MC group(P < 0.05). The level of serum IFN- γ in MC group was significantly lower than that in NC group, while the levels of IFN- γ in IF and IF + CTX groups were significantly higher than that in MC group and CTX group(P < 0.05). Pathologically,the tumor cells in the MC group grew well, numerous and closely arranged. While in the CTX, IF and IF + CTX groups, tumor cells arranged loosely, focal necrosis and nuclear pyknosis of necrotic cells could be seen in many places. Conclusion The combination of IF and CTX has an additive anti-tumor effect on H22 tumor-bearing mice, which can reduce immunosuppression and myelosup-pression caused by CTX, and have immunomodulatory function. 【Key words】 Isaria felina; H22 tumor-bearing mice; combined administration; immunomodulation
-
Establishment of qPCR method for detection of Staphylococcus xylosus and its application
YU LINGZHI, FENG LIPING, KONG ZHIHAO, ZHU QI, WEI XIAOFENG
Abstract:
Objective To establish and evaluate a method for rapid and sensitive Staphylococcus xylosus detection using qPCR. Methods This study selected the specific gehM gene fragment as the target for Staphylococcus xylosus, synthesized a set of specific primers and established a qPCR method for detection of Staphylococcus xylosus. Staphylococcus xylosus standard strain and other non taeget strains were chosen for specific analysis. Diluted the DNA of Staphylococcus xylosus to 10 times to determine its sensitivity. Clinical samples were tested and positive products were sequenced. The results were compared with those of bacterial culture. Results Staphylococcus xylosus had a specific amplification curve, while other non-Staphylococcus xylosus species did not show it, indicating that the primers were specific for Staphylococcus xylosus. The sensitivity was 100 fg DNA. The repeatabilities within and between groups are less than 3%. A total of 60 clinical samples were detected, of which 5 samples had a typical S curve. The PCR products were sequenced and BLAST. The similarity of the gene sequence was 99.63%, indicating that the sample was positive for the nucleic acid of Staphylococcus xylosus gehM gene, with a positive rate of 8.3%. However, the positive rate of bacterial culture was 6.7%. The positive rate of qPCR was slighterly higher than the culture. Conclusions The qPCR method established has the advantages of fast, high sensitivity and specificity, and can be used for the detection of Staphylococcus xylosus.
-
Guanxinning tablet improves doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis in rats with heart failure by inhibiting NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 pathway
shi jia jun, yang qin qin, fu dan ting, zheng chun wei, zhang yan, chen yu
Abstract:
【摘要】目的 研究冠心宁片对扩张型心肌病(dilated ca rdiomyopathy,DCM)的保护作用,并从NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1通路深入探讨其对心肌细胞焦亡的作用机制。方法 随机将大鼠分为冠心宁片低剂量组、冠心宁片高剂量组、阳性药地高辛组、模型对照组和正常对照组,通过阿霉素(doxorubicin,DOX)累积注射17.5 mg/kg诱导大鼠DCM模型,同时连续给药10周。超声心动图检测心功能指标,ELISA检测血清IL-1β和IL-18水平,RT-PCR法检测心肌组织NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1、NF-κB、TXNIP、IL-1β和IL-18的mRNA表达,免疫组化、免疫荧光染色和western blotting检测NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1、IL-1β、IL-18、GSDMD、GSDMD-NT的蛋白表达及TUNEL染色结果,透射电镜观察心肌细胞显微结构的变化。结果 与正常对照组比,模型对照组的IVSs、IVSd、LVPWs、FS、SV、EF和HR显著降低,LVIDs、ESV及血清IL-1β、IL-18显著增加,NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1、NF-κB、TXNIP、IL-1β和IL-18的mRNA表达均显著增加,NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1、IL-1β、IL-18的蛋白表达及TUNEL染色面积明显增加,显微结构明显改变。与模型对照组相比,冠心宁片可显著增加IVSs、SV、FS、EF和HR,显著降低LVIDs、ESV和血清IL-1β、IL-18水平,降低心衰大鼠的NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1、NF-κB、TXNIP、IL-1β、IL-18的mRNA和NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1、IL-1β、IL-18的蛋白水平及TUNEL染色面积,显微结构明显改善。结论 冠心宁片可以有效改善阿霉素诱导的扩张型心肌病,可能是通过抑制NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1通路改善扩张型心肌病大鼠的心肌细胞焦亡实现的。
-
Preparation of a rat model of diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome induced by acetic acid enema combined with binding tail-clamping stress
laibiyu, hongmengying, heyongjia, chenyao, lixinwu, lixing, she chang, lidan, shijia, tianzihan
Abstract:
【Abstract】 Objective To establish an ideal modeling method for Diarrhea Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS-D) with anxiety and depression in rats, and to provide an animal model for clinical study of IBS-D (IBS-D). Methods In the first stage, 20 rats were randomly divided into blank group, 3% acetic acid enema group, 4% acetic acid enema group and 5% acetic acid enema group. On the first day of intervention, the rats were given acetic acid enema with 3%, 4% and 5% concentration, respectively. After observation for 1 week, the appropriate acetic acid concentration was evaluated. In stage 2, 40 rats were randomly divided into blank group, acetic acid enema group, acetic acid + binding group, acetic acid + binding + tail clip group, and were treated with different interventions for a total of 8 days. After the intervention, the general condition, diarrhea-related index, open field test score and colonic histopathology of rats were evaluated. Results In the first stage, compared with the blank group, the fecal trait score of 4% acetic acid enema group increased at 1-3 days after intervention (P < 0.05), and gradually decreased at 4-7 days after intervention, and there was no significant difference between the group and the blank group at 7 days (P > 0.05), and the body mass was relatively lower at 1 week after intervention (P < 0.05). Fecal water content increased (P < 0.01); Compared with blank group, body mass of 5% acetic acid enema group was decreased (P < 0.05), fecal trait score, fecal water content and diarrhea index were increased (P < 0.01). There was no significant difference between 3% acetic acid enema group and blank group. Compared with the blank group in the second stage, the body mass of the simple acetic acid enema group was lower (P < 0.01), and the fecal water content and diarrhea index were increased (P < 0.01). Compared with the blank group and the simple acetic acid enema group, the body mass of the acetic acid + restraint group and the acetic acid + restraint + tail clip-on group was lower (P < 0.01). Fecal trait score, fecal water content and diarrhea index increased (P < 0.01), and colon running time decreased (P < 0.01). In the open field test score, compared with the blank group and the simple acetic acid group, the open field test distance, standing times and upright times in the acetic acid + bound group and the acetic acid + bound + clip group were all the same (P < 0.01). Compared with acetic acid + binding group, the open field experiment distance, standing times and upright times in acetic acid + binding + tail group were all different (P < 0.05). The pathological tissue of colon showed that compared with the blank group, the mucosa structure of 4% acetic acid enema group was complete with a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration, and the pathological tissue score had no significant difference (P > 0.05), while the 5% acetic acid enema group had a medium to large amount of inflammatory cell infiltration, and the pathological tissue score was increased (P < 0.05). The mucosal structure of colon tissues in each group in stage 2 was intact, and a small amount of inflammatory cells infiltrated in different degrees. Conclusion 4% acetic acid concentration is the appropriate concentration for IBS-D modeling. After superposition and binding, IBS-D diarrhea and internal hypersensitivity characteristic state can be better simulated. After superposition of tail clip, IBS-D model of liver-stagnation and spleen-deficiency can be successfully prepared.
-
The protective effection on allergic asthma rats of Xiebaisan based on Non-targeted Metabolomics and Intestinal bacterial flora
yangzongtong, Xu Dongchuan, Liu Jin, LI Xiaojing, Zhang Huimin, WANG Wenhui, Sui Zaiyun
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To explore the possible mechanism of Xiebaisan in protecting allergic asthma rats from the perspective of host-intestinal flora-metabolism. Methods The SPF SD rats were divided into normal group (NC Group) , model group (M group) and Xiebaisan Group (Xiebaisan Group); Allergic asthma rat model was established by ovalbumin (OVA); The changes of lung histopathology in rats were observed by stained with Hematoxylin-HE. Colon contents were harvested for 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing to observe the changes of intestinal flora structure and function; Serum and lung tissue samples were collected for non-targeted metabolomics analysis by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Results The results of HE showed that, Xiebaisan group could improve the lung histomorphology of asthmatic rats to some extent compared with M Group; The results of 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing showed that, the diversity of intestinal flora decreased in M group, and the diversity of intestinal flora was improved in Xiebaisan group compared with M group; The results of serum non-targeted metabolomics test showed that, Xiebaisan group could regulate amino acid metabolism and mTOR pathway, and reversed the differential metabolite expression induced by M group partially; The results of non-targeted metabonomics of lung tissue samples showed that, the Xiebaisan group could regulate carbon metabolism, vascular smooth muscle and cAMP signaling pathways, and reversed the differential metabolite expression induced by M group partially. Conclusion The protective effects of Xiebaisan on allergic asthma in rats may be related to the improvement of the morphological structure of lung tissue, the diversity of intestinal flora, and the regulation of mTOR pathway, Vascular smooth muscle contraction pathway and cAMP pathway, which affect the metabolism of amino acids and carbon.
-
Construction and Evaluation of a Mouse Model of Chronic Restraint Intestinal Stress Injury
ZHENG Jianhua, CHEN Jingqing, DONG qiaoyan, FA Yunzhi, QIU Yefeng
Abstract:
Objective Given that psychosocial stress can contribute to a series of diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome, we aimed to establish an experimental chronic restraint mouse intestinal stress injury model as a basis for exploring the pathogenic mechanism of chronic restraint stress-induced gastrointestinal diseases, and for developing preventive and curative measures. Methods Eighteen male SPF-grade BALB/c mice were acclimatized for 7 days and then divided into a control group and a chronic restraint stress group according to body weight, using a randomized numerical table method. The mice were subjected to restraint stress for 3 hours per day for 14 days to establish an intestinal injury model. The model was evaluated by observing body weight, pathological changes in intestinal histomorphology, expression of tight junction proteins, apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells, and mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cytokines. Results After 14 days of chronic restraint stress, model mice showed weight loss, shortened duodenal villus height, abnormal crypt structure, a decreased villus/crypt ratio, colonic mucosal inflammatory cell infiltration, and irregular crypt structure. Protein immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence staining showed that the expression levels of the duodenal and colonic tight junction proteins occludin and claudin-1 were significantly decreased in mice after chronic restraint stress (P < 0.05), while expression levels of the apoptotic protein cleaved-caspase-3 in intestinal epithelial cells were significantly increased (P < 0.05). Regarding the mRNA expression levels of intestinal inflammatory factors and chemokines, chronic restraint stress for 14 days significantly increased the gene expression levels of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor-α, and IL-10 in the duodenum of mice (P < 0.05), and significantly increased the gene expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and MCP-1 in the colon (P < 0.001). Conclusions The use of a behavioral restriction device to restrain mice continuously for 14 days led to abnormal intestinal tissue structure, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis, and triggered an intestinal inflammatory response in the stressed mice, indicating successful establishment of a mouse model of intestinal injury by chronic restraint stress.
-
Establishment and Analysis of NLRP3-/- Mouse Models of Ulcerative Colitis
wangzhuhuan, zhangerxin, zhengqinwei, haoweiwei
Abstract:
To induce NLRP3-/- mouse ulcerative colitis (UC) model using different concentrations of Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS) and administration time, and to analyze and evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of its preparation, in order to provide a more clinical animal model for the study of UC pathogenesis and the development of therapeutic drugs.Method: 48 NLRP3-/- mice of SPF level were randomly divided into groups and induced UC mouse models using a combination of different concentrations of DSS and administration time (blank group, 2.5% 7 days, 3% 7 days, and 3% 5 days). The physical weight, DAI score, HE staining, measurement of colon length and related indicator molecules (IL-6, TNF) of the mice were observed and evaluated- α Compare the effect of modeling with the expression level of tight junction protein.Result: 1. Each group was able to induce UC membrane type at different concentrations and administration times; 2. As the concentration gradient increases and the administration time prolongs, the physical weight of the mice decreases more significantly, the fecal occult blood is more positive, the DAI score is higher, and the mice die; 3. HE staining showed that the longer the time and the higher the concentration of DSS, the more severe the damage to the intestinal mucosal tissue in mice; 4. Using immunohistochemistry to detect inflammatory factors and tight junction proteins, compared to the blank group, the inflammatory factors (TNF-α) in the model group were detected,The expression levels of IL-6 and IL-6 increased, while the expression level of tight junction protein (ZO-1) decreased compared to the blank group.Conclusion: 1. NLRP3-/- mice can induce UC models under conditions of 2.5% 7 days, 3% 7 days, and 3% 5 days; 2. Combining DAI score, HE staining, and related indicators detection, as well as mouse survival rate, NLRP3-/- mice induced UC model under 3% DSS-5d conditions are more suitable for clinical manifestations of UC and more favorable for later drug intervention.
-
The AOM/DSS Inflammation-cancer Transformation Model Optimized and Explored the Changes of Intestinal Microbiota in Mice with Colon Cancer
ZHU Lin, WANG Dunfang, FENG Xue, ZHANG Caijuan, LIU Haifan, LIU Yaqing, LIU Bin, LIU Li, YANG Weipeng
Abstract:
【Abstract】 Objective To optimize the method of combining azomethane oxide (AOM) and dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) to create a colitis-associated colon cancer (CAC) model, and to explore the pathogenesis of the intestinal flora in CAC. Method Model groups A and B were established by one and two injections of AOM, respectively, combined with free drinking of DSS, and a normal control group was injected intraperitoneally with normal saline combined with purified water (n=10 mice per group). The better modeling scheme was selected by comprehensive evaluation of the disease activity index score, colon length, tumor rate, and mortality. Serum levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and tumor markers CA199, CEA, and CA724 were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Colon lesions were evaluated by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. Changes in the intestinal microbiota in CAC mice were detected by 16S rDNA high-throughput gene sequencing analysis of mouse feces. Results Both single and enhanced AOM injections combined with DSS induced CAC mice; however, colon growths were larger, more closely arranged, and their morphological size was more consistent in group B compared with group A, with a tumor-formation rate of 100%. IL-6 and TNF-α levels were increased in the model group compared with the normal group (P<0.05, P>0.05, respectively). The CA199 and CEA levels were also significantly increased (P<0.05), but CA724 levels were not. Infiltration of inflammatory cells in the colon detected by HE pathology was accompanied by high-grade intraepithelial tumor-like changes on the surface of the lumen. The diversity and abundance of intestinal bacteria were decreased in CAC mice compared with normal mice: phyla Verrucomicrobiota and Actinobacteriota were significantly increased (P<0.05), Bacteroidota and Campilobacterota were significantly decreased (P<0.05). Akkermansia, Prevotellaceae, Ruminococcus, and Bifidobacterium were significantly increased (P<0.05), and Roseburia, Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, Anaeroplasma, and Muribaculaceae were significantly decreased (P<0.05). Conclusion Two injections of AOM combined with 1.5% (1.5 g/100 ml) DSS induced CAC model mice with a high colon-tumorigenesis rate, uniform tumor morphology, and low mortality, and may thus be the preferred modeling scheme for pharmacodynamic experiments. Disorders or dysfunction of the intestinal flora may lead to increased permeability, loss of intestinal mucosal barrier function, and the release of enterogenic endotoxins, resulting in a sustained inflammatory response, as an indirect or direct cause of CAC pathogenesis.
-
Construction of HIF-1α gene knockout plasmid and functional verification of naked mole rats based on CRISPR/Cas9 system
Zhang Jingyuan, JIANG Xiaolong, CUI Shufang
Abstract:
Objective Plasmids construction and knocking out HIF-1α gene of NSF cell line by CRISPR/Cas9 genomic editing technology, providing an in vitro cell model for studying the mechanism of hypoxia tolerance and the occurrence and development of hypoxia related diseases in naked mole-rats. Methods Design four pairs of sgRNA sequences which targeted exon 1-4 of NSF HIF-1α gene and successfully construct an expression plasmid. The plasmid with optimal sgRNA was identified and transfected into 293T cells, and the supernatant was used for detecting the virus titer. Furthermore, lentivirus particles carring sgRNAs of HIF-1α infected NSF cells which have been infected with Cas9 lentivirus particles based on the protocol of manufacture previously. After drug screening of post transfection, fluorescence signals were observed under fluorescent microscope, and the expression of HIF-1α in NSF cells were detected by Western blot and T7E1 enzyme. Results The Sanger sequencing results showed that the designed sgRNA was successfully inserted into pX459 and pKLV2-U6-sgRNA2 vectors, demonstrating that the recombinant plasmid used for the transfection were successfully constructed;The T7E1 digestion experiment successfully removed 3 bands, the target efficiency of sgRNA was 54%, and the Western blotting results showed that the HIF-1α gene was successfully knocked out and the protein level was significantly reduced in NSF cells of naked mole rats (P=0.0019). Moreover, no obvious changes in the morphology of HIF-1α knockout cells were found under the microscope, and gene knockout had no obvious effect on cell proliferation. Conclusion The HIF-1α knockout cell line was successfully constructed using CRISPR/Cas9 technology, which will provide experimental basis for the further study of the HIF-1α biological function. Furthermore, it will be beneficial for the study of the mechanism of hypoxia tolerance in naked mole mice and provide theoretical foundation for the prevention and treatment of hypoxia related diseases.
-
Development of inflammation and coagulation disorders in Sepsis
hou yuan lu, zhao ru ru, gao lei, li qi feng, yao zheng, li ming hong
Abstract:
Objective:To study the changes in coagulation function and inflammation levels during sepsis. Methods: Multiple infection sepsis model (MIM), based on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), was apllied to establish a rat model of sepsis. Forty-eight male SD rats were randomly divided into blank group (control group, n=8), sham operation group (sham group, n=8), 4-hour sepsis group (4h group, n=8), 8-hour sepsis group (8h group, n=8), 12-hour sepsis group (12h group, n=8), and 16-hour sepsis group (16h group, n = 8). ELISA and coagulation analysis were used to detect inflammatory markers and coagulation-related indicators. Results: (1) Compared with the sham group, the content of LPS and IL-6 in the model rats of all time points increased significantly(p<0.001). The LPS and IL-6 gradually increased as the disease progressed, however no significant changes after 12 hours. (2) In the middle and late stages of the septic model(starting from the 8h), PT was significantly prolonged compared with that in the sham groups(p<0.01). (3) Compared with the sham group, APTT time was significantly prolonged in 8h,12h,and 16h groups(P<0.05,P<0.01). The APTT time gradually lengthened from 8h group, and gradually approached control group after that. (4) Except for 8h group, the Fbg content in septic groups of all time points increased significantly than sham group (p < 0.01). (5) There was a significant difference between control group and sham group in FDP (p < 0.01), but no significant difference between sham group and septic groups. (6) Compared with the sham group, the level of AT-III in each period of progression in sepsis was decrease(p < 0.01), and there were significant differences in the proportions of 4h group,8h group, and 16h group. Conclusion: In the progression of sepsis, infection and inflammation levels gradually increase and cause coagulation dysfunction. The Fbg increases rapidly in the disease progresses, indicating the rapid activation of ogenous after model surgery. However, the PT and APTT time significantly increase in the middle and late stages of sepsis, suggesting the coagulation factors gradually depleted to induce DIC. At the same periods, multiorgan damage caused by sepsis leads to reduced expression of AT-III, further aggravating the coagulation/anticoagulant disorders. In addition, during the disease progression, a large amount of FDP interferes with fibrin polymerization, resulting in hemorrhagetendency and worsening DIC.
-
WNK2 delays the proliferation and invasion of HCC by inhibiting tyrosine phosphatase activity
Abstract:
Abstract: Objective To investigate the effect of WNK2 on the expression of SHP2 (tyrosine phosphatase) in HCC and to explore the effect on the proliferation and migration of HCC. Methods HepG2 cells were transfected with WNK2-mimic, WNK2-inhibitor, and corresponding negative control. The effect of WNK2 on the proliferation of HCC was examined by subcutaneous tumorigenesis assay in Balb/c nude mice. The expressions of WNK2, p-SHP2, p-AKT, and p-ERK1/2 in tumor tissues were detected by Western blot. After treatment with SHP2 inhibitor PHPS1, the expressions of WNK2, p-SHP2, p-AKT, and p-ERK1/2 in HepG2 cells were detected by Western blot. The migration ability and invasion ability of HepG2 cells were detected by cell scratch assay and Transwell. The proliferation ability of HepG2 cells was detected by monoclonal proliferation assay. Results Compared with the NC group, the tumor volume of nude mice in the sh-RNA WNK2 group was significantly increased (p<0.01), while that of nude mice in the WNK2-mimic group was significantly decreased (p<0.01). Western blot results showed that compared with the NC group, the expression of WNK2 in the sh-RNA WNK2 group was significantly decreased (p<0.01), while the expressions of p-SHP2, p-AKT, and p-ERK1/2 were significantly increased (p<0.01). However, the expression of WNK2 was significantly increased in the WNK2-mimic group (p<0.01), and the expressions of p-SHP2, p-AKT, and p-ERK1/2 were significantly decreased (p<0.01). In vitro experiment, compared with the NC group, the expression of WNK2 was significantly decreased in the WNK2-inhibitor group (p<0.01), while the expressions of p-SHP2, p-AKT and p-ERK1/2 were significantly increased in the WNK2-inhibitor group (p<0.01). Compared with the NC PHPS1 group, the expression of WNK2 was significantly decreased in the WNK2-inhibitor PHPS1 group (p<0.01), while the expressions of p-SHP2, p-AKT, and p-ERK1/2 were reversed and had no significant differences compared with the NC PHPS1 group (p>0.05). The cell scratch assay and Transwell results showed that the migration and invasion ability of HepG2 cells in the WNK2-inhibitor group was significantly increased compared with the NC group (p<0.01). The migration and invasion ability of HepG2 cells in the NC PHPS1 group and WNK2-inhibitor PHPS1 group were significantly decreased with no significant difference (p>0.05). The results of the monoclonal proliferation experiment showed that the proliferation capacity of HepG2 cells in the WNK2-inhibitor group was significantly increased compared with the NC group (p<0.01), while the proliferation ability of HepG2 cells in the NC PHPS1 group and WNK2-inhibitor PHPS1 group was significantly decreased with no significant difference (p>0.05). Conclusion WNK2 inhibits the expression of SHP2 in HCC by regulating the level of oxidative stress, delaying the proliferation and migration of HCC.
-
IL2rg-/- knockout rats support human RSV a prolonged infection
FAN CHANGFA, XIONG RUI, WU YONG, YANG YANWEI, QU ZHE, LIU SUSU, WANG YUYA, MA LIYING, FU RUI, PENG YIHONG, LIANG CHUNNAN
Abstract:
Human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) is the second leading aetiology of lower respiratory infection deaths in the world. Disease animal models play an important role in the development of vaccine and therapeutic drugs, and a variety of animals, including non-human primates such as chimpanzees, have been made to develop models of hRSV infection. However, the limitations such as semi-permissiveness and short duration of infection have impeded their applications in both the pathogenesis of hRSV and therapeutics development. Here, we presented an hRSV infection model based on IL2rg gene deficient rat using TALEN technology. IL2rg-/- knockout rats can sustain high viral loads in nasal cavity upon intranasal inoculation with hRSV. The average peak titer rapidly reached 1?010 copies/g in nasal tissue, as well as 1?07 copies/g up to 5 weeks post infection. Since IL2rg-/- knockout rats is genetically heritable, with stable traits and easy production, which facilitate the standardization of disease models. Compared with mice, rats have the advantages of being larger and more convenient for collecting sufficient samples. This IL2rg-/- rat model can be used to study the transmission and pathogenesis of hRSV and is a useful tool for evaluating therapies.
-
Methodological discussion based on preclinical studies of fecal bacteria transplantation in rodents
sunshiqi, Liu Lu, Hu Shuangyuan, Wang Yuyan, Sun Mingsheng, Zhao Ling
Abstract:
Fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) is a therapeutic modality that targets intestinal microorganisms by transplanting fecal microorganisms from the donor into the recipient's gastrointestinal tract in order to reconstitute the recipient's intestinal flora. However, the mechanism of action and adverse effects of FMT in response to different diseases have not yet been clarified, and thus it cannot be widely applied in the clinic, and still needs to rely on in-depth preclinical studies. The highly inconsistent or incomplete experimental details in current reports, coupled with the lack of authoritative standards and recommendations, not only seriously affect the interpretation of their findings and the replication of experimental procedures, but also hinder the clinical translation of the results. We review and discuss the key steps of recipient selection and graft sample collection, storage, graft material preparation, and grafting route, with the aim of improving the utilization of experimental animals, consumables, and labor, and providing methodological recommendations and references to achieve replicability and standardization of FMT preclinical studies.
-
Effects of resistance exercise on lncRNA and mRNA gene expression profiles of SAMP8 mice skeletal muscle
FU ZETING, LI ZHONGHAO, LI LUNYU, LIU HONGZHENG, DING HAILI
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To explore the potential regulatory mechanism of resistance exercise on senescence accelerated-prone mouse (SAMP8) by comparing the differential expression of lncRNA and mRNA in quadriceps between exercise group and control group by RNA-seq technology. Methods: Twenty-eight-week-old male SAMP8 mice were divided into a model group and resistance exercise group, with six mice in each group. Another eight SAMR1 mice of the same age were used as the control group. The resistance exercise group received 8 weeks of increasing weight climbing exercise training. The relative grip strength was performed every 1 weeks and the rotarod test was performed every 2 weeks. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to observe the histological changes of the right quadriceps femoris, and take the left quadriceps for RNA-seq (RNA-sequencing). The differentially expressed long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and mRNA were screened. These Genes were then analyzed for enrichment by Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). Finally, the key differentially expressed genes were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) to verify the accuracy of RNA-seq results. Results: (1) Compared with the control group, the relative grip strength and rotarod test time of model group were decreased significantly(P < 0.01). After 8 weeks of resistance exercise, compared with model group, the relative grasping strength and the rotarod test time of resistance exercise groups were increased significantly(P < 0.01). (2) The results of Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed that compared with the C group, the cross-sectional area of muscle fibers in M group was significantly lower(P < 0.01), compared with the M group, the cross-sectional area of muscle fibers in R group was significantly increased (P < 0.01). (3) Through differential expression analysis, we found 182 upregulated and 218 downregulated lncRNAs, and 454 upregulated and 289 downregulated mRNAs in the comparison between the M group and the R group. The KEGG pathways of lncRNA target genes between the M group and the R group were significantly enriched in Intestinal immune network for IgA production、NF-kappa B signaling pathway、inflammatory bowel disease, etc. Conclusions: (1) This study demonstrated that resistance exercise can improve skeletal muscle function in SAMP8 mice with sarcopenia, and evaluated the differentially expressed lncRNA and mRNA in M group and R group by RNA-seq. These genes may be the target of sarcopenia therapy. (2) By analyzing the biological information of the target genes of differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs, it is possible to further understand the mechanism of resistance exercise to improve sarcopenia.
-
Comparison of different Regimens in Isoprenaline-induced Chronic Heart Failure Models
Abstract:
Objective: To compare animal models prepared by three different protocols and to explore a stable, reliable and reproducible mouse model of chronic heart failure. Methods: Twenty-five male C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into four groups, namely blank group (ZC), model A group (MA), B group (MB) and C group (MC). The model group adopted different preparation protocols for continuous injection of ISO, in which the MA group and the MB group were dose-decreasing modeling, and the MA group (10 mg·kg-1 on the first day, 5 mg·kg-1 on the second day, 2.5 mg·kg-1·d-1 on the 3rd~30th day; subcutaneous injection for 30 days); MB group (20 mg·kg-1 on day 1, 10 mg·kg-1 on day 2, 5 mg·kg-1·d-1 on day 3~14; Subcutaneous injection for 14 days), MC group (constant dose 7.5 mg·kg-1·d-1, intraperitoneal injection for 28 days), CHF model was constructed. The day after the end of injection, the survival and mold formation rates of each group of mice were calculated. Cardiac function was measured by cardiac ultrasound and serum levels of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-pro BNP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) were measured in serum. Results: After the end of injection at the end of the fourth week, all model groups were effective in inducing CHF. However, based on the comprehensive test results, it was found that the mold-making situation of the MC group with a concentration of 7.5mg/kg was the most stable, which was more suitable for subsequent research on traditional Chinese medicine. Conclusion: ISO prepared mouse CHF model with constant 7.5 mg·kg-1·d-1 and continuous intraperitoneal injection for 28 days.
-
Research advances on the use of pigeon in animal robot
Li Mengmeng, Yang Long, Yang Lifang, Wan Hong, Shang Zhigang
Abstract:
Pigeons have the habits of clustering and homing, which are good at long-distance weight-bearing and continuous flight with excellent navigation and spatial cognitive abilities. Pigeons have been widely used in animal robot research in recent years. Pigeon robot achieves motor behavior control by applying neural information intervention to specific neural targets in the pigeon’s brain. According to the distribution of hierarchical multi-level neural regulatory targets in the pigeon’s brain, this review summarizes the research progress of pigeon robot based on the sensory system, motivation and emotional system or cortex and midbrain motor area respectively. This review aims to provide reference and guidance for further application research of pigeon robot in space perception, reconnaissance and anti-terrorism search and rescue.
-
Analysis of the regulatory effect of Angelica dahurica on the MrgprD-TRPA1 pathway in neuropathic pain
Gu Leying, Yang Niuniu, Yu Kangying, Meng Yaqin, Song Shaozheng
Abstract:
Objective Neuropathic pain was a kind of chronic pain caused by central or peripheral nervous system injury, dysfunction or transient disorder. Its mechanism was related to some receptors. In order to analyze the analgesic effect of Angelica dahurica in neuropathic pain and its regulation on MrgprD-TRPA1 signaling pathway. Methods Firstly, the CCI mouse model was prepared by using sterile surgical ligation and wrapping of the sciatic nerve in 30 mice. Secondly, the VonFrey experiment was used to detect the behavioral changes in pain induced by mechanical stimulation in mice, and the thermal radiation experiment was used to evaluate the thermal hyperalgesia of Angelica dahurica in mice. Then, the effects of Angelica dahurica on the expression of MrgprD and TRPA1 proteins, the number of DRG positive neurons, and the mRNA levels of MrgprD and TRPA1 in mice were detected by Western blot, immunofluorescence, and RT-PCR, respectively. Finally, the differences in fluorescence signal intensity were analyzed through calcium imaging experiments on HEK293 cells after single transfection and co-transfection of MrgprD and TRPA1 plasmids, respectively. Results A total of 25 CCI mouse models were successfully prepared, with a modeling rate of 83.33% (25/30). After the 7th day, CCI mice showed the most significant differences in mechanical stimulation threshold and thermal radiation foot contraction latency, and reached the lowest value.The mechanical threshold and foot retraction latency of CCI mice treated with Angelica dahurica were significantly higher than those treated with pure water and CCI mice not treated with Angelica dahurica (P<0.05). The expression levels of MrgprD and TRPA1 proteins in CCI mice treated with Angelica dahurica were significantly lower than those in CCI mice treated with pure water (0.73 ± 0.11 vs 2.69 ± 0.23, 0.42 ± 0.09 vs 2.03 ± 0.18, P<0.05). The number of MrgprD and TRPA1 positive neurons in DRG of CCI mice treated with Angelica dahurica was significantly lower than that of CCI mice treated with pure water (654 ± 47 vs 1162 ± 63, P<0.05). The relative expression levels of MrgprD and TRPA1 mRNA in CCI mice treated with Angelica dahurica were significantly lower than those in CCI mice treated with pure water and CCI mice not treated with Angelica dahurica(P<0.05). The fluorescence intensity in HEK293 cells co transfected with MrgprD and TRPA1 plasmids was significantly higher than that in single transfected and blank controls (P<0.05). Conclusion This study successfully established a mouse CCI model through ligation and winding, exploring the analgesic effect and mechanism of Angelica dahurica in the CCI model, and proving that MrgprD-TRPA1 is an important target for neuropathic pain. Angelica dahurica can inhibit the degree of neuropathic pain by regulating the signal transduction pathway of MrgprD-TRPA1, which laid a foundation for further research on the development of new clinical analgesic drugs and analgesic mechanisms.
-
Mechanism of Icariin regulating NLRP3 inflammasome against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion
Abstract:
Objective: To investigate the therapeutic effect of Icariin on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Methods: The rat model of focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion was established by the method of thread bolt. After 24 hours,rats were randomly divided into sham operation group,model group,Butylphthalide group(70 mg穔g-1),and high,medium and low dose groups (80、40、20 mg穔g-1) of Icariin. The volume of gastric administration was 10 mL穔g-1 once a day for 13 d. The changes in neurological deficit symptoms of rats were detected by neurological function score,while the pathological damage of cerebral cortex were detected by HE,the expression changes of IL-1β and IL-18 protein were detected by Immunohistochemistry,the protein expressions of NLRP3,ASC and Caspase-1 in cerebral cortex were detected by Western blot. Results: Compared with the sham operation group,the neurological score of the model group increased. The pathological results showed that neurons necrosis or glial cell proliferation in different degrees could be seen in the marginal area of each group. The contents of IL-18 and IL-1β protein in the brain tissue of the model group increased significantly,and the expressions of NLRP3,ASC and Caspase-1 protein in the brain tissue of the model group increased significantly (P < 0.01, P < 0.05). After Icariin treatment,compared with the model group,the neurological function score of the treatment group was improved. The pathological results showed that the degree of neuronal necrosis was significantly reduced,and the contents of IL-1β and IL-18 protein in the brain were significantly reduced.;The expression of NLRP3,ASC and Caspase-1 protein in rat cerebral cortex decreased significantly (P < 0.01, P < 0.05). Conclusions: Icariin in the treatment of cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury may be related to regulation NLRP3 inflammasome.
-
Research Progress in experimental models of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
LI Zhi-hui, YU Xue-qing, yanshuguang, Yu Ning xia, 臧丹阳
Abstract:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis ( IPF ) is a chronic, progressive interstitial lung disease. The incidence of IPF is increasing year by year, with high mortality and poor prognosis. At present, the pathogenesis of IPF is still unclear, and its treatment measures are limited. The experimental model is a key tool for further studying the pathogenesis of IPF and exploring effective prevention and treatment measures. In recent years, its modeling methods have been continuously developed and optimized. In view of this, this study summarizes the construction methods and research progress of IPF experimental models in recent years, in order to provide ideas and references for preclinical research to select appropriate experimental models.
-
Construction and evaluation of the orthotopic transplantation tumor model derived from transgenic mouse with spontaneous pancreatic cancer
AN Qingling, TAN Dengxu, ZHAO Ya, ZHANG Caiqin, SHI Changhong
Abstract:
Objective To construct the orthotopic transplantation tumor model with pancreatic cancer derived from transgenic LSL-KrasG12D/+, LSL-Trp53R172 H/ +, Pdx1-Cre(KPC) mice. To provide a stable and reliable preclinical animal model for studying the development mechanism and treatment strategy of pancreatic cancer. Methods The tumor tissue derived KPC transgenic mice with spontaneous pancreatic cancer was transplanted into C57BL/6J mouse pancreas. Ultrasound detection was used to monitor the growth of tumor. H E staining and immunofluorescence staining were used to evaluate the pathological characteristics of this model. Results The tumor derived from KPC mice could grow steadily on the pancreas of C57BL/6J mice. Tumor proliferation index Ki67, matrix fibrosis marker αSMA, immune cell markers CD45 and CD206 were all stably expressed in the tumor. The model stably retains the pathological features of primary pancreatic cancer. Widespread tumor metastases were development in this model, which was similar to those observed in patients with pancreatic cancer. Conclusion The orthotopic transplantation model derived from transgenic mouse with spontaneous pancreatic cancer was established successfully. The model can simulate the stromal environment and immune cell infiltration of pancreatic cancer, and retains strong stability and uniformity with original tumor. It can be used as an effective preclinical model to study pancreatic cancer progression and treatment strategies.
-
Based on TRL4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway to explore the protective effect of Periplaneta americana powder on rats with spinal cord injury.
Li jie, ZHOU Bang-yu, MA Yan-bo, RUAN Yu-shan, LI Shao-bo
Abstract:
Abstract: Objective To explore the protective effect and possible mechanism of Periplaneta americana powder on rats with spinal cord injury. Methods Forty-eight male SD rats were randomly divided into sham operation group, saline group, periplaneta americana powder group, and Toll-like receptors-4 inhibitor group. Except for the sham operation group, the rat spinal cord hemitransection injury model was constructed in the other three groups. The sham operation group received no treatment after operation, the saline group and the periplaneta americana powder group were given intragastric administration of equal volumes of normal saline and periplaneta americana powder (630 mg/kg), and the TLR4 inhibitor group was given intraperitoneal injection of TLR4 inhibitor (3 mg/kg ) deal with. On the 1 d, 3 d, 7 d, and 14 d after the operation, the motor function of the rat hind limbs was evaluated by BBB score, the histopathological changes of the spinal cord were observed by hematoxylin-eosin staining, and the changes in the number of neurons were observed by immunohistochemistry. The expressions of inflammatory factors IL-1, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α were detected by ELISA, and the expressions of TLR4, myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) and NF-κB p65 were detected by Western blot. Results Compared with the sham operation group, the BBB score and the number of neurons in the saline group were significantly decreased, while the degree of pathological damage, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB p65 levels were significantly increased (P < 0.05), compared with the saline group, the periplaneta americana powder group and the TLR4 inhibitor group increased the BBB score, the number of neurons, decreased the degree of pathological damage, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB p65 levels (P < 0.05), compared with the TLR4 inhibitor group, the periplaneta americana powder group better increased the BBB score, the number of neurons, decreased the degree of pathological damage, and the expression of IL-1 and TNF-α. Conclusions Periplaneta americana powder can reduce the production of inflammatory factors after spinal cord injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway, and play a role in protecting nerves and promoting motor recovery.
-
Establishment of a mouse model of thoracic aortic dissection with acute lung injury by β-aminopropionitrile
maizhiyan, jiang li qing, zhuhanzhao, zhangliyun, wangyun, duanweixun
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective A feasible and stable mouse model of thoracic aortic dissection (TAD) combined with acute lung injury (ALI) was constructed using β-aminopropionitrile monfumarate (BAPN,1g/kg/d) administered by drinking water. The mouse model of TAD combined with acute lung injury (ALI) was constructed to provide a rational platform for the study of TAD combined with ALI. Methods Forty-five SPF-grade 3-week-old C57BL/6J male mice were selected and randomly divided into 15 mice in the CON group (normal dietary water) and 30 mice in the BAPN group (drinking water administration with sterile water configured as a solution of 1 g/kg/d) for 4 weeks. During the experimental period, the general condition and modeling rate of mice in the two groups were observed, and the TAD model of mice was validated and the BAPN group was divided into TAD and Non-TAD groups by measuring the maximum diameter of the ascending aorta and H&E staining of the aortic tissues of the mice. The pathological staining of H&E, wet/dry weight ratio (W/D) and total protein level in alveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) expression in the alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) to validate the TAD combined ALI model of mouse. Results BAPN intervention significantly delayed the increase in body mass and water intake in mice. Compared with the CON and Non-TAD groups, the maximum diameter of the ascending aorta of mice in the TAD group was significantly thickened (P < 0.05), H&E staining of the aorta showed significant thickening of the aortic wall, reduction in the number of smooth muscle cells, and fracture and disorder of elastic fibers, and H&E staining of the lung tissues showed significant interstitial edema and inflammatory exudation accompanied by thickening of the alveolar wall and enlargement of alveolar lumen, and a significant increase in the pathological scores of lung injury (P < 0.05), and total protein level and expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in lung tissue W/D and BALF were also significantly increased (P < 0.05), while there was no significant difference in the above indexes between the other two groups. Conclusion A mouse model of thoracic aortic dissection combined with acute lung injury can be successfully established by BAPN drinking water administration.
-
Establishment of the human α-synuclein nuclear localization signal transgenic mice
Abstract:
【Abstract】 Objective To establish a human α-synuclein nuclear localization signal transgenic mouse model and investigate the effects of α-synuclein nuclear localization on the behavior of mice. Methods Human α-synuclein nuclear localization signal and EGFP lentiviral vectors were constructed.The transgenic mice were created with the microinjection method. Using PCR and Western blotting methods to identify the genotypes and protein expression of the transgenic founder mice and their offsprings. The immunofluorescence was used to examine the localization of human α-synuclein in the mouse brain tissue . The behavioral changes of the transgenic mice were evaluated by the open field test, rotarod test, and O maze test. Results Transgenic mice with human α-synuclein nuclear localization signal were successfully established. Human α-synuclein was widely expressed in various tissues of mice and showed obvious nuclear localization. Further studies found that human α-synuclein nuclear localization signal transgenic mice had significant motor dysfunction, astrocyte proliferation and inflammatory response at 2 months of age and exhibited significant anxiety-like symptoms and reduced expression of the γ-aminobutyric acid(GABA) gene at 9 months of age, which persisted until 12 months of age. Conclusion A human α-synuclein nuclear localization signal transgenic mouse model has been successfully established, human α-syn is widely expressed in various tissues of the mice with evident nuclear localization. The mice exhibit significant motor dysfunction and anxiety-like symptoms. The successful establishment of this model provides a foundation for studying the role of α-syn nuclear localization in Parkinson's disease.
-
Establishment and evaluation of a rat model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction induced by compound factors
shiyujiao, Yang chen guang, Qiao wen bo, Liu yong cheng, Liu si yu, Dong guo ju
Abstract:
【Abstract】 Objective To evaluate the characteristics of a rat model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) induced by combined factors and to investigate the correlation of myocardial strain parameters with myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis. Methods Eight WKY rats and eight spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) served as control groups and were given normal feed until the end of the experiment. Thirty two SHR rats were equally divided into SHR+S, SHR+F, SHR+SF, and SHR+ combined groups. They were fed with high salt feed, high fat feed, high salt-fat feed, and high salt-fat-sugar feed in combination with streptozotocin intraperitoneally for 30 weeks, respectively. After modeling, heart weight/body weight (HW/BW), systolic blood pressure (SBP), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were measured; Echocardiography was performed to measure left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic internal diameter (LVIDd), LV anterior wall thickness (LVAWd), LV posterior wall thickness (LVPWd), LV ejection fraction (LVEF), isovolumetric diastolic time (IVRT), and peak early diastolic passive filling velocity (E) / early diastolic mitral annular velocity (e'); Speckle tracking echocardiography was conducted to determine global longitudinal strain (GLS) and strain rate (GLSr), global radial strain (GRS) and strain rate (GRSr), as well as global circumferential strain (GCS) and strain rate (GCSr); Serum is used to detect triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), glucose (GLU), and glycated serum protein (GSP); ELISA was used to examine serum B-type brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), angiotensin II (AngII),and Galectin-3 (Gal-3); Myocardium was subjected to HE and Masson staining for cardiomyocyte and myocardial fibrosis, and cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area (CSA) and collagen volume fraction (CVF) were calculated; In addition, the correlation of myocardial strain parameters with CSA and CVF was analyzed. Results Compared with the control group, in the model groups, especially in the SHR+Combined group, HW/BW, SBP, DBP, serum indexes (TC, TG, LDL-C, GLU, GSP, BNP, AngII, and Gal-3), and echocardiographic parameters (LVIDd, LVAWd, LVPWd, IVRT, and E/e') were significantly up-regulated; Absolute values of speckle-tracking echocardiographic parameters (GLS, GLSr, GRS, GRSr, GCS, and GCSr) were decreased considerably; HE and Masson staining of myocardial tissues suggested marked cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and fibrosis, and there were significant increases in CSA and CVF (P<0.01 or 0.05). Correlation analysis showed that GLSr, GCS, and GCSr were strongly linked to CSA; GLS, GLSr, and GCSr were strongly linked to CVF (P<0.01). Conclusions A rat model of HFpEF induced by hypertension and dysregulation of glucolipid metabolism replicated the basic characteristics of HFpEF in terms of etiology, clinical features, and myocardial pathologic changes and might be a reliable animal model of metabolic syndrome-related HFpEF. Moreover, myocardial strain indices are closely related to myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis and might indirectly reflect subtle myocardial lesions and dysfunction.
-
Effect of Qinji Liangxue mixture on similar animal models of hemorrhoids
ZHOU Mengen, LI Peng, JIN Wenqi, WANG Ruolin, GUO Xiutian
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of Qinji Liangxue mixture (QLM) on similar animal models of hemorrhoid. Methods Animal models of acute hemorrhoid in rats were made by using croton oil preparation (COP) and glacial acetic acid respectively. Eighty SD female rats were randomly divided into control group, model group, low-dose QLM group (QLM-L), high-dose QLM group (QLM-H) and diosmin group (DOSM), with 8 rats in each group. Except for the control group, all the other groups were treated with COP or glacial acetic acid, and then treated with different drugs for 7 days. HE staining was used to observe the anorectal histomorphology induced by COP and glacial acetic acid, and ELISA was used to detect the levels of IL-8 and TNF-α in serum of rats induced by COP, and the area of perianal ulcer induced by glacial acetic acid was recorded. Twenty-four C57 mice were randomly divided into control group, QLM-L group, QLM-H group and adrenal chromazone tablet group (CT), with 6 mice in each group for 7 days. The hemostatic effect of QLM was evaluated by capillary method and tail cutting method. Results QLM can significantly improve the pathological injury of animal models with similar hemorrhoid diseases, reduce the score of pathological changes induced by COP (P < 0.05), reduce the levels of serum IL-8 and TNF-α(P < 0.05),, reduce the area of perianal ulcer induced by glacial acetic acid (P < 0.05),, and shorten the time of coagulation and bleeding(P < 0.05). Conclusions QLM has good anti-hemorrhoid activity, which may be achieved by anti-inflammation, hemostasis and reducing tissue damage.
-
Effects of exercise regulating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway on improving HFFC diet-induced oxidative stress in hepatocytes
ping ye, zhang pei wen, yuan xin meng, xiang meng qi, yang meng fan, lin xiao xia, dong shi ru, liu yu ting, zhang yuan
Abstract:
Objective To explore whether voluntary wheel running affects liver oxidative stress by regulating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, thereby alleviating HFFC diet-related lipid deposition in liver. Methods 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into normal diet group (NC group, n=10) and high fat, fructose and cholesterol diet group (HFFC group, n=20) after a week of adaptive feeding. Ten weeks of feeding later, mice in HFFC group were divided into quiet group (HFFC group, n=10) and HFFC combined with exercise intervention group (HFFC+EX group, n=10). HFFC+EX group mice were caged with voluntary running wheels for free movement, and the number of running wheels was recorded every day for 8 weeks. After the last intervention, the mice were sacrificed by fasting for 12 hours at an interval of 24 hours, and the blood and liver were taken for detection. Results (1) The body weight, liver weight and liver index of mice induced by HFFC diet were significantly higher than those of NC group, and significantly decreased after exercise intervention (P<0.05). (2) Compared with NC group, HDL-C and LDL-C in HFFC group were significantly increased, and LDL-C level was significantly decreased after 8 weeks of exercise intervention (P<0.05). (3) The liver fat drop area and liver TG content in HFFC group were significantly higher than those in NC group, while those in HFFC+EX group were significantly decreased (P<0.05). (4) Compared with NC group, the content of oxidase MDA and the expression level of HO-1 in HFFC group were significantly increased, and the nuclear translocation and gene expression of Nrf2 were significantly decreased. After exercise intervention, the activities of SOD and T-AOC were significantly decreased, and the nuclear translocation and gene expression of Nrf2, the expression levels of HO-1 and SOD-1 were significantly increased (P<0.05). (5) The number of hepatocyte apoptosis and CHOP expression in HFFC diet group were significantly higher than those in NC group, while the number of hepatocyte apoptosis, CHOP and Bax/Bcl-2 expression in exercise group were significantly lower than those in NC group (P<0.05). Conclusions Voluntary wheel running can alleviate liver lipid deposition induced by HFFC diet by regulating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, thereby alleviating oxidative stress and reducing apoptosis in liver cells.
-
Screening and validation of age-related DNA methylation microhaplotypes in mouse blood
TIAN Yibo, WU Yujing, XIAO Junhua, ZHOU Yuxun, LI Kai
Abstract:
Objective DNA methylation microhaplotype (DMH) refers to the combination of multiple methylation sites in a very short range, and its haplotypes are rich in diversity. Screening and validation of age-related DNA methylation microhaplotypes in mouse blood. Methods First, a theoretical dataset of DNA methylation microhaplotypes based on the mouse reference genome was constructed. Second, age-related DNA methylation microhaplotypes were screened by Spearman's rank correlation analysis using high-throughput sequencing information of DNA methylation in mouse blood from a network database. Finally, cross-validation was performed with a validation dataset. Results The number of DNA methylation microhaplotype sites within 50 bp in the mouse genome totaled 6,787,142, and DNA methylation microhaplotypes consisting of single-digit CpG sites accounted for 98.64 %. A total of 5,835 age-associated DNA methylation microhaplotypes were screened in 58 mouse blood samples (Spearman's rank correlation test, |rho| > 0.5, P < 0.01), and they accounted for 0.086 % of DNA methylation microhaplotypes. Finally, the top one hundred age-associated DNA methylation microhaplotypes with high correlation were validated in 95 independent samples, resulting in 44 loci. Conclusion The age-associated DNA methylation microhaplotypes screened in this study can be useful for future mouse blood apparent age prediction and aging studies.
-
Research progress on evaluation of diarrhea irritable bowel syndrome animal model
zhangjiahe, zhuwang, shendanting, yangxiling, liufengbin, houqiuke
Abstract:
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is one of the most common functional gastrointestinal disorders, of which diarrhea-predominant IBS (IBS-D) accounts for the largest proportion. The pathogenesis of IBS-D is complicated and diverse, and there is currently a lack of clinically effective drugs. The establishment of animal models is an essential tool for further studies of the disease mechanisms, evaluation of clinical efficacy, and drug development, and the preparation and evaluation standards of models are important factors affecting the quality of the research. Based on the currently accepted pathogenesis of IBS-D and the previous modeling experience of our research group, this review systematically summarizes the evaluation methods used in animal models of IBS-D in terms of diarrhea observation, visceral sensitivity tests, and intestinal motility tests, to provide a reference for future studies.
-
Research progress on the construction and evaluation indicators of skin wound animal models based on physical methods
OU Xue, YU Zhijie, HE Yao, ZHENG Xiaoyuan
Abstract:
Skin wounds are global public problems, especially in terms of the difficult healing of chronic wounds, which may seriously affect patients’ lives. Most skin-wound animal models are currently established by physical methods, and different animal models have different biological characteristics. This review therefore classifies mouse, rat, and other animal models of skin wounds according to the literature, summarizes and analyzes the construction of skin-wound animal models based on physical methods and evaluation indicators, and considers the advantages and disadvantages of different animal models, to provide a basis for the rational construction of skin-wound animal models and drug research and development.
-
Analysis of animal models of vertigo based on the characteristics of clinical conditions in Chinese and Western medicine
liyaqing, wangxiaoyi, wangcan, miaomingsan
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To classify and analyze the existing animal models of vertigo based on the clinical characteristics of Chinese and Western medicine, evaluate the clinical fit of the models and their advantages and disadvantages, in order to improve the existing animal models and provide a more intuitive reference for clinical research. Methods The existing animal models of vertigo in the database were searched, and the models were classified according to the modeling method, combined with the characteristics of Chinese and Western medicine clinical conditions of vertigo and the existing animal model evaluation methods, and assigned values to evaluate the clinical fit and the advantages and disadvantages of the models. Results The existing animal models of vertigo were neck surgery model, motor stimulation model, otogenic stimulation model, sclerotherapy injection model, flight variation pressure model, vertebral artery ligation model, and stasis injection model; among them, the Western medical fit was high (fit ≥ 60%) for neck surgery model (65%) and otogenic stimulation model (65%), and all models had moderate Chinese medical fit (50% ≤ fit < All models had moderate (50% ≤ 60%) or low (< 50%) TCM anastomosis, and there was no model with both high TCM and WCM anastomosis. Conclusion At present, the animal models of vertigo are mainly Western medicine disease models, and there is a lack of Chinese medicine evidence models, and there are few models with high clinical fit between Chinese and Western medicine, which fail to highlight the characteristics of Chinese medicine. Therefore, the construction of animal models of vertigo that are closely integrated with the clinical characteristics of Chinese and Western medicine can provide more reasonable and comprehensive experimental support for the development, screening and clinical evaluation of new anti-vertigo drugs.
-
A mice model of hypothyroidism: comparison of two surgical procedures
Lan Haomiao, Che Hongying, Zhang Li, Mao Yu, Xie LinJun
Abstract:
Objective Hypothyroidism is a serious endocrine disease and an independent risk factor for systemic diseases. Studies of hypothyroidism can't be done without establishing animal models. C57BL/6 and KunMing (KM) mice are ideal animal vectors for the study of endocrine and other diseases. However, there are few studies describing total thyroidectomy in mice in detail. Methods In this study, total thyroidectomy was performed in C57BL/6 and KM mice by ligation (operation method I) and hemostasis (operation method II), and the detailed operation process was recorded. Elisa was used to detect and compare the serum TT3, TT4 and TSH levels, body weight and neck tissue HE staining of mice before and after surgery to verify the model. Results The serum TT3 and TT4 were decreased (P< 0.05) and TSH was increased (P< 0.001) in the two model groups. The survival rate within 28 days after operation in group I and Group II was 40% and 60%, respectively. In KM mice, it was 50% and 40%. The body weight of the two groups of mice was significantly higher than that of the sham group. HE staining and microscopic observation showed that the cervical tissue of the two species of mice was thyroid tissue, and the back membrane of the thyroid was intact after isolation. Conclusion Both surgical methods can cause hypothyroidism in both types of mice. However, it is necessary to be familiar with the anatomical relationship of mouse thyroid gland and surrounding tissue, improve the proficiency of surgical operation, prevent the occurrence of postoperative hypocalcemia and infection, and thus improve the survival rate of mice after modeling.
-
Analytical methodology of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in mouse tissues and their tissue distribution of NOG mice after single intravenous injection
Chen Guoyu, Pan Ruolang, Ye Zhichao, Shi Yuhua, Gu Liqiang, Xia Lijuan, Lin Xiaobo, Zhang Qiang, Xu Shasha, Shao Jinjin, Zhang Lijiang
Abstract:
ABSTRACT: Objective To establish a quantitative PCR method for the analysis of human-derived SRY gene DNA in mouse tissues, and to study the tissue distribution of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in immunodeficient NOG mice after a single intravenous injection. Method A quantitative PCR method for the analysis of human SRY gene DNA in mouse tissues was established, and the methodological validation of standard curve and linear range, accuracy and precision, and stability was performed. Thirty-six NOG mice, one half of each sex, were given HUCMSCs 3.5?07 cells/kg by single intravenous injection, and six mice were anesthetized at 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 72 h, 1 w and 2 w, respectively, and dissected after blood collection (EDTA anticoagulation). DNA was extracted from lung, kidney, heart, liver, brain, spinal cord, stomach, small intestine, fat, skin, spleen and testis (uterus and ovary), and the distribution of HUCMSCs in each tissue was determined by the validated method of quantitative PCR analysis of human-derived SRY gene in mouse tissues. In addition, 18 NOG mice, half males and half females, were divided into control group (6 mice) and treating group (12 mice), which were injected intravenously with 0.9% sodium chloride injection and HUCMSCs 3.5?07 cells/kg. The acute toxic reactions of mice were observed during the administration period, and four animals were dissected at 72 h, 2 w and 4 w after the administration to observe the gross organs, and the mitochondrial protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry in paraffin sections of lung tissues to analyze the colonization of HUCMSCs in lung tissues. Results The established quantitative PCR method for human-derived SRY gene DNA in mouse tissues met the validation criteria for each index. After a single intravenous injection in NOG mice, HUCMSCs were mainly distributed in the lungs and bloodwithin 1w after administration, with higher concentrations in lung tissues than in blood, and the concentration of HUCMSCs in lung tissue and blood maintained relatively stable levels within 6h~24h and 6h~72h, respectively, and then decreased over time. The distribution of HUCMSCs was not measured in other tissues at all sampling points . The colonization results showed that HUCMSCs were detected in lungs 72h after intravenous injection, but not at 2w and 4w. No obvious acute toxicity was observed in NOG mice after single intravenous administration of HUCMSCs. Conclusion The established method for analyzing the distribution of HUCMSCs in mouse tissue is reliable and feasible. HUCMSCs were mainly distributed in lung and blood of NOG mice within 1w after single intravenous injection, and mainly colonized in lung tissue at 72h. The single intravenous administration of HUCMSCs has a good safety profile.
-
Progress of animal model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
wangbo, songqinghua, tanghuimeng, liuyang, xieyang, tianyange
Abstract:
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a progressive, interstitial fibrotic lung disease characterized by persistent scar formation in the lung parenchyma and a reduced quality of life and poor prognosis for patients. The pathogenesis of PF is unknown and there is a lack of effective therapeutic agents, and animal models are the main tool to explore the pathogenesis of the disease and to find effective therapeutic agents. A variety of factors can induce fibrosis formation, and PF models can be induced to different degrees according to known etiology. Among them, bleomycin-induced models are widely used because of their reproducibility and similarity between fibrosis pathology and clinical conditions, and their induction methods mainly include intratracheal drip, intratracheal nebulization, tail vein injection, intraperitoneal injection and transnasal inhalation, and they are classified into single dose and multiple doses according to the frequency of induction. Based on the relevant literature, this paper summarizes the characteristics of the PF model established by BLM with different induction frequencies and induction methods, and provides a basis for the application of this model.
-
Effects of Oral Probiotics on Gut Microbiota Structure in Subcutaneous Tumor of Colon Cancer Mice Based on 16S rRNA Sequencing Technology
Zhang Shuling, Wang Junwei, Zuo Luyu, Hu Shiliang, Sun Junzhi, Wang Chun
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of oral probiotics on gut microbiota diversity, colony structure, and intergroup differences in mice with subcutaneous colon cancer tumors, based on 16S rRNA sequencing technology. Method Twenty-four 6-week-old male BALB/c mice were divided randomly into normal control (NC, n=8), model (M, n=8), and probiotic+model groups (PM, n=8) after adaptive feeding for 1 week. Mice in the PM group were given 200 μL probiotic mixed solution (Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus mixed lyophilized powder, 2×108 colony-forming units) by gavage three times/week for 7 weeks, while the M and PM groups received 200 μL normal saline. At 10 weeks old, 0.2 mL CT26.WT cell suspension (1×107/mL) was inoculated subcutaneously into the left hind limbs of M and PM mice, while NC mice were inoculated with 0.2 mL normal saline. The general condition of the mice and growth of subcutaneous tumors, and changes in the gut microbiota structure by 16S rRNA sequencing were monitored. Results The subcutaneous tumors of the M group were prominent, and the subcutaneous tumor volume and weight of the PM group were significantly reduced (P<0.05). Compared with NC group, Alpha diversity index was lower in the M group, and a significant difference of Beta diversity inter groups (P<0.01).And supplementation of probiotics had a certain effect on gut microbiota diversity in the M group. Compared with M group, the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Muribaculaceae, Bacteroides were higher in the PM group, while the relative abundance of Firmicutes, Desulfobacterota, Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group, Alistipes were lower in the PM group. LEfSe analysis showed that Muribaculaceae and Bacteroides in the PM group were different species with high abundance (LDA values >4). Conclusions Oral probiotics may improve the gut microbiota by increasing the relative abundance of beneficial Muribaculaceae and Bacteroides in subcutaneous tumors in mice with colon cancer.
-
Advances in the application of 5XFAD transgenic mice in Alzheimer's disease research
Abstract:
5×FAD mice (Transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer's disease) are APP/PS1 transgenic mice carrying five familial gene mutations. With beta-amyloid precursor protein (amyloid precursor protein, APP) related to the mutation of K670N/M671L (Swedish), 1716 v (Florida) and V7171 (London), and the old element - 1 (early presenilin 1, PS1) were MI46L and L286. 5×FAD mice had A large amount of β-amyloid (Aβ) in the brain at 1.5 months of age, and neuritic plaques (NP) began to appear at 2 months of age. The pathological phenotypes of 5×FAD mice included amyloid plaque aggregation, neuronal loss, gliosis, and memory dysfunction.The biological characteristics of 5×FAD mice may involve changes in the formation of brain Aβ plaques, hyperphosphorylation of Tau protein, synaptic dysfunction, neuroinflammatory response, mitochondrial dysfunction, blood-brain barrier injury, neuronal injury, endoplasmic reticulum stress and eye lesions. As a classic animal model of Alzheimer's disease, 5×FAD transgenic mice can simulate the neuropathological process and behavioral manifestations of AD patients in the late stage, and are widely used in the pathogenesis of AD and the development of new drugs for AD. In this paper, the model construction, biological background, biological characteristics of 5×FAD transgenic mice and the development and application of AD prevention and treatment drugs were summarized and reviewed, in order to provide reference for the application of 5×FAD transgenic mice in AD research.
-
Effect of different sterilization methods on the nutritional composition of pig specific formula milk powder
GUO ya-xi, Liuruixue, Duxiaopeng, Zhuhua
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective Using different sterilization methods to sterilize pig specific formula milk powder, exploring the sterilization method and conditions that minimize the loss of nutritional components in formula milk powder. Method Pig-specific formula milk powder was divided into high-pressure sterilization and irradiation sterilization groups. Formula milk powder in the high-pressure group was sterilized using different sterilization conditions and that in the irradiation group was sterilized using different 60Co γ-radiation doses. The sterility and the nutritional contents of the sterilized formula milk powders were determined according to national standards. Results The sterility tests for both groups of formula milk powder were negative. Compared to control group, the crude protein contents were significantly lower in formula in the high-pressure group sterilized at 121℃ for 30 min and in the irradiation liquid group sterilized at 50 kGy (P < 0.01). The water, crude protein, and calcium contents were significantly lower (P < 0.001) in the irradiation group sterilized at 50 kGy. There was no significant difference in the valine, isoleucine, or leucine content under 50 kGy sterilization conditions in the irradiation sterilized group, but all amino acid contents were decreased in the high-pressure sterilization and irradiation sterilized liquid groups (P < 0.001). Analysis of trace elements showed an increased iron content (P < 0.001) in formula sterilized at 121℃ for 30 min in the high-pressure sterilization group, increased iron and potassium contents (P < 0.001) under 25 kGy sterilization conditions in the irradiation sterilization liquid group, and increased magnesium content (P < 0.01). The magnesium (P < 0.05) and sodium contents (P < 0.01) differed significantly in formula treated under 50 kGy sterilization conditions in the irradiation sterilized powder group. Vitamin E and Vitamin B2 contents were increased in formula sterilized at 121℃ for 30 min in the high-pressure sterilization group (P < 0.001), the Vitamin E content was increased (P < 0.05) and the Vitamin B2 content was decreased (P < 0.001) in formula sterilized under 50 kGy conditions in the irradiation sterilization liquid group, and the Vitamin E and Vitamin A contents were decreased in formula sterilized at 25 kGy in the irradiation sterilized powder group (P < 0.001). Conclusion Sterilization at 121℃ for 30 min resulted in the least loss of nutritional components in the high-pressure sterilization group, while irradiation sterilization resulted in the least loss of nutrients at a dose of 50 kGy. Comparing the two sterilization methods, irradiation of milk powder at 50 kGy resulted in the least loss of nutrient content.
-
Research progress of pig in biology as model animal
wangyan, Xing Kai, Cao Yong Chun
Abstract:
Animal models of human diseases include experimental animals and related materials established during biomedical research, which in turn play a vital role in medical research. Pigs and humans are similar in terms of their anatomy, physiology, immunology, and genetics. Pigs are thus suitable model animals for biomedical research and have various advantages compared with other model animals. Recent advances in biotechnology, such as genetic engineering, have contributed to a rapid increase in the use of pig models for human disease research. In addition to serving as xenotransplant organ donors and as tools in drug-design studies, pigs can also be used as model animals to study human developmental processes, congenital diseases, and disease-response mechanisms, thus making important contributions to improving human health. This review considers the current status and future applications of pigs as research models for studies of human cardiovascular diseases, cancer, ophthalmology, craniofacial, musculoskeletal, and skin research, reproductive and fetal development, nutrition, microbiome research, brain and neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, infectious diseases, and vaccine design, as well as for xenotransplantation.
-
Syndrome evaluation of hot flash model rats induced by bilateral oophorectomy and tamoxifen administration
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To explore the animal model of syndrome used in the study of hot flash phenomenon in women. Methods Twenty-four female SD rats were randomly divided into three groups: sham operation group, bilateral oophorectomy group and tamoxifen group, with 8 rats in each group. Two kinds of hot flash animal models were induced by bilateral oophorectomy and tamoxifen intragastory at 10 mg/kg/d, respectively. On the 14th and 28th days of modeling, the open field activity, anal temperature and body surface infrared thermogram of rats were detected. On the 29th day, the rats were killed, and the uterus was weighed and pathological sections were made. Blood estradiol and epinephrine were determined by ELISA. The gene expressions of adrenal sex hormone synthetase (Star, Cyp11a1, Cyp17a1, Cyp19a1, Por, Hsd3b2, Hsd17b1) and catecholamine substance synthetase (Th, Ddc, Dbh, Pnmt) in adrenal medulla were detected by RT-qPCR. Results Compared with sham operation group, the body weight of rats in bilateral ovariectomy group increased significantly (P < 0.01), while the body weight of tamoxifen group increased slowly. In the bilateral ovariectomies group, the maximum body surface temperature was significantly decreased on day 28 (P < 0.01), the difference between the maximum temperature and the minimum temperature in the abdomen was significantly increased on day 14 (P < 0.05), the difference between the maximum temperature and the minimum temperature in the back was significantly increased on day 28 (P < 0.01), and the open field activity of the rats was decreased (P < 0.01). The maximum body surface temperature of the tamoxifen group was significantly decreased (P < 0.01), but the open field activity of the rats was increased (P < 0.01). The uterine index of rats decreased significantly in both models (P < 0.01). Compared with sham operation group, E2 in bilateral oophorectomy group and tamoxifen group was significantly decreased (P < 0.01), NE and Epi were significantly decreased (P < 0.05), β-EP in bilateral oophorectomy group was also significantly decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with sham operation group, the adrenal Cyp11a1 gene expression in bilateral ovariectomized rats was significantly increased (P < 0.05), while the Cyp17a1 and Hsd17b1 gene expressions were significantly decreased (P < 0.05). The gene expressions of Star and Por in tamoxifen group were significantly increased (P < 0.01), while the gene expression of Cyp17a1 was significantly decreased (P < 0.01). Pnmt gene expression was significantly down-regulated in bilateral oophorectomy group (P < 0.01). conclusion Bilateral ovariectomized rats can be used for the study of perimenopausal hot flashes, whose syndromes are similar to those of kidney Yang deficiency and Yin deficiency in traditional Chinese medicine.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of C57BL/6N-Tg(1.28HBV)/Vst Hepatitis B virus transgenic mice
li rongrong, sunxin, huangkai, zhaozhimin, pengyuan, liuchenghai
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To observe the characteristics of C57BL/6N-Tg (1.28mer HBV)/Vst transgenic Hepatitis B virus (HBV-Tg) mouse model and analyze the transcriptomic characteristics of HBV-Tg mouse model. Methods 10 male HBV-Tg mice were used as experimental group and 10 wild-type mice as control group. The level of HBV DNA, HBsAg, HBeAg in serum and the expression of HBsAg and HBcAg in liver tissue were used to evaluate the virological characteristics of the model mice. The levels of serum ALT, AST, HE, Sirius red staining and Hyp in liver tissue were detected to evaluate the degree of liver inflammation and fibrosis. Liver tissue samples from 3 mice in each group were randomly selected for RNA extraction for high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. The significantly expressed differential genes were obtained by R software analysis, the functional enrichment of differential genes was obtained by GO and KEGG analysis, and then the genes with significant differences were verified by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). Results Compared with normal group, ALT and AST levels in model group were increased, and ALT was more significant (P<0.05). HE staining of liver tissue in model group showed the enlargement of liver nucleus and swelling of some hepatocytes. The results of Sirius red staining showed that there was a small amount of collagen deposition in the sink area and interlobule of HBV transgenic group, which was in the shape of thin lines. A total of 1352 differential genes were obtained by screening conditions (logFC>2x and P<0.05), including 703 up-regulated genes and 649 down-regulated genes. KEGG analysis suggested that differential genes were mainly enriched in PPAR signaling pathway, retinol metabolism, fatty acid degradation and other pathways (P<0.05). Significantly up-regulated differential genes mainly included Cyp4a10, Cyp4a14, Acot1, Acot3, Ehhadh, etc. Significantly down-regulated genes included Adh4, dnajb11, hspa5, scn5a, apol10b, etc. The trend was consistent after qRT-PCR detection (P<0.05). Conclusions HBV-Tg mice have a tendency of spontaneous fibrosis.Transcriptomic analysis shows that the potential mechanism of CHB mainly involves PPAR signaling pathway, retinol metabolism,fatty acid degradation,drug metabolism and other pathways.
-
Research new progress in aging models of rodent animal
LI Xuechan, HAN Le, WANG Xuewen, LIU Lijun, WANG Jing
Abstract:
Aging is a process of degenerative change that occurs as a result of time-related accumulation, associated with age-related diseases. Understanding the causes and mechanisms of aging and finding drugs that can effectively delay aging and prevent and cure age-related diseases currently present a great challenge for humans. Aging animal models thus represent an important tool in aging research, and various aging animal models have been created using different aging mechanisms. These different models having specific advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different research purposes. This review considers aging rodent models to provide information for aging research.
-
Construction and evaluation for chemotherapeutic phlebitis rats induced by vinorelbine through dorsalis pedis vein
Abstract:
To establish and evaluate for chemotherapeutic phlebitis rats induced by vinorelbine through dorsalis pedis vein. Methods The rats were randomly divided into the control and model group. Rats injected 0.1ml normal saline through the dorsalis pedis vein of the hind limb served as the control. While the rats in model group were injected with different concentrations of vinorelbine (2-5mg/ml) as above. General observation was performed and the hind limb volume was measured daily to calculate the swelling rate for 7 consecutive days. Then the rats were killed to collect the dorsalis pedis vein, and the histological changes were observed by HE staining. The microstructure changes on the surface of the vascular endometrium were observed by scanning electron microscopy. Results Rats injected with 2-5 mg/ml vinorelbine via dorsalis pedis vein could significantly induce hind limb swelling. The swelling rate increased with increasing concentration, and the peak of each group is reached on 3rd day. On the 7th day, the phlebitis rate in the 2 mg/ml group was 50%, while in the 3 mg/ml group of 83.3%. The 4 mg/ml group and 5 mg/ml group were all sucessful with grade Ⅲ accounting for 66.7% and grade Ⅳ accounting for 83.3%, respectively. Histopathology showed inflammatory cell infiltration, wall thickening, lumen stenosis and thrombosis in the surrounding tissues of veins. Scanning electron microscopy also showed that the tight junction of venous endothelial cells were destroyed, and the surface of the vascular lining were rough that resulting in blood cells adhesion. Conclusion Rats injected with 0.1ml 3-5mg/ml vinorelbine through the dorsalis pedis vein could induce red, swollen and cord like veins in lesions. Inflammatory cells infiltration around the vein, thickened vein wall, lumen stenosis and thrombosis were seen. Also, the surface of the vein intima was rough and adhered to a large number of blood cells. All of those were consistent with clinical chemotherapeutic phlebitis in terms of symptoms and pathological structure.
-
Establishment and evaluation of a rat model of coronary microvascular disease with qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome
kangjing, yang li li, wang ziyan, You yue, shiyue, ma yanlei, meng hongxu, lilei
Abstract:
Objective To explore the establishment and evaluation of a rat model of coronary microvascular disease with Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome. Methods 45 male SD rats were randomly divided into sham operation group, coronary microvascular disease group and coronary microvascular qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome group, with 15 rats in each group. The rats in the group of coronary microvascular disease with Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome were randomly deprived of sleep for 14 to 16 hours every day for 6 weeks, and the model of Qi deficiency syndrome was established. The animals in the sham operation group and the coronary microvascular disease group were fed normally for 6 weeks. Six weeks after the experiment, rats in the coronary microvascular disease group and coronary microvascular qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome group were anesthetized, and then opened their chest and injected embolic microspheres (40~120μm) into the left ventricle,The animals in the sham operation group underwent thoracotomy without injection of embolic microspheres. On the 7th day after operation, relevant detection indicators were measured in each group. Results In the group of coronary microvascular disease, microsphere embolism was found in coronary microvascular, left ventricular ejection fraction and left ventricular shortening rate were significantly decreased, and the activities of creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were significantly increased. The heart function, hemorheology, myocardial enzyme index and the degree of myocardial cell damage in the coronary microvascular Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome group were significantly different from those in the sham operation group. Conclusion Sleep deprivation combined with intraventricular injection of embolic microsphere can successfully establish a rat model of coronary microvascular disease with qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome, which is more suitable for the study of pathogenesis and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine
-
The ferroptosis pathway mediated by GSH/GPx4 might play an important role in preventing hepatocyte peroxidative injury by aerobic exercise in elderly mice model
Liu Yuqian, Yang Wenqian, Wang haitao
Abstract:
Objective To elucidate the role of Glutathione (GSH)/Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4) -mediated ferroptosis pathway in preventing age-related hepatocyte peroxidation injury by aerobic exercise in mice, and to provide a new target for improving liver aging and metabolism disorders. Methods 20 SPF C57BL/6 male mice aged 52 weeks were randomly divided into the elderly control group, (EC) and the elderly exercise group (EE), with 10 mice in each group. The mice performed 16 w moderate intensity exercise with the incremental load (1~2 w 14 m/min, 3~4 w 15 m/min, 5~10 w 16 m/min, 11~16 w 17 m/min, 60 min/d, slope 0?. After perfusion of the ascending aorta, the lateral lobes of the liver were harvested for HE sections and ultrathin transmission electron microscope sections. The levels of 8-hydroxy-2 deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) in liver and serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) were detected by ELISA. Hepatic glycogen, triglyceride (TG), malondialdehyde (MDA), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), and glutathione (GSH) were determined by colorimetry. Hepatic GPx4, glucose transporter (GLUT2) and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1(NQO1) and solute carrier protein 7 family member 11 (SLC7A11) were detected by Western blot. Results ① The oxidative damage of hepatocytes in elderly exercise mice were effectively delayed, and the normal structure of mitochondria and glycogen storage in hepatocytes were maintained. ② Compared with the elderly control group, the content of hepatic GSH and NADPH in the elderly exercise group were increased significantly (P<0.01). ③ Compared with the elderly control group, 8-OHdG, 4-HNE, MDA and non-heme iron in liver of the elderly exercise group were decreased significantly (P<0.01). ④ The expression of GPx4, NQO1 and SLC7A11 in the liver of the elderly exercise group were increased (P<0.01), while the expression of NOX2 was decreased (P<0.01). Conclusions The synthesis of GSH was increased in aged mice after aerobic exercise, which provided sufficient reaction substrates for GPx4, and GSH /GPx4 pathway was activated. The ferroptosis process was inhibited, which improved hepatocyte peroxidation damage caused by aging, and maintained the normal structure and physiological function of hepatocytes.
-
Role of monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) in prostate cancer progression
CHEN Hanmu, LI Hui, ZHAO Jumei, SHIChanghong
Abstract:
Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative deamination of monoamine neurotransmitters and dietary amines. It plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis, progress, and treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. Recent studies have revealed that elevated expression of MAOA in prostate cancer (PCa) is closely associated with tumor progression and drives the heterogeneity of PCa. In this review, we summarize the role of MAOA in the development of PCa in different disease stages, including oncogenesis, development, invasion, metastasis, and drug resistance. We also discuss the involvement of MAOA in the tumor microenvironment and explore the potential utility of MAOA inhibitors. We further propose therapeutic strategies based on targeting MAOA in preclinical models to promote relevant clinical trials. This review aims to provide new potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of PCa.
-
Research progress on the application of zebrafish in breast cancer
ZHANG Min, ZHANG Jingjing, NING Guozhu
Abstract:
Zebrafish xenograft model is of great importance in cancer modelling, especially xenografting of breast cancer. It facilitates real-time observation of tumor cell growth, metastasis, and interactions with the immune system, thus providing novel insights and experimental foundations for breast cancer treatment. Furthermore, the zebrafish xenograft model offers a valuable tool for high-throughput drug screening. This review provides an overview of how zebrafish xenograft model contribute in elucidating the underlying mechanisms in breast cancer development, as well as their use in screening anti-tumor drugs and conducting therapeutic research.
-
Establishment and evaluation of anterior cervical discectomy fusion optimization model in small tailed Han sheep model
DOU Xinyu, LIU YU, LIU Xiao, ZHU Bin, JIA Fei, WANG Linbang, SHEN Fei, LIU Xiaoguang
Abstract:
Objective Cervical disc herniation (CDH) is one of the common orthopaedic diseases. With the in-depth study of it and the development of cervical implants, the establishment of cervical fusion animal models has become an indispensable part. At present, there are few reported researches about the establishment and evaluation of cervical fusion animal models in China. The aim of this study is to provide a good animal model and evaluation scheme of implants for cervical spine-related research. Methods Small tailed Han sheep were chosen for anterior cervical discectomy fusion (ACDF) after modified operation and polyetheretherketone (PEEK) interbody fusion cage (Cage) (control group), 3D-printed Ti6Al4V Cage (experimental group 1) and new method Ti6Al4V Cage (experimental group 2) were implanted in different cervical segments (C2/3-C4/5) of each sheep respectively. After surgery, hematology and histopathological analysis were performed to evaluate the recovery of sheep and the biosafety of the materials. X-ray, CT, Micro-CT and quantitative analysis, hard tissue section staining and biomechanical tests were executed to assess the conditions of bone in-growth and bone fusion. Results The modified ACDF ovine model was established successfully. There was no significant difference in the important indexes of hematology (P< 0.05), and histopathological analysis showed there were no pathological changes such as inflammatory cell infiltration. The implants had a good biosafety..Furthermore, X-ray and CT showed the position of internal fixation and the interbody fusion were good. The results of Micro-CT and quantitative analysis at 3 and 6 months after operation showed that compared with PEEK Cage group, the bone volume/total volume and trabecular number in the new method Ti6Al4V Cage group and 3D-printed Ti6Al4V Cage group were significantly increased (all P < 0.01), while the trabecular spacing decreased significantly (all P < 0.01). Moreover, the new method Ti6Al4V Cage group had more bone growth (P < 0.01). Hard tissue section staining demonstrated that the pores of the new method Ti6Al4V Cage and 3D-printed Ti6Al4V Cage had obvious bone growth and were relatively dense, and the combination was slightly better than that of PEEK Cage. Biomechanical evaluation indicated that compared with PEEK Cage, the new method Ti6Al4V Cage and 3D-printed Ti6Al4V Cage reduced the range of cervical flexion-extention , lateral bending and axial rotation to a certain extent (all P < 0.05), at the same time enhanced the stability of cervical vertebra, and the new method Ti6Al4V Cage was more advantageous (all P < 0.05). Conclusions After the establishment of the modified ACDF ovine model, reasonable and effective assessment methods were used to demonstrate the rationality and effectiveness of the model, and good biosecurity of the Cages of the three materials. Compared with PEEK Cage, the new method Ti6Al4V Cage and 3D-printed Ti6Al4V Cage had better performance in bone growth and bone fusion, which could enhance the stability of cervical vertebrae, and the new method Ti6Al4V Cage had more advantages.
-
Establishment and Evaluation of Constipated Irritable Bowel Syndrome Model with Liver Depression Syndrome
He Jiahui, He Jieying, Zhang Bairong, Zhang Shuidi, Wei Yuanjun, Yang Chaoyan, Chen Yanfen
Abstract:
Objective Through single factor modeling method and multi factor combined modeling method, to prepare the rat models of liver stagnation syndrome constipation type irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C), and provide ideal experimental animal models of IBS-C by comparing different indicators. Methods 42 sprague-dawley rats were randomly divided into blank group (Normal group), cold water gavage group (Cold group), restraint group (Restrain group), tail clipping group (Tail group), cold water gavage+restraint group (C+R group), and cold water gavage+tail clipping group (C+T group). During the modeling period, the body weight, food intake, water intake, and survival status of each group of rats, and open field behavior, fecal Bristol score, visceral sensitivity, and small intestine propulsion were observed. HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of the rat colon, and ELISA method was used to detect the content of 5-HT and VIP in serum and colon. Results After modeling, the weight loss of rats in each model group decreased (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), the amount of food and water decreased, and the content of 5-HT in serum of each model group increased. In the Cold group, the number of fecal particles and Bristol score decreased, while the content of 5-HT in the colon increased (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01); the total distance and average speed of the restraint group in the open field decreased (P < 0.01); the preference for sugar water in the Tail group decreased (P < 0.01); in the C+T group, the preference rate for sugar water, total open field distance, small intestine propulsion rate, defecation particles, and Bristol score decreased, while the content of 5-HT in the colon increased and the VIP content decreased (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01); the total distance, average speed, and VIP content in the colon of the C+R group decreased (P < 0.05). Except for the Tail group, all other model groups showed visceral hypersensitivity (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01) at various pressure values on the 7th and 14th day of modeling; pathological observation showed that no significant inflammatory cell infiltration or pathological changes were observed in each model group. Conclusions The combination of ice water gastric lavage and tail clamping method can successfully establish a rat model of liver depression syndrome in IBS-C, which maybe the first choice of five methods and lays the foundation for systematic and in-depth research on the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in preventing and treating IBS-C.
-
Research progress of candidate pathogenic genes related to depression
Li Mengyao, Gao Feng, Zheng Fanfan, He Mengze, He Zhao, Li Youlei
Abstract:
Depression is a complex mental disease with polygenic inheritance and a high incidence. Our understanding of the clinical manifestations and pathogenesis of depression has recently improved. Continuous progress in gene-editing technologies has increased the construction efficiency and reduced the cost of gene-knockout animals, leading to their increasing use in the fields of basic research and drug development for depression and providing a powerful tool for revealing the pathogenesis of depression. In this review, we summarize recent progress in understanding the roles and mechanisms of candidate genes in depression using knockout model mice.
-
Prox-1 induces new lymphatic vessels to participate in the repair of spinal cord acupuncture injury
Abstract:
Objective To observe the distribution and characteristics of lymphatic vessels in normal and injured mouse spinal cord, and to explore whether lymphatic vessels participate in the repair of spinal cord injury. Methods Adult male Kunming mice were randomly divided into two groups (n=36), the normal group did not damage the spinal cord, the experimental group used acupuncture to prepare a spinal cord injury model. The distribution of lymphatic endothelial cells(LECs) in the spinal cord was detected by immunohistochemistry, and the expressions of lymphatic endothelial cell markers Prospero-related homobox-1 (Prox-1), lymphatic vessel endothelial cell hyaluronic acid receptor-1 (LYVE-1), flat foot protein (podoplanin) and the vascular endothelial cell marker CD34 in the spinal cord of normal and acupuncture-injured mice were observed. The spinal cord samples were subjected to immunofluorescence staining, and the source of new LECs was explored by observing the co-expression of LYVE-1/prox-1, LYVE-1/podoplanin and CD34/Prox-1. Results Lymphangoid structures are present in the spinal cord of normal adult mice, and are distributed in segments, walking laterally between white matter and gray matter; nascent lymphangoid-like structures appear in the spinal cord at the site of acupuncture injury, and Prox-1, podoplanin, LYVE-1, and CD34 are expressed simultaneously, and the expression of Prox-1 is time-ordered; after scarring at spinal cord injury, the nascent lymphangoid-like structure disappears. Conclusion: Segmental, transversely distributed lymphangoid-like structures are present in the spinal cord of normal adult mice, and the neonatal lymphangoid-like structures are involved in the reconstruction of spinal cord injury, and the nascent lymphatic endothelial cells may originate from the surrounding existing lymphatic vessels or vascular endothelial cells.
-
Establishment of a novel composite rat model of chronic skeletal muscle injury
Abstract:
:The purpose of this study was to establish a new composite rat model of chronic skeletal muscle injury to explore the mechanisms and treatment methods of skeletal muscle injury. The model was established by combining vertical impact with prolonged forced sitting, and significant pathological changes and physiological dysfunction were observed. The model group rats had significantly lower open-field distances than the blank group, and HE staining showed muscle atrophy and rupture, as well as infiltration of inflammatory cells. The volcano plot in the sequencing results suggested significant differences in the Pf4 gene. The muscle tissue Go analysis of the model group rats showed upregulation of the oxygen binding and oxygen carrier activity pathways. KEGG analysis suggested that the chemokine signaling pathway and AMPK signaling pathway were activated. In conclusion, this study successfully established a composite model of skeletal muscle injury in rats, which can be used to study the pathological changes of skeletal muscle injury and evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of treatment methods, with practical application value.
-
A Brief Review of the cultivation and utilization of the rat resources
Abstract:
Rats are one of the representative experimental animals since the genetic and environmental effects is comparatively easy to control and standardize. The rat is rather suitable as model for physiology, neuroethology, pathology and toxicology due to an approximately ten times larger body size compared to a mouse, offering several unique advantages in surgical procedures and clinical sampling of blood, tissues, etc. This paper review the cultivation and utilization history of the rat resources abroad to provide references of collecting, sharing and utilizing laboratory rat resources in our country.
-
NK cells and the application of their immunotherapy in tumor immunity
Abstract:
Abstract Natural killer cells (NK) are important immune cells that recognize and eliminate virus-infected cells and tumor cells. NK cells play a crucial role in anti-tumor immunity by modulating the immune response through a variety of cytotoxic mechanisms and cytokine production. This article reviews the development and classification of NK cells, the mechanism of action, and the application of NK cell-based immunotherapy in tumor immunity, and clarifies the principle, status quo and development trend of NK cell-based anti-tumor immunotherapy, in order to provide ideas for the future research and development of NK cells.
-
Analysis of glaucoma animal models based on data mining
Abstract:
Objective :To study the application of animal model of glaucoma and provide reference for the improvement of animal experimental methods and model. Methods Methods With“glaucoma ”and “animal models” as the main topics, literature related to animal models of glaucoma from 2012 to 2022 was collected from CNI and PubMed, and the species, gender, modeling methods and detection indexes of experimental animals were summarized, and the database was established for statistical analysis.Results A total of 400 articles conforming to the criteria were selected. Most of the experimental animals were C57BL / 6J mice, and most of them were male. Most of the modeling methods were anterior chamber injection induced type, transgenic type and laser photocoagulation induced type. The high frequency detection indicators mainly included intraocular pressure measurement, histopathology, western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry. Conclusions: at present, there are many methods to construct glaucoma animal models, but the intervention of related TCM factors is less. It is suggested to increase the glaucoma animal model combined with disease and syndrome. In this study, different animal models were evaluated by mining and analyzing the animal model experiments of glaucoma, and the mining contents provided references for the construction of animal models with high success rate of modeling, good reproducibility and high clinical coincidence, and provided ideas for the model improvement.
-
Exploring the protective effect of Helleborus thibetanus Franch alcohol extract on bone destruction in CIA rats based on OPG/RANK/RANKL signaling pathway
Abstract:
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of Helleborus thibetanus Franchon on collagen induced arthritis (CIA) model rats and the effect on OPG/RANK/RANKL signaling pathway. METHODS Sixty female wistar rats were divided into (1) normal group (Control), (2) model group (Model), (3) positive drug group (methotrexate, MTX), (4) low-dose group, (5) medium-dose group, and (6) high-dose group. The CIA rat model was established by injecting bovine type II collagen into the tail root of rats using the collagen antibody induction method, and the drugs were administered by gavage after the model was successfully established. Normal group: 10 mL/(kg·d) of saline was given; model group: 10 mL/(kg·d) of saline was given; the positive drug group was given 2.0 mg/(kg·d) of MTX each time, three times a week; the iron chopsticks low, medium, and high dose groups were given 0.25g, 0.5g, 1.0g/(kg·d) each time; continuous gavage treatment for 25 day. Body mass of rats was recorded to observe the degree of foot swelling;rat ankle arthritis index score;micro-CT observation of histopathologic changes in ankle joint bone; hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining for pathological changes in ankle joint bone tissue and synovial membrane of the rats;tests to observe changes in the number of osteoclasts were performed with anti-tartaric acid phosphatase (TRAP) ; PCR to detect the mRNA levels of osteoprotegerin (OPG), nuclear factor-κB receptor activator (RANK), RANK ligand (RANKL), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), and bone-forming protein 2 (BMP-2);Relative expression of OPG, RANK, RANKL, TNF-α and BMP-2 proteins were detected by protein immunoblotting (Western blot)Helleborus thibetanus Franchon on rats with rheumatoid arthritis and its potential pharmacological mechanism for osteoarthritic protection. Results The statistical results of the data showed that compared with the normal group, CIA rats showed slower growth of body mass (P<0.05), increased thickness of the plantar foot (P<0.05), narrowing of the joint cavity in the ankle joint, gnawing-like bone destruction of the bone tissues, and pathologic changes in the synovium,Such as inflammatory cell proliferation and abnormal synovial hyperplasia infiltration; Micro-CT results showed that: compared with the normal group, the model group, low and medium dose group, the ankle joint surface was uneven, incomplete in shape, and the ankle joint surface showed gnawing-like bone destruction, and the high-dose group had no significant changes in all indexes compared with the normal group; HE staining found that the ankle joint of the model group showed joint cavity narrowing, gnawing-like bone destruction, synovial tissue proliferation and inflammatory cell infiltration. The pathological changes such as destruction of bone tissue, synovial tissue hyperplasia and inflammatory cell infiltration were found in the ankle joint of rats in the model group; compared with the model group, bone tissue hyperplasia and inflammatory infiltration in the ankle joint of rats in the low, medium and high dose groups were significantly improved; TRAP staining observed that compared with the normal group, the model group had the largest number of osteoclasts, and the number of TRAP staining positive osteoclasts was reduced under the intervention of the low, medium and high dose groups; the results of qRT-PCR showed that, compared with the model group. The relative expression of OPG, BMP-2 mRNA was increased in the low, medium and high dose groups (P<0.05), and the relative expression of RANK, RANKL, and TNF-α mRNA was decreased in the low, medium, and high dose groups (P<0.05); the results of WB, compared with the model group, the relative expression of OPG, BMP-2 protein was increased in the low, medium, and high dose groups (P<0.05), and the relative expression of RANK, RANKL , and TNF-α protein relative expression decreased (P<0.05). Conclusion Helleborus thibetanus Franchon may alleviate the inflammatory response in vivo in RA rats by regulating the OPG/RANK/RANKL signaling pathway and exert its role as an anti-rheumatoid arthritis mechanism.
-
Biochemical characteristics of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its microvascular complications in animal models
daihaoran, wangyue, wangxu, luijing, wuxiuhong
Abstract:
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia, which is seriously harmful to human health. Its prevalence rate is increasing throughout the country. Patients with chronic hyperglycemia develop severe microvascular complications such as diabetic nephropathy (DN), diabetic foot (DF), and diabetic retinopathy (DR). Nowadays, T2DM has become a public health problem in the world. How to effectively treat T2DM and prevent microvascular complications has become an important medical issue to be solved urgently. So far, animal models are still the main tools to study the pathophysiology and treatment of T2DM and its microvascular complications, and it is urgent to establish highly consistent animal models. Biochemical indicators are the most direct reflection of the physiological state and body health of animals, and are crucial in evaluating the success of models, often affecting the experimental results. At the same time, biochemical indexes are also important reference basis for disease diagnosis and drug intervention. In this study, the experimental data of the animal model of T2DM and its microvascular complications were summarized, and the biochemical indexes were analyzed, in order to provide theoretical reference for future related experiments.
-
Establishment and evaluation of mild to moderate closed traumatic brain injury mouse model
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To establish a stable mouse model of mild to moderate closed head injury and evaluate its effectiveness. Methods A total of 170 SPF-grade ICR mice were divided into the sham group(n=34) and the TBI group (n=136). The TBI group was subjected to brain injury by impact under conditions A-D, with 34 mice in each subgroup. After modeling, the score of mNss, fatigue rotating test, and Morris water maze test were used to assess the balance and learning ability of the mice; brain water content experiment, Evans blue experiment, HE staining, GFAP immunohistochemistry, and TUNEL immunofluorescence were used to analyze pathological changes in brain tissue. Results Compared with Sham group, mNss score and water maze escape latency were increased to varying degrees in TBI group, while stick stay time was decreased significantly, indicating that severe neurological dysfunction occurred in TBI group. Brain water content and evans blue content in brain tissue of TBI group mice were significantly higher than those in sham group, suggesting that they suffered from blood-brain barrier damage and brain edema. Histopathological examination showed that the neurons in the brain tissue of the TBI group showed obvious degeneration and contraction, the astrocyte proliferation and the proportion of apoptotic cells increased significantly, and the damage degree increased with the increase of the weight of the blow. Comprehensive analysis revealed that a weight of 60 g or 80 g with a height of injury at 20 cm could simulate mild closed head injury in mice; while a weight of 100 g or 120 g could simulate moderate closed head injury in mice. Conclusion A stable mouse model of mild to moderate closed head injury was established based on the principle of free fall, which laid the foundation for studying the mechanism and treatment strategies for mmTBI.
-
Based on modified bilateral carotid artery ligation way to establish vascular dementia rat model and to investigate the changing rules of cerebral blood flow and its effects on angiogenesis related pr
chen jie, tang xin, chen pan, xie ziwei, xie haihua, zhang hong, zou yinjie, tan jie
Abstract:
【Abstract】 Objective Through the modified bilateral carotid artery ligation way to establish VD rat model to observe the changes of cerebral blood flow and the expression of angiogenic proteins. Methods 36 Sprague-Dawley male rats were randomized into sham group(n=18)and model group(n=18). In the sham group, only the bilateral carotid artery was isolated without ligation, while in the model group, bilateral carotid artery were ligated to establish VD model. Morris water maze behavior test was applied before and 14 days after modeling, the variation of cerebral blood flow was detected by laser speckle contrast imaging. The protein expressions of HIF-1α, VEGF and HO-1 were detected by Western Blotting and the contents of IL-4 and IL-10 were detected by ELISA. Results 14 days after modeling,the escape latency was significantly prolonged and the frequency of crossing the platform had significant decrease for model group as compared with the sham group (P < 0.05). 2 hours,3 days,7 days after modeling, the cerebral blood flow of the model group was significantly lower than that of the sham group (P < 0.05). 14 and 21 days after modeling, there was no significant difference in cerebral blood flow between the sham group and model group (P > 0.05).In the model group, cerebral blood flow decreased to a minimum at 2 hours after modeling (P < 0.05), and then began to recover. The peak of recovery occurred at 3 to 7 days after modeling, and returned to the level before modeling on the 14th day after modeling.At day 21 postoperatively, the expression of HIF-1α, VEGF and HO-1 proteins in hippocampus of the model group were increased remarkably (P < 0.05)and the contents of IL-4 and IL-10 in serum of the model group were significantly rose in comparison with sham group(P < 0.05). Conclusion The variation of cerebral blood flow in VD rats model establish by the modified bilateral carotid artery ligation way showed a certain time rule.At day 21 postoperatively, HIF-1α, VEGF and HO-1 in hippocampus increased significantly, accompanied by increased levels IL-4 and IL-10.
-
Preliminary study on the mechanism of infertility in female SD rats with spontaneous dwarfism
long hong, Huo Chunmao, Li Kang, Bao FengYun, Qin TingYang, Zhao YuJia, Zhang ShiBin
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the causes of infertility and its pathogenic mechanism in female SD rats with spontaneous dwarfism (short stature rat, SSR).Methods Adult wild-type and SSR female SD rats were used for the study. Vaginal smear was used to observe the changes of motile cycle; ovulation promotion was compared using the simultaneous oestrus supernumerary ovulation method; ovarian and uterine weight and body weight, ovarian and uterine indices were measured; AMH, E2, FSH, LH, FSH/LH levels in serum were measured; transcriptomic sequencing of ovarian tissues will be performed to analyze gene expression differences.Results There were no abnormalities in the estrous cycle of SSR female rats., the body weight of SSR female rats was significantly lower than that of wild type, and their ovarian index and uterine index were significantly higher than that of wild type. The mean number of ovulation was significantly higher in wild-type SD rats than in SSR female infertile rats (p<0.001); serum AMH (p<0.01) and E2 (p<0.05) levels were significantly higher in wild-type SD rats than in SSR female infertile rats, and serum FSH (p<0.01), LH (p<0.01) and FSH/LH (p<0.05) The levels of FSH, LH and FSH/LH (p<0.05) were significantly lower in SSR infertile females than in SSR infertile rats, while PROG was not significant; transcriptome sequencing yielded 250 differentially expressed genes, including 190 up-regulated genes and 60 down-regulated genes. p53 signaling pathway and cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. The MCC, MNC, EPC and Degree calculations of CytoHubba plug-in were used to screen the top 10 significant nodes, respectively, and the intersection was taken to finally obtain 9 Hub genes, namely Cxcl1, Cxcl2, Il1a, Il1b, Cd80, Mmp13, Mmp8, Fgf3 and Ptgs2.Conclusions Infertility in SSR female rats may be related to decreased ovarian reserve function and poor ovarian response. At the same time, Cxcl1, Cxcl2, Il1a, Il1b, Cd80, Mmp13, Mmp8, Fgf3, and Ptgs2 were screened to be associated with infertility, laying a theoretical foundation for further exploration of infertility mechanisms.
-
Research progress on the effects of different ketogenic diets on skeletal muscle performance and fatigue recovery
Li tingting, ZHANG Hui, ZHANG Mingchen, WANG Hongying, ZHANG Pingping, WANG Xiaowen, SUN Zhongguang
Abstract:
Objective: To summarize the effects of ketogenic diet on sports performance and fatigue recovery of animals and human beings, so as to provide a diet plan for competitive sports and rehabilitation training. Methods: Database PubMed, Web of Science, Embase and CNKI, VIP, WANFANG, CBM were selected. With "(ketogenic diet) and (athletic performance) or (exercise fatigue recovery)"as the retrieval formula, the retrieval period is not limited, and according to the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria, 42 related literatures were finally included. Results: Ketogenic diet can increase blood ketone, provide energy for skeletal muscle, and play a certain regulatory role in skeletal muscle performance and fatigue recovery. ①Ketogenic diet transforms muscle fiber Ⅱb into Ⅱa through axonal germination and nerve reinnervation, improves the quality and function of mitochondria of fast muscle, and increases histone acetyltransferase to enhance skeletal muscle strength; ②Ketogenic diet uses ketone bodies to provide energy, which can reduce glycolysis and improve the ability of fatty acid oxidation in slow muscles to improve skeletal exercise endurance; ③Ketogenic diet can reduce endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction of skeletal muscle, protect the body from injury, reduce the consumption of muscle glycogen and the accumulation of lactic acid, relieve fatigue after exercise and promote fatigue recovery. Conclusion: Ketogenic diet has low negative effects on the body, can improve the sports performance and fatigue recovery of animals, plays a maintenance role in humans, and can be used as a diet scheme in competitive sports and rehabilitation training.
-
Advances in the Application of Cortisol in Evaluating Stress in Dogs
SUN Ning, FU Jialin, XU Shu, YU Xi, SHUI Yingyi, ZHU Qiwen
Abstract:
In recent years, cortisol had been used as a biomarker to assess stress in dogs. In order to evaluate the welfare of dogs,we reviewed the cortisol levels and changes in dogs under various stress and explored the influential factors which could relieve stress according to the variation law of cortisol levels ,so?as?to improve the measures to reduce stress in dogs. It is recommended to apply cortisol measurement and behavioral observation comprehensively to evaluate stress in dogs more accurately.
-
Mouse and monkey animal models for SARS-CoV-2 infection and pathology
Dong E, ZhangBo, ChenTingwei, Li-Xiaozhuo, Li-Tianqing
Abstract:
As the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) continues to spread globally, its genome undergoes ongoing mutations and evolutions, giving rise to different strains such as α, β, γ, δ, etc. Therefore, continuously development of drugs and vaccines targeting different strains becomes pivotal in addressing the COVID-19 pandemic. Constructing animal models of SARS-CoV-2 not only enables studying the pathogenesis of the virus but also stands as a crucial means for evaluating the efficacy of drugs and vaccines related to SARS-CoV-2. However, commonly used animal models such as mice exhibit limited susceptibility to wild-type SARS-CoV-2, underscoring the urgent need for animal models that can be infected with the novel coronavirus and better simulating human pathological and physiological conditions. This review summarizes the animal models used for studying SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission, as well as their progress in characterizing the viral immunopathology.
-
The improvement of the preparation method for type II cardiorenal syndrome rat model
Liu Qian, Wang Xin Ting, Cheng Pei Pei, Rong Jing Feng, Yang Tian Shu, Zhou Hua
Abstract:
Objective To establish an improved type II cardio-renal syndrome rat model and evaluate it. Methods Twenty male SD rats were randomly divided into the sham group and the model group,with 7 rats in the sham group and 13 rats in the model group. The model group used the method of squeezing the heart under a small animal anesthesia machine to permanently ligate the left anterior descending branch of the coronary artery to cause myocardial infarction. One week later,unilateral nephrectomy (right nephrectomy) was performed. Two groups of rats underwent cardiac echocardiography,pathological staining,and blood and urine tests three weeks after right nephrectomy to verify the establishment of the model. Results Compared with the sham group,the cardiac function detected by echocardiography and the endogenous creatinine clearance rate in the model group rats significantly decreased (P<0.01),the level of brain natriuretic peptide,blood creatinine, urea nitrogen,and 24-hour urine protein in the model group significantly increased (P<0.01). HE staining revealed disordered myocardial arrangement,atrophy of glomerulus,and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the model group rats. Picric acid Sirius red staining showed a significant increase in myocardial collagen fibers,irregular arrangement of renal tubules,and a large amount of collagen deposition in the model group rats. The positive staining area ratio was significantly increased (P<0.01). Conclusions This improved modeling method can provide a type II cardio-renal syndrome rat model with simple operation,minimal surgical trauma,and low mortality rate. This model simulates the early onset of cardiac and renal function damage and pathological changes in type II CRS,laying the foundation for systematic and in-depth research on the pathogenesis and pharmacological mechanism of type II cardio-renal syndrome.
-
Model construction and progress of focused gene therapy for dilated cardiomyopathy
Abstract:
【Abstract】 Dilated cardiomyopathy is one of the main diseases causing heart failure, and there is etiological heterogeneity. Nearly 1/4 of the patients with dilated cardiomyopathy are related to genetics, and ventricular dilation and myocardial systolic dysfunction are the main characteristics of the disease.LMNA mutation is an important cause of hereditary dilated cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmia is an important clinical manifestation of hereditary dilated cardiomyopathy with LMNA mutation.In recent years, the construction and intervention of rodent dilated cardiomyopathy model based on the focused gene therapy of mice with C57/B6 genetic background has been a focus of research, and some important conclusions have been drawn from the construction of large animal models of dogs and pigs. However, large animals, especially non-human primates, are still more close to human models.At present, dilated cardiomyopathy is not involved in the heart disease model of non-human primates. Therefore, this paper reviews the studies on the rodent and large animal models of dilated cardiomyopathy at the genetic level, and also proposes the idea of developing a non-human primate dilated cardiomyopathy model based on the current research.It provides a new idea to study the pathogenesis and clinical treatment in the future.
-
Study on the pathogenesis of hyperlipidemia rats under different dietary conditions based on intestinal flora and short-chain fatty acid metabolism
yangzongtong, SUN Tiefeng, lixiaojing, xudongchuan, yuanmin, jinguangqian, wangwenhui
Abstract:
Objective The purpose of this study was to compare the changes of intestinal flora and the characteristics of short-chain fatty acid metabolism in hyperlipidemic rats induced by two different high-fat diets, and to explore the possible microscopic mechanism of hyperlipidemia from the point of view of host-intestinal flora-metabolism. Methods SPF SD rats were divided into two groups: (1) normal diet group (CG group), fed with high fat diet group (HFD1 group), fed with high fat diet group (HFD1 group), and fed with high fat diet group (HFD2 group). Rats were fed with 80g high fat diet and unlimited maintenance diet.燗fter 8 weeks, the levels of serum total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) were measured, and the pathological changes of liver tissue and perirenal fat were observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining.燭he contents of colon were taken for 16s rRNA high-throughput sequencing to observe the changes of the structure and function of intestinal flora and the content of short-chain fatty acids in colon contents. Result Compared with CG group, food intake decreased and body weight increased in HFD1 group and HFD2 group, serum TC, TG and LDL-C increased significantly, liver tissue showed obvious steatosis and perirenal fat showed inflammatory lesions. After high-fat intervention, the relative abundance of intestinal microflora in rats changed significantly and there were gender differences, in which the relative abundance of Lactobacillus decreased significantly, and the structure and function of Lactobacillus decreased significantly, including total short-chain fatty acids, acetic acid, butyric acid and isobutyric acid. Conclusion The two kinds of high-fat diet can cause hyperlipidemia in rats, and the pathogenesis is basically the same, which is related to lipid metabolism and intestinal flora disorder. Daily restriction of a certain amount of high-fat diet can not only reduce the effect of high-fat diet on rat appetite, but also improve the stability of rat hyperlipidemia model preparation.
-
Effects of bear bile powder on promotion stage of early hepatocarcinogenesis in SD rats
dongrui, zhangmei, hongzexuan, tangqian, zouxinyu, jiaguiyang, niyuanping, Shibutani Makoto, jinmeilan
Abstract:
Objective Bear bile powder (BBP), a natural Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), has antioxidant and anticancer effects. To clarify the modification effect of bear bile powder (BBP) on early period of hepatocarcinoma formation, we conducted an anticancer efficacy experiment using short-term carcinogenesis bioassay models. Method Forty 5-week-old male SD rats were divided randomly into the following 4 groups with 10 animals per group: DEN alone, DEN+PBO, DEN+PBO+BBP-L (200mg/kg BBP), DEN+PBO+BBP-H (400mg/kg BBP). All rats were injected intraperitoneally with 200 mg/kg N-diethylnitrosamine (DEN) and three groups given a diet containing 0.5% piperonyl butoxide (PBO). In addition, the rats of last two groups were orally administered 200 or 400 mg/kg BBP for 8 weeks. Results The relative and absolute liver weights in PBO-treated groups significantly increased compared to DEN alone group. However, the number and area of GST-P+ foci were significantly decreased in only DEN+PBO+BBP-L group compared to DEN+PBO group. In addition, the Ki-67+ cell ratio which are significantly increased by DEN and PBO were significantly decreased after treatment with BBP in both BBP-treated groups. Interestingly, the mRNA levels of Ccne1, Cdkn1b related to cell cycle Caspase 8 and Caspase 9 related to apoptosis were significantly increased only in the BBP-H group. However, these changes were not observed in the BBP-L group. Conclusion These results indicated that BBP has a suppressive effect in the early period of hepatocarcinoma formation, leading to the inhibition of preneoplastic lesions. In addition, these results suggested that the suppression mechanism of BBP is strongly involved in the inhibition of cell proliferation activity and induction of apoptosis. Furthermore, that a high dose of BBP may influence BBP’s inhibitory effect on the preneoplastic lesions.
-
Plantar injection of complete Freund's adjuvant induced behavioral and monoamine neurotransmitter changes in pain and depression comorbid model rats
Abstract:
Objective To observe the effects of plantar injection of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) on pain-depressive behavior and changes in hippocampal monoamine neurotransmitters in rats, with the aim of establishing an animal model of related comorbidity. Methods 16 male, 8-week-old, SPF-grade healthy SD rats were randomly divided into a model group and control group with 8 rats in each group. In the model group, rats were anesthetized and injected with 100 μL of CFA in the left hind paw to induce the comorbid pain and depression model. In the control group, rats were injected with the same volume of saline. Pain thresholds were measured using the von Frey hair and thermal radiation instrument, and depressive-like behaviors were assessed using open field test (OFT), tail suspension test (TST), and forced swim test (FST). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the content of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), dopamine (DA), and norepinephrine (NE) in the rat hippocampal tissue, and histological changes in the hippocampal area were observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. Results Compared with the control group, the mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) and thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) in the model group were significantly decreased at 3, 7, and 14 days (P < 0.01); the total distance in the OFT was significantly reduced at 7 and 14 days (P < 0.01), and the time spent in the center zone was significantly decreased at 14 days (P < 0.01); the immobility time in the TST was significantly increased at 14 days (P < 0.01), and the immobility time in the FST was significantly increased at 7 and 14 days (P < 0.05, P < 0.01); the content of 5-HT, DA, and NE in the hippocampal tissue of the model group rats was significantly reduced compared with the control group (P < 0.01), and the hippocampal tissue in the model group showed pathological changes, including irregular neuronal shapes, loose and disordered arrangement, increased intercellular space, some unclear cell nuclei, and some neuronal contraction and apoptosis. Conclusion Injection of 100 μL of CFA in the footpad can cause pain hypersensitivity, depressive-like behavior, significant reduction of monoaminergic neurotransmitters in the hippocampus, and histological changes in the hippocampus, effectively simulating the manifestations of comorbid pain and depression, and is an experimental model for studying the pathological mechanisms of comorbid pain and depression.
-
The welfare and untilization of experimental animals in tumor research
Abstract:
As an important intermediate link between in vitro cell experiments and clinical experiments, animal models are often preferred in the research of tumor mechanisms, prevention,diagnosis, and treatment. The results of animal experiments are directly related to animal welfare, and are important factors affecting the scientific and accurate results of the research. This article summarizes the relevant aspects of experimental animals involved in tumor research, including tumor animal models, animal welfare related to tumor models and humane endpoints.
-
Progress in the study of animal models of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and macrophage activation syndrome
Abstract:
Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) is the most frequent rheumatic disease complicated by macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), which can be life-threatening in children. Current experimental animal models show only some of the characteristics of sJIA and MAS, and there is no perfect animal model that can replicate the whole process of sJIA and MAS. This article reviews the clinical features, advantages and shortcomings of these models, with the aim of providing ideas for exploring more representative animal models of sJIA and MAS.
-
Research Progress of Neurotransmitter Detection Technology in Living Brain
Zhu Mingyu, Cui Lili, Chen Huan, Hou Hongwei, HU Qingyuan
Abstract:
As an endogenous chemical substance, neurotransmitter plays a vital role in maintaining normal life activities of people. Abnormal levels of neurotransmitters can lead to physical, mental and some neurodegenerative diseases. However, the ultra-low concentration, complex chemical properties and release modes of neurotransmitters make their accurate detection in vivo a great challenge.In order to accurately monitor neurotransmitters in the brain and accurately understand the release kinetics of neurotransmitters, several commonly used methods for detecting neurotransmitters in vivo in the past five years and their research progress were reviewed.The basic principle and applicability of microdialysis, electrochemical sensor and fluorescence sensor are introduced in detail.
-
Research progress on animal models of acute exacerbation of various respiratory diseases induced by compound factors
Qiu Zhiguang, SHAO Xuejie, LU Ruilong, TAN Yange, REN Zhouxin
Abstract:
Based on the compound factors of clinical practice, some progress has been made in acute exacerbation models of respiratory diseases by "two-hit" method. In this review, the current research on acute exacerbation models of pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchial asthma constructed by compound factors is summarized. Furthermore, the characteristics and scope of application of each model are compared and analyzed in animal strain selection, model preparation methods and major histopathological changes, providing reference for researchers to further improve and perfect the model or rationally select the animal models.
-
Effect of miR-185-5p on proliferation, invasion and migration of mouse breast cancer PY8119 cells
Liu Lu, Zhao Yanqiao, Wang Xiaona, Wang Kun, Yin Chonggao, Liu Qinghua, Li Hongli
Abstract:
Object To investigate the effect of miR-185-5p on the proliferation, invasion and migration of mouse breast cancer PY8119 cells. Methods Mirna: miR-185-5p with significantly down-regulated expression in breast cancer was obtained by previous research group. The sequence of miR-185-5p gene from human and mouse was consistent by NCBI. The effects of overexpression and knockdown of miR-185-5p on the proliferation of PY8119 cells were detected by EdU proliferation experiment. The effects of overexpression and knockdown of miR-185-5p on the invasion ability of PY8119 cells were detected by Transwell invasion experiment. The effects of overexpression and knockdown of miR-185-5p on the migration ability of PY8119 cells were detected by scratch healing experiment. The effects of overexpression and knockdown of miR-185-5p on the apoptosis of PY8119 cells were detected by flow cytometry. The effect of overexpression of miR-185-5p on tumor proliferation in vivo was detected by C57BL/6 mouse subcutaneous tumor model. Lung metastasis of mice overexpressing miR-185-5p was observed by tail vein injection. Results The results of EdU proliferation experiment, Transwell invasion experiment, scratch healing experiment and flow cytometry showed that knocking down miR-185-5p significantly enhanced the proliferation, invasion and migration of PY8119 cells and inhibited apoptosis. Overexpression of miR-185-5p inhibited the proliferation, invasion and migration of PY8119 cells and promoted apoptosis. In vivo tumorigenesis experiment of C57BL/6 mice showed that overexpression of miR-185-5p slowed down the tumor growth rate in C57BL/6 mice. Lung metastasis experiment showed that overexpression of miR-185-5p inhibited the lung metastasis of C57BL/6 mice. Conclusion miR-185-5p can inhibit the proliferation, invasion and migration of mouse breast cancer PY8119 cells in vitro and in vivo as a tumor suppressor gene.
-
Research hotspots and trends of Alzheimer's disease animal experiments: CiteSpace bibliometric analysis based on WOS database
YANG Jia-hui, LIN Yin, CHEN Lai, luoxiaoquan
Abstract:
Objective Alzheimer's disease (AD) brings a huge burden to patients and society. As an important means of studying AD, animal experiments provide a lot of scientific basis for clinical and scientific researchers. This paper adopts the method of bibliometric analysis to reveal the research status, hotspots and trends in the field of AD animal experiments. Methods We obtained publications in the field of AD animal experiments from 2018 to 2022 from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database. We use the analysis software CiteSpace 6.2.R2 (Advanced) to analyze the general information and keywords of publications in this field. Results After analyzing 4015 articles included in this study from 2018 to 2022, it was found that the annual publication volume of papers has gradually increased. In terms of the number of articles, the United States, the University of California System, Saito T, and the International Journal of Molecular Science are the countries, institutions, authors, and journals with the largest number of articles. "Alzheimer's disease" had the highest frequency of occurrence, and "anxiety" had the highest central degree. Conclusion This field focuses on the study of pathogenesis and treatment methods, and the plasticity of entorhinal cortex, neurons and synapses is a hotspot of current research. Future research trends may mainly focus on Aβ plaque formation, tau hyperphosphorylation, neurofibrillary tangle accumulation, glial inflammation, and ultimately loss of proper neuroplasticity. This article visually analyzes the hotspots and trends of AD animal experiments to help researchers understand the latest situation.
-
Study on the expression and methylation level of hippocampal Notch signaling pathway genes in perimenopausal depression rats
shen jian ying, liang wen na, chen hui fang, zhang ling yuan, zhuang yuan ying, chen xiao yang, chen ya ru, xiao qiong qiong, yang min, gong lin, min li
Abstract:
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of perimenopausal depression on the expression of key genes of Notch signaling pathway and DNA methylation of its promoter in rat hippocampus from the perspective of DNA methylation of epigenetics. Methods 12-month-old female SD rats were randomly divided into control group and model group. Open field tests, sugar consumption tests, and forced swimming tests were used for behavioral evaluation. Real-time PCR was used to detect the expression of key genes of Notch signaling pathway in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of different groups. Bisulfite sequencing (BSP) was used to analyze methylation sites and methylation levels in the promoter region of key genes of the Notch signaling pathway. Results In perimenopausal depression rats, the horizontal and vertical scores of open field test and the rate of sugar water consumption decreased significantly; the expression of the key genes Jagged1, Notch1 and Hes5 on Notch signaling pathway was significantly down regulated in the hippocampus of perimenopausal depression rats (P<0.01 or P<0.05) ; among them, some methylation sites and methylation rates of Hes5 gene increased significantly, while the methylation sites and methylation rates of Jagged1 and Notch1 genes were not statistically significant (P>0.05) . Conclusion The expression of key genes of Notch1 signaling pathway in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of perimenopausal depression rats is significantly down regulated, and the down-regulation of Hes5 gene may be related to the increase of promoter DNA methylation level.
-
Establishment and evaluation of rats model of rheumatoid arthritis with depression
liyuanyuan, zhangbitao, fanpeijian, cuizilong, wangshaoxian
Abstract:
Objective To prepare and evaluate the animal model of rheumatoid arthritis with depression (RAD). Methods Thirty-two rats were randomly divided into normal group (N group), depression group (D group), arthritis group (RA group) and model group (RAD group), with 8 rats in each group. The N group was fed normally, while the D group was fed solitary rearing for 1 week and chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) for 3 weeks, RA group was induced by collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) to establish the arthritis model. In RAD group, RAD animal model was established on the basis of CIA animal model, meanwhile, adding 1 week solitary rearing and 3 weeks CUMS. Toe volume, arthrits index (AI), Synovial and ankle joint pathology, serum levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were used to evaluate whether the rat model of rheumatoid arthritis was successfully established; the depression status of rats was evaluated by measuring body weight, food intake, sugar water preference rate, open field behavior (total number of motion cells, number of standing uprights), serum levels of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), corticosterone (CORT), and pathological changes of hippocampus. The RAD animal model was successfully prepared if depression and rheumatoid arthritis were both tested in the rats. Results Compared with the N group, toe volume, AI score and the levels of IL-1β, IL-6 in serum of RA group and RAD group were significantly increased (P<0.05 or P<0.01), the joint space widened, synovial hyperplasia was obvious and extended to the joint cavity, and a large number of inflammatory cells were seen; in D group and RAD group, body weight, food intake, total number of motion cells, number of standing uprights and sugar water preference rate of rats were decreased to different degrees, and the levels of CRH, ACTH, CORT in serum were increased in different degrees (P<0.05 or P<0.01), the neuron cells arranged loosely, gap increased, the number decreased, accompanied by some nucleus pyknosis, dissolution, rupture, especially in the model group. Conclusion CIA combined with solitary rearing and CUMS can better simulate the changes in the external manifestations and internal indicators of RAD model animals, which can provide reference for the study of RAD disease animal models.
-
Quantitative inhalation method to established the model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in rats
Abstract:
Objective To compare the differences of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) models induced by smoke inhalation through nose-mouth plus LPS or smoke exposure through wholebody plus LPS in rats, providing a new model for COPD model construction. Methods 90 male SD rats were randomly divided into normal control group, wholebody exposure group and nose-mouth inhalation group, with 30 rats/group. The wholebody exposure group were exposed in a homemade smoke box where smoke contacted with whole body of rats , and the smoke nose-mouth inhalation group were inhaled with somke via nose-mouth only in a "quantitative smoking device". Animals in both groups were exposed to smoke once a day for 60mins/time for 8 weeks, and LPS (1mg/kg) was injected through the trachea on day 1, 7, 15 and 21, respectively, to induce the COPD model. The quality control of smoke generated by quantitative smoking devices included the verification of the stability and uniformity of the concentration of smoke particles and the size distribution of smoke particles. At 4, 6 and 8 weeks of modeling period, pulmonary function examination, the content of inflammatory factor interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in alveolar lavage fluid and histopathological examination were performed to compare the differences between the two modeling methods. Results Quantitative smoking devices could produce smoke with stable concentrations of 1.1mg/L (counted as total particles) and 0.1mg/L (counted as nicotine), respectively, with a median mass particle size of 0.693μm (in nicotine) and a GSD of 1.463. Compared with the whole body exposure group, the indexes of pulmonary function FEV0.2/FVC and pulmonary compliance (Cdyn) in the nose-mouth inhalation group decreased more significantly, and the airway resistance (Penh) increased more significantly. The levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in the alveolar lavage fluid of rats in the nose-mouth inhalation group were significantly increased at 6 weeks after modeling, while those indexs in the wholebody exposure group were increased at 8 weeks after modeling. The lesion severity of bronchial inflammation after modeling was similar between the oral-nasal inhalation group and the wholebody exposure group, but the lesion severity of emphysema was more serious in the oral-nasal inhalation group (the time when appeared statistic difference: oral-nasal inhalation vs. wholebody exposure = 6 weeks of modeling vs. 8 weeks of modeling). The mean linear intercept (MLI) in the oral-nasal inhalation group increased significantly at 4-8 weeks of modeling, and the mean alveolar numbers (MAN) decreased significantly at 6-8 weeks of modeling. MLI increased significantly and MAN decreased significantly in the whole body exposure group after 8 weeks of modeling. In the oral-nasal inhalation group, significant abnormal changes were observed in pulmonary function indexes (FEV0.2/FVC, Cdyn, Penh), cytokine levels in Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (IL-6, TNF-α), and alveolar histopathological changes (bronchial severity and emphysema pathological score, MLI, MAN) after modeling. However, the coefficient of variation (CV%) of each index was significantly lower than that of the whole body exposure group. Conclusion LPS (1mg/kg) endotracheal drip combined with smoke wholebody exposured or via oral-nasal inhalation both could establish a typical rat COPD model. Rats Inhalated smoke via oral-nasal could shorten the modeling period. The model could be completed after 6 weeks of continuous modeling, presenting typical symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (pulmonary ventilation dysfunction, broncho-lung chronic inflammatory infiltration, accompanied by emphysema), and the difference between individual model animals were smaller (vs smoke exposure, CV% values were smaller).
-
Research progress of animal metacognition
Abstract:
It is widely believed that metacognition is a special cognitive capacity that only humans possess. A contentious debate in the field of comparative psychology is whether animals have metacognition. The exploration of this question has become an important way to uncover the phylogenetic roots of metacognition and to map the evolutionary history of higher cognitive functions in humans. This paper reviewed the main animal metacognition studies in the past 25 years. We summarize three common research paradigms and corresponding measures: the uncertainty monitoring paradigm, the information seeking paradigm, and the confidence judgment paradigm. Two opposing explanatory tendencies and their rationales are outlined in the field of animal metacognition research: the associative model and the metacognitive model. In response to the debate between the associative model and the metacognitive model, two future research orientations are proposed to improve the research paradigm to test the metacognitive model and the innovation theory to integrate the model.
-
Data mining based animal model for dilated cardiomyopathy
Abstract:
Objective To review the animal species, modelling methods and evaluation indexes of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) animal models at home and abroad, to provide suggestions for improving the success rate of modelling and establishing DCM animal models with Chinese medicine characteristics in the future, and to provide reference for the establishment of future DCM animal models. Methods The literature on animal models of dilated cardiomyopathy in the past 10 years was searched, and relevant reports were collected and summarized. Relevant parameters of experimental animals (species, sex, body weight, etc.), modelling methods, modelling cycles, positive control drug species and cycles, and model evaluation indexes were summarized and analysed. Results A total of 128 papers were included. Animal models of dilated cardiomyopathy were mostly prepared in SD rats and Wistar rats using the anthracycline adriamycin, with a cycle of 30 d
-
To investigate the effect of TMAO on lipid metabolism in spleen deficiency hyperlipemia rats and the intervention effect of Xiangsha Liujunzi decoction
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of TMAO, a metabolite of intestinal flora, on hepatic lipid metabolism in rats with splenic deficiency and hyperlipidemia, and to further explore the possible mechanism of Xiangsha Liujunzi Decoction in the intervention of hepatic lipid metabolism disorder. Methods SD rats were divided into: (1) Blank control group (group C), (2) blank control group DMB (group C D), DMB is TMAO inhibitor, (3) spleen deficiency hyperlipidemia group (PG group), (4) spleen deficiency hyperlipidemia DMB group (PG D), (5) Spleen deficiency hyperlipidemia Xiangsha Liujunzi Decoction group (PG XS group), Except group C and group C D, the other groups were constructed to establish spleen deficiency hyperlipidemia model (12 weeks of modeling) by combining excessive fatigue and high-fat diet. After model establishment, group C D and PG D were given 1%DMB in drinking water every day, and group PG XS was given Xiangsha Liujunzi decoction (11.34 g crude drug /kg/ day) every day. The other groups were given the same amount of normal saline. The blood lipid level of each group was detected by automatic biochemical method after 4 weeks of intragastric administration. The morphological changes of liver were observed by HE staining. The lipid deposition in the liver of each group was observed by oil red O method. Liver FFA, TG and TC were detected by ELISA. The plasma TMAO content was detected by LC-MS. The relative expression levels of PERK, FOXO1, SREBP-2, ABCA1 and miR-33 mRNA in liver were detected by qRT-PCR. The contents of SREBP-2 and ABCA1 gene protein in liver were detected by WB. Results (1) The content of TC, TG and LDL-C in serum of PG group was significantly higher than that in C group, and the content of HDL-C was significantly lower than that in C group; The contents of FFA, TG and TC in liver tissue of PG rats were significantly increased compared with those of C group. Compared with group C, lipid deposition in liver was aggravated and fat vacuoles were increased significantly. There was no difference between group C D and group C in the above indexes. Compared with the PG group, PG D and PG XS groups could significantly reduce the contents of TC, TG and LDL-C in serum, increase the content of HDL-C, reduce the contents of FFA, TG and TC in liver tissue, alleviate the phenomenon of lipid deposition in liver tissue and reduce liver vacuoles. There was no significant difference between PG D group and PG XS group. (2) Compared with group C, the plasma TMAO content of PG group was significantly increased, the liver PERK, FOXO1 and miR-33a mRNA expressions were significantly increased, and the liver SREBP-2 and ABCA1 mRNA and protein expressions were significantly decreased; There was no difference between group C D and group C in the above indexes. Compared with the PG group, PG D and PG XS groups could significantly reduce the plasma TMAO content, decrease the liver PERK, FOXO1 and miR-33a mRNA expressions, and increase the liver SREBP-2 and ABCA1 mRNA and protein expressions. There was no significant difference between PG D group and PG XS group. Conclusion TMAO may regulate the SREBP-2/miR-33a/ABCA1 signaling pathway through PERK/FOXO1 axis to cause liver lipid metabolism disorders in rats, and Xiangsha Liujunzi Decoction may inhibit liver lipid metabolism disorders by inhibiting TMAO content.
-
Study on the effect of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction on bile acid metabolism in SD rats based on serum metabolomics
yangguangyong, duhaiyang, zhanggengxin, sugang, tuxiaohua, heguangzhi
Abstract:
Objective To study the effect of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction(HLJD) on the physiological function of healthy SD rats through serum non-targeted metabolomics. Methods After 7 days of adaptive feeding, 24 rats were randomly divided into blank group (group N) and high-dose HLJD group (group H), medium-dose HLJD group (group M), and low-dose HLJD group (group L) with six rats per group. Group N was gavaged with physiological saline, and H, M, and L groups were gavaged with 6.250, 3.125, and 1.560 g/kg HLJD, respectively. Rats were gavaged with 1 mL twice per day for 21 d. Before collecting serum samples, fasting and water deprivation were performed for 12 h. After anesthesia, blood was collected from the abdominal aorta, and serum was separated. Changes in metabolic products in the serum were detected by Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry(GC-TOF-MS). Multivariate analysis by Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures Discriminant Analysis(OPLS-DA) and univariate statistical methods were used to screen differential metabolites, and then metabolic pathway analysis was conducted using the Metabo Analyst platform. Results Compared with the group N, metabolic small molecules were significantly altered in the serum of group H, group M, and group L, which mainly included cholesterol, cholic acid, ribose, paclitaxel, cortisol, oleic acid, succinic acid, linolenic acid, acetic acid, and acetone alcohol (P < 0.05). Correlation analysis showed that HLJD significantly affected the metabolism of primary bile acids, alanine, aspartic acid, and glutamate in α-linolenic acid and glycerol phospholipid metabolism, and its in vivo effects may be related to the intake dose, providing a reference to further reveal the mechanism of HLJD in promoting bile acid metabolism. Conclusions HLJD promotes the production of primary bile acids in vivo and enhances the effects of the bile acid metabolic pathway.
-
The model of ulcerative colitis with spleen deficiency and dampness syndrome and the changes of T lymphocytes
qiuping xiao, zhong youbao, yu songren, li shangshang, luo xiaoquan, chen liling, liu xuan
Abstract:
Objective A mouse model of ulcerative colitis with spleen deficiency and dampness syndrome was established, and the role of T lymphocytes in this model was studied. Methods C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided equally into Control, FXY, 3% DSS, FXY+3% DSS and FXY+2% DSS groups. A mouse model of ulcerative colitis with spleen deficiency and dampness syndrome was established by DSS and senna leaf. At the end of moulding, HE staining was performed to observe structural changes in the colon tissue. Elisa assay was performed to detect the concentrations of inflammatory cytokines in the colon tissues. Flow cytometry was used to detect the levels of CD4/CD8 T lymphocytes, Th1/Th2, Th17/Treg cells. Results In the FXY group, the clinical symptoms of mice with spleen deficiency and dampness were mainly diarrhea, and mice with 3% DSS colitis mostly showed blood in stool, while mice with spleen deficiency and dampness colitis in the FXY+3%DSS and FXY+2%DSS groups mostly showed diarrhea and blood in stool, but the survival rate of mice in the FXY+3%DSS group was as low as 50%. Compared with the Control group, body weight, colon length and concentrations of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β1 were significantly lower in the 3%DSS, FXY+3%DSS and FXY+2%DSS groups, while concentrations of DAI, colon weight, colon weight index, colon weight/colon length, pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-ɑ, IL-1β and IL-6 were significantly increased, and significant ulcer formation and inflammatory cell infiltration were observed under light microscopy. Compared with the Control group, the percentages of CD4, Th1 and Th17 cells in the mesenteric lymph nodes of FXY+3% DSS and FXY+2% DSS groups were significantly increased, while CD8, Th2 and Treg cells were significantly decreased. Conclusion The combination of Senna and 2% DSS could successfully construct a model of mice with ulcerative colitis with spleen deficiency and dampness evidence, showing typical CD4/CD8, Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg cell imbalance characteristics.
-
Progress in the application of the zebrafish model in the study of neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract:
【Abstract】 With the process of the aging society, the incidence rate of neurodegenerative diseases is increasing year by year. Zebrafish have many advantages that other model organisms do not have, such as unique growth and development mode, low price and easy reproduction, and highly similar to human genes. In the past decades, zebrafish as a model organism has been widely used in various research fields of medicine and life science. This article reviews the application and progress of zebrafish in the research of several common neurodegenerative diseases in recent years, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal muscular atrophy, hereditary spastic paraplegia, and other diseases related to the nervous system. This review article analyzes and summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of zebrafish as an ideal model organism. In future research, especially in the mechanism research of neurodegenerative diseases and large-scale screening of therapeutic drugs, zebrafish has considerable application prospects.
-
Research progress on animal model construction and evaluation of different TCM syndromes of gastric ulcer
Wang Wen, Hou Yujun, Wang Lu, Yan Xiangyun, Li Yanqiu, Sun Luqiang, Chen Shuai, Shi Yinzhou, Zheng Qianhua, Li Ying
Abstract:
Gastric ulcer is a common digestive system disease. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a significant effect in treatment of this disease. However, its treatment mechanism is unclear. Establishing a scientific and objective animal model and model evaluation system is of great significance to promote development of TCM in this field. This article organizes the literature related to treatment of gastric ulcer by TCM in the past 10 years and summarizes methods for establishing and evaluating animal models of TCM syndromes relating to gastric ulcer. The methods were reviewed for liver and stomach disharmony syndrome, spleen and stomach dampness-heat syndrome, blood stasis in stomach syndrome, deficiency cold of spleen and stomach syndrome, stomach Yin deficiency syndrome, and liver depression and spleen deficiency syndrome. The current animal models of gastric ulcer had the following problems: the typing of TCM syndromes was not unified, the methods and syndrome types of the models were limited, the standards of model establishment methods were different, the combination of disease and syndrome of models was not close enough, and the model evaluation system was not standardized. Suggestions for model improvement are proposed to provide a reference for research in this field.
-
Analysis of pathological changes of knee joint and intestinal tissue in cynotonic spondylitis monkeys
huangyuye, caiyanzhen, caichunmei, zhuhepeng, dinghuangguan, xiaowende, chenjun, luli
Abstract:
Objective: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is an immune-mediated chronic disease involving axial joints, peripheral joints and intestines, but the etiology of peripheral knee and intestine has been unknown. This study aimed to study the main pathological changes and mechanisms of knee joint and intestine in cynomolgus monkeys with AS. Methods: Through histomorphological analysis and immunohistochemical experiments, the key characteristics of peripheral knee joint and intestinal tissues of AS were studied and the possible pathogenesis was preliminarily analyzed. Results: The pathological characteristics of peripheral knee joints in AS cynomolgus monkeys mainly showed cartilage erosion on the joint surface, exposed subchondral bone, and jagged joint surface in the early stage. In the late stage, it is mainly manifested as ectopic hyperplasia of cartilage superficial hypertrophy of chondrocytes, and osteophytes are formed through chondroplaginous osteogenesis and fibroogenesis, and cartilage is basically lost. The expression of MMP-3 in cartilage and blood vessels is upregulated, causing cartilage destruction and stimulating angiogenesis. AS cynomolgus monkeys have severe atrophy of small intestinal villi and obvious crypt hyperplasia, and a large number of γδ T cells can be seen in the mucosal intestinal glands of the jejunum and ileum. Conclusion: In this study, the pathological analysis of knee joint and intestine of AS cynomolgus monkey obtained the key characteristics of knee joint and intestinal tissue of this spontaneous model, and proposed a possible pathogenesis. This paper provides new insights into the potential link between autoimmunity in bone tissue and intestinal tissue lesions in AS.
-
Langendorff Cardiac Perfusion Technique (for Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion) applications and developments
Linan, Zhang Chen, Sun yanjun, Gao Shengwei, Li Duojing, Wang xinrui, Wang Baohe
Abstract:
The Langendorff ex vivo cardiac perfusion model technique is reproducible, easy to administer and has low technical requirements, and is often used to study myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury diseases. This article reviews the steps of this technique, selection of animals, perfusion patterns, selection of perfusate, indices of detection, ischemic modalities, and selection of ischemia and perfusion times.
-
Study on the antidiarrheal effect of new "Ershen pills", a composition of new sliced nutmeg Koji
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the antidiarrheal effect of new ershen pills composed of nutmeg koji instead of bran stewed nutmeg.Method Kunming mice were randomly divided into normal group, model group, Ershen pills Ⅰ (salt psoralen + bran stewed nutmeg), Ershen pills Ⅱ (salt psoralen + nutmeg koji), Ershen pills Ⅲ (salt psoralen + nutmeg raw product), salt psoralen group, and nutmeg koji group. The combined modeling method of "hydrocortisone + senna leaf" was used to establish the diarrhea mouse model with spleen-kidney Yang deficiency. The general signs and pathological changes of each organ were observed. The levels of various organs index, small intestine propulsion rate, gastric residual rate, serum motilin (MTL), gastrin (GAS), adrenal ketone (CORT), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), testosterone (T), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β) were detected. 16S rDNA sequencing and information analysis were conducted for fecal microorganisms. Results After modeling, compared with normal group, the weight and activity of mice in model group were reduced, small intestine propulsion rate was significantly increased, gastric residual rate and organ index were significantly decreased, serum GAS, CORT, TSH and T levels were significantly decreased, MTL, TNF-α and IL-β levels were significantly increased, and intestinal flora species diversity was decreased. After administration, the above indexes and symptoms were improved in different degrees in each administration group, and Ershen Pills group Ⅱ was better than Ershen Pills group Ⅰ, Ershen Pills group Ⅲ, salt-psoralea and myristoqu groups. Conclusion The combined use of nutmeg koji and salt psoralen has a remarkable effect on the diarrhea of spleen and kidney Yang deficiency. The fermented nutmeg can reduce its toxic risk and enhance its effect of warming spleen and preventing diarrhea, which laid a foundation for the development of nutmeg koji.
-
Characteristics and application analysis of ovarian cancer animal model
yi chu, zhan sha, ma xin yi, wu yang jie, bu jun yi, ma min, yan xian xin
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To study the characteristics and application status of animal models of ovarian cancer and provide guidance for standardized preparation of ovarian cancer models. Methods Using “ovarian cancer” and “animal model” as the main topics in CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, and PubMed databases, the databases were searched for animal experimentation literature on ovarian cancer from establishment of the database to March 1, 2023. A total of 1428 relevant articles were collected. From the experimental animal species, age, experimental modeling methods, detection indicators, and other aspects of the summary, we established a database for systematic analysis. Results A total of 178 studies were obtained after screening. Female BALB/c mice were selected to establish the animal model of ovarian cancer. Most choices were 4 ~ 6 and 6 ~ 8 weeks of age. The most common modeling method was ectopic transplantation, which was mostly subcutaneous injection in the axilla. In terms of modeling methods of ovarian cancer in animals, transplantable models were the most used, and ectopic transplantation was more often employed than orthotopic transplantation. The ovarian cancer cell lines used were mostly human. Most detection indexes were the appearance of tumor tissue, tumor pathology, and immunohistochemistry. Conclusion Animal models of ovarian cancer are widely used in ovarian cancer research, but standard preparation and evaluations are lacking. We analyzed the application status of animal models of ovarian cancer in detail through literature collation and data classification analysis to provide a reference to establish standardized animal models of ovarian cancer. BALB/c mice are the most selected, and human ovarian cancer cell line SKOV3 at 1 × 107 cells/ml is commonly injected into the subcutaneous axillary area for 10 days. A large number of models can be obtained in a short time with a high tumor formation rate and small individual differences, which provide a reference to study ovarian cancer.
-
Model establishment and evaluation of rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with chronic kidney disease
Fanzhengyuan, Li Ya, LI Suyun, LI Gaofeng, LI Jingmei
Abstract:
Objective To establish and evaluate a model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) combined with chronic kidney disease (CKD) in rats. Methods Forty SPF grade SD rats were randomly divided into control, COPD, CKD, and COPD combined with CKD model (COPD+CKD) groups, with 10 rats in each group. The COPD rat model was prepared by cigarette smoke exposure combined with the bacterial drip method, the CKD rat model was established by adenine induction, and the COPD combined with CKD rat model was prepared by both methods. Results After successful modeling, lung function indexes incluidng forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 0.1s (FEV0.1), and FEV0.1/FVC were significantly reduced in the COPD+CKD group (P < 0.01), and lung histopathology showed emphysematous changes with alveolar wall fracture and fusion as well as inflammatory cell infiltration. Serum Cr, BUN, and 24 h urine protein were significantly increased (P < 0.01). Renal histopathology showed glomerular mesentery proliferation, basement membrane thickening, tubular dilatation, and interstitial fibrosis. The ultrastructure showed that glomerular capillary loops were partially closed, foot processes were fused, renal tubule mitochondria were fused and disintegrated, and lysosome was increased. Serum IL-6, IL-13, IL-1β, and TGF-β1 levels were significantly increased (P < 0.01) and were significantly higher than those in single model groups (P < 0.01). Conclusions Cigarette smoke exposure combined with bacterial infection and 2.5% adenine induction successfully establishes a model of COPD complicated with CKD in rats, and the inflammatory response might play a major role in the process of COPD complicated with CKD.
-
Research progress of functional dyspepsia animal model based on the combination of disease and syndrome
liuhao, wangxinai, liwenjing, wuyaxuan, wangchenqi, xiaohongling
Abstract:
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a non-organic disease mainly due to regional dysfunction of stomach and duodenum. In traditional Chinese medicine(TCM), it is classified as "epigastric fullness" and "epigastric pain", and divided into the syndrome types of spleen deficiency and qi stagnation, spleen-stomach deficiency-cold(weak), spleen-stomach damp-heat, liver-stomach disharmony, and cold- heat complicated. TCM has a significant effect and high acceptance in the treatment of FD, and the animal model with the combination of disease and syndrome is the basis and prerequisite for relevant research. Therefore, this paper organized and summarized the existing research on animal models of FD combined with disease and syndrome, explored the reasons for the selection of specific modeling methods and evaluation indicators, and proposed the shortcomings of the current research, in order to provide support for the future research on animal models of FD combined with disease and syndrome.
-
Collagen peptide combined with sodium alginate improved intrauterine adhesions in mice by down-regulating the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome
chengyiyi, zhaoweiwei, song zhenfeng, tongfuwen, liugang, zhanghua, shileilei, guozhikun, wangxianwei, panying, sunyongkun
Abstract:
【Abstract】Objective To investigate the repair effect and mechanism of collagen peptides (CP) combined with sodium alginate (SA) on endometrial injury. Methods Forty-eight SPF female C57BL/6N mice were randomly divided into sham group (16 mice), model group (16 mice) and CP SA group (16 mice). In the model group, 95% ethanol was injected into the uterine cavity through the cervix to induce endometrial injury, and the intrauterine adhesion model was established. The sham operation group was injected with 0.9% normal saline into the uterine cavity. The treatment group was injected with the mixture of CP SA after the injection of 95% ethanol into the uterine cavity. After 7 days of modeling, 8 mice in each group were selected to collect samples for each test. HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of mouse uterine tissue. Modified Masson tri-color staining was used to observe endometrial fibrosis. Western blot was used to detect the protein expression levels of inflammatory factors NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1, IL-1β and IL-18 in uterine tissues. ELISA was used to detect the expression of IL-1β and IL-18 in serum. The remaining 8 mice in each group were cohoused according to the male-female ratio of 1:2, and the number of pregnant mice in each group was recorded. Pregnant mice were euthanized in the 14th day of pregnancy, and the number of embryos was recorded. Results (1) Compared with the sham operation group, the model group showed thinner endometrial thickness, increased endometrial fibrosis, and inflammatory cell infiltration. In addition, the protein expression levels of inflammatory factors NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1, IL-1β and IL-18 in uterine tissue and the levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in serum in the model group were significantly lower than those in the sham operation group (P<0.05). (2) Compared with the model group, the treatment group showed that the degree of endometrial injury, endometrial fibrosis and inflammatory cell infiltration were reduced. In addition, the protein expression levels of inflammatory factors NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1, IL-1β and IL-18 in uterine tissue and the levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in serum in the model group were significantly decreased than those in the sham operation group (P< 0.05). (3) Compared with the sham group, the reproductive ability of the model group decreased (P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the reproductive ability of the treatment group was significantly improved(P<0.05). Conclusions The combined application of CP and SA can effectively improve the pathological changes of uterine tissue, reduce endometrial injury, inflammatory response and fibrosis, and improve the reproductive ability of mice. The mechanism may be related to the down-regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome expression, which provides a reliable experimental basis for the combined application of CP and SA in the treatment of intrauterine adhesion.
-
Research progress of bronchoalveolar lavage in mice
Wu Zhihao, Yang Luyin, Ren Wei, Zhou Yanan, Wang Hong, LeiYun, Yu Hong, Yang Sijin
Abstract:
Bronchoalveolar lavage is an important technique for studying respiratory diseases and has been widely used in disease research. Currently, the operation procedure of bronchoalveolar lavage in clinical patients has been gradually standardized, while mice, as one of the important model animals for studying lung diseases, still need a standard collection and testing procedure for bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for mice. An unstandardized procedure can hinder the promotion and application of this technique in research, and also affect the accuracy and reliability of experimental results. This paper presents a systematic summary of bronchoalveolar lavage methods for mice in domestic and international studies, with the aim of providing reference and guidance for researchers to apply and establish a standardized lavage procedure in the future.
-
Advances in Animal model for studying albumin-related drugs
Ziyin, Ning Li, Tang Chengcheng, Zhou Xiaoqing
Abstract:
The main challenges of therapeutic peptides or proteins is their short plasma half-life. The drugs combining these peptides or proteins were defined as albumin-related drugs. Such combination can effectively prolong the plasma half-life. Animal model is an important and indispensable tool for studying drug pharmacokinetics. This review summarizes two main animal models; rodents (wild-type mice, gene-modified mouse models, rat models) and non-rodents (monkeys), and their development and application in albumin-related drugs. This review can provide a reference for further studies on albumin-related drugs.
-
Research progress on the establishment of mouse atherosclerosis model by different intervention factors
baixufeng, cao qingyu, 胡, wang shuwen, liu yali
Abstract:
Atherosclerosis (AS) is a potential risk factor for common cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Prevention and treatment of AS and research and development of anti-AS drugs have been a focus in the field of medicine. Selection of the ideal AS animal model is important to study prevention and control measures of AS and to research and develop traditional Chinese medicine for AS. The ideal animal model of AS should have similar pathogenesis to human AS, consistent pathological and biochemical reactions, high repeatability, simple operation, and easy adoption. Mice have the characteristics of strong reproduction, high heritability, good plasticity, and fast modeling of AS, and they have become ideal animals for AS research. In this article, the replication methods of the mouse AS model established by various intervention factors were compared and analyzed to provide a reference and ideas for prevention and treatment of AS and research and development of traditional Chinese medicine for AS.
-
Application and development of germ-free animals for the gut microbiome research
Hu Yaqian, Wang Shanshan, Zhang Tong, Yuan Jiali, 胡
Abstract:
In recent years, with the introduction of the concept of metagenomics, human metagenomics has also become a new approach to reveal the development and health of humankind. As the largest microflora in the human body, the gut microbiome has been found to play an important role in the normal physiological functions of the human body and the occurrence and development of diseases. The variety and quantity of gut microbiome are abundant. In the study of gut microbiome, the application of germ-free animals makes the experiment more accurate and convenient. It is an ideal basic animal model. Not only that, models developed on this basis are also of great significance to this type of research. This review summarizes the understanding of germ-free animals, the application of germ-free animals in experimental research and the prospects of germ-free animal models, to review the application and development of germ-free animals in the gut microbiome.
-
2016,24(3):321-326, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2016.03.020
Abstract:
The incidence of depressive illness is high worldwide, and the inadequacy of currently available drug treatments contributes to the significant health burden associated with depression. Animal models of depression used as the main methods to study the pathogenesis mechanism and select effective drugs receive increasing concerns. Current popular models of depression creatively merge ethologically valid behavioral assays with the latest technological advances in molecular biology. In this context, this study aims to review the animal models of depression and pathogenesis related with face validity, construct validity, and predictive validity of these models. These models include stress-induced models, injury-induced models, drug-induced models and transgenic models which all mimic the depression symptoms of human to some degree and are of great value for developing new antidepressant drugs and studying the pathogenesis of this disease.
-
CHEN Zhaoyang, YAO Ru, WANG Lu, WANG Chenyang, GUO Min, SONG Guohua, ZHANG Ruihu
2018,26(3):343-348, DOI: 10.3969/j. issn. 1005 -4847. 2018. 03. 012
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of Liensinine on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)?induced acute lung injury (ALI) in mice. Methods BALB/ c mice were randomly divided into six group: control group, LPS group, LPS + Liensinine (2 mg/ kg, 4 mg/ kg, 8 mg/ kg) groups, and dexamethasone group. Acute lung injury in mice was induced by nasal instillation of LPS. After 12 h, the pathological changes of lung tissue were observed. The levels of TNF?α, IL?6 and IL?1β in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were detected by ELISA. The number of neutrophils in BALF was detected using Wright?Giemsa staining. Total protein content was detected by BCA protein quantification assay. The pulmonary capillary permeability was examined with Evans blue. The MPO activity, MDA content, SOD activity, and GSH content in lung homogenate supernatant were detected by spectrophotometry. The content of ROS in lung tissue was detected by flow cytometry. Results The LPS group showed inflammatory cell infiltration, thickening of bronchial alveolar wall and pulmonary congestion in the lung tissue, while Liensinine improved the lung injury. In the LPS group, the contents of TNF?α, IL?6 and IL?1β in BALF were significantly increased, the number of neutrophils and the content of total protein were significantly increased, pulmonary capillary permeability, MPO activity and MDA content were increased, SOD activity and GSH content were decreased, the content of ROS was increased; while the Liensinine group reduced the contents of TNF?α, IL?6, IL?1β in BALF, reduced the number of neutrophils and total protein content, decreased the pulmonary capillary permeability, attenuated MPO activity and MDA contents and increased SOD activity and GSH content, and reduced ROS content in the LPS?challenged lung tissue. Conclusions Liensinine protects mice from LPS?induced acute lung injury by its anti?inflammatory and anti?oxidative activities.
-
WU Ya-qi, ZHONG Gen-shen, WU Min-na
2015,23(3):249-255, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2015.03.006
Abstract:
Objective To explore the objectivity and scientificity of fecal sampling, and to provide reference for investigating the relationship between intestinal microbes and diseases. Methods Terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism, degeneration gradient gel electrophoresis and real time fluorescent quantitative PCR techniques were applied to differentially analyze the bacterial community composition and abundance of intestinal contents and feces taken from different sites of BALB/c mouse intestine. Results The predominant T-RFLP fragments (T-RFs) in feces in the rectum and colon were 244 bp, 255 bp and 449 bp, however, those in feces of the small intestine including duodenum, jejunum and ileum were 60 bp, 73 bp, 261 bp, 268 bp and 272 bp, and with a larger variation of the bacterial community composition in various parts of the small intestine. The bacterial abundance in the contents of duodenum and jejunum were 6.9 log (copies)/g and 8.3 log (copies)/g, fewer than in the other parts of the intestine, while the bacterial abundance in the feces was as high as 11.8 log (copies)/g, being about 2 times higher than that in the duodenum and jejunum (P<0.05), and similar to that in the ileum and colon content (P>0.05). Conclusions The inter-mouse variations of bacterial community composition in the large intestine contents are small. The bacterial composition and abundance are similar suggest that studies on the relationship between large intestine especially colorectal microbiota and diseases may be conducted via fecal sampling.
-
WU Pengpeng, LIU Sensen, ZHANG Caiqin, ZHAO Yong, BAI Bing, WANG Jie, SHI Changhong
2021,29(4):440-447, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2021. 04. 003
Abstract:
Objective We aimed to characterize the relationship between the expression of the Alu gene in a model of human gastric cancer metastasis and the degree of gastric cancer metastasis in tissues and organs and establish a molecular biological method for the early evaluation of gastric cancer metastasis. Methods Alu gene expression plasmids were constructed from the genomic DNA of human gastric cancer cell lines SGC- 7901, MKN45 and the normal gastric mucosal cell line GES1. Alu gene expression in various concentration of gastric cancer cells SGC-7901, which was widely mentioned as human gastric metastasis cell line, was measured by real-time PCR. The relationship between different Alu expression of various concentration was measured by cycle threshold (Ct) value to modelling the standard curve. A human gastric cancer cell xenograft metastasis model was established by the subcutaneous inoculation of SGC-7901 and MKN45 cells into nude mice. The expression of Alu in the resulting tumors in the mice (in the liver, spleen, lung, kidney, and subcutaneous tissues) was then measured by real-time PCR, and a curve for the relationship between the expression of Alu and the degree of tumor metastasis in each tissue was constructed. Subsequently, fresh tumor samples from patients with gastric cancer were subcutaneously inoculated into nude mice to construct a xenograft model, and the relationships between Alu expression in the tissues of the mice and the degree of tumor metastasis in the organs of nude mice was similarly evaluated. Results The number of SGC-7901 cells negatively correlated with the cycle threshold (Ct) value for the Alu gene (R2 = 0. 9239). In the xenograft metastasis model, the expression of the Alu gene was higher in subcutaneous tumors than that in lung and liver metastases, and the expression of the Alu gene in lung and liver metastases was higer than normal nude mice. This was consistent with the result of histopathological examination. In the gastric cancer patient xenograft model, if there was no visible metastasis in the organs of nude mice, the expression of Alu gene (Ct 17. 86) was significantly higher(P< 0. 05)than that of normal nude mice (Ct 22. 18), and if there were metastatic lesions that were visible through the naked eye, the expression of Alu (Ct 14. 29) was very significantly higher than that of normal nude mice (P< 0. 01). Conclusions In a model of human gastric cancer metastasis, the expression of the Alu gene positively correlates with the degree of metastasis, namely the higher expression of Alu, the more metastatic tumor cells were present and the more obvious the metastatic foci were in each tissue.
-
DING Jun-ying, GAO Xiang, HONG Yan-ying, GUI Hong, WEI Zhi-you, LU You-ran, AN Shi-dong, CUI Xu-ran, GUO Yu-hong, LIU Qing-quan
2017,25(6):600-604, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2017.06.003
Abstract:
Objective To explore the preparation of a rat model of pneumonia model induced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa(PA) using different methods,and to lay the foundation for further studies.Methods 48 SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups:the control group (A),the intratracheal injection group (B),the trachea cannulation group (C) and the intranasal inoculation group (D).After intervention with different treatment modalities,the body weight,temperature,white blood cell count and lung pathological changes in the rats of all groups were detected at 5,10,15 days.Results 1.The behavior,body weight,temperature,leukocytes and pathological inflammatory changes of the lung in rats of the model groups were significantly different from that of control group.2.Pseudomonas aeruginosa was detected in rats of all the model groups,but the control group was negative.Conclusions Rat model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infected pneumonia can be successfully established by intranasal inoculation.This method can avoid the inflammatory interference from operation,and is simple and suitable for popularization.
-
MIAO Jinxin, SONG Shaohe, LI Xiumin
2020,28(2):0-0, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2020. 02. 018
Abstract:
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide, and the morbidity and mortality rate is increasing year by year with patients tending to be younger. The colorectal cancer mouse model increases our understanding of human colorectal cancer characteristics and cancer prevention and treatment. Murine models of colorectal cancer can be divided into spontaneous, induced, transplanted tumor, and transgenic models. However, none recapitulate all the characteristics of human colorectal cancer. The use of a specific mouse colorectal cancer model to address specific colorectal cancer research issues is critical. This paper has examined research literature both domestic and foreign to provide a review of the research progress of different mouse models of colorectal carcinoma over the past 20 years. The aim is to establish a suitable mouse model for the study of colorectal cancer.
-
LIAO Hui-dan, LONG Ling-ling, YAN Jie
2015,23(4):410-414, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2015.04.015
Abstract:
Objective To compare three methods for culture of fetal cortical neurons of SD rats and find out the suitable culture conditions of fetal cortical neurons in vitro. Methods The cortex of 16-18-day embryonic rat was used for culture in this study. Mechanical dissociation, trypsin digestion and papain digestion were applied respectively to the neuron culture. The morphological characteristics of neuronal cells at different time points were observed and neuron purity was identified by immunofluorescence staining assay. Results High purity of the fetal rat cortical neurons was successfully achieved by all the three culture methods, and each had distinct morphological characteristics at different time points. The purity of neurons was 96.28%, 95.63% and 97.34%, respectively, with no significant differences among the three groups (P>0.05).Conclusions The three culture methods are improved in our study. Stable neurons with high purity can be obtained by all the three methods respectively, and each of these methods has distinct characteristics.
-
ZHU Ming-hao, LU Tao-feng, NIU Yin-jie, ZHAO Li-li, CHEN Hong-yan
2016,24(3):288-292, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2016.03.014
Abstract:
Objective To describe the phenotype of NK cells in Bama miniature pigs, and establish an efficient activation and culture method for porcine cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells in vitro. Methods The porcine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by Percoll gradient centrifugation, and the phenotype of NK cells was tested by detecting the CD2+/CD8+/CD3- cell compartment. To establish an efficient activation and culture method for porcine CIK cells, we optimized the culture conditions to improve the CIK activation efficiency. Results Using the optimized induction culture conditions, the ratio of CIK (CD2+/CD8+/CD3-) cells was up to 43.63% at the fifth day, approximately 5.59 times increased compared with the initially separated PBMCs. Cell proliferation experiments showed that three obvious fluorescence peaks were observed on the fifth day. The results indicated that the induced CIK cells underwent three times cell division, in theory, about increased 8-fold compared with the initial separation of PBMCs. Furthermore, the qRT-PCR result of the surface markers of porcine NK cells also showed a similar variation tendency as the flow cytometry results. Conclusions Our findings demonstrate the successful establishment of an efficient activation and culture method for porcine CIK cells in vitro.
-
YE Miaoyong, ZHAO Fan, MA Ke, ZHANG Lizong, FANG Mingsun, SHOU Qiyang, MA Yinfeng, HUANG Wenjie, LYU Bodong
2019,27(6):753-759, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2019. 06. 010
Abstract:
Objective To explore the method for detecting intracavernosal pressure ( ICP) under electrostimulation of the cavernous nerve, and to compare the difference between two catheter materials (PE-50 tube needle and intravenous infusion needle) for measurent of ICP. Methods Thirty-six male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly selected: 16 were randomly selected as the control group, and the remaining 20 were used as the experimental group. Intraperitoneal injections of streptozotocin (60 mg/ kg) were given. After 8 weeks, 16 mice of type 1 diabetes were screened. The control and diabetic groups were further divided into two subgroups, with eight rats in each subgroup. ICP was evaluated using PE- 50 tube needles and other eight rats with intravenous infusion needles. Masson trichrome staining and apomorphine experiment confirmed that the diabetic erectile dysfunction (ED) rat model was successfully developed. After confirming the successful establishment of the model, the ICP tests of the penis were performed, and the erectile function data recorded using the PE-50 tube needle and the intravenous infusion needle were compared. Results Masson trichrome staining showed that the diabetic model group had a smaller area of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle, increased collagen area, and decreased ratio of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle area/ collagen area, all of which were statistically significant ( P < 0. 05). The number of erections in the diabetic model group was significantly lower than that in the control group ( P < 0. 01). Maximum ICP, ICP/ mean arterial pressure, and the area under the curve recorded in the normal and diabetic groups using PE-50 tube needles and intravenous infusion needles were not statistically significantly different ( P > 0. 05), but the slopes were significantly different ( P < 0. 05 or P < 0. 01). Conclusion Both the PE-50 tube needle and intravenous infusion needle can be used in the measurement of ICP during electrostimulation of the cavernous nerve.
-
PANG Lin-lin, ZHANG Hui-yong, YANG Guan-lin
2014,22(1):94-98, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2014.01.020
Abstract:
As one of the major domestic minipig strains, Guangxi Bama minipigs have the following characteristics: genetic stability, fecund species, lighter weight, large area of body surface covered with white hairs, many tissues and organs and biochemical indicators similar to those of humans and so on. All these characteristics make them being widely applied in medical research. Because of the similar anatomy and physiology in cardiovascular system, Bama minipigs have been used in the research of cardiovascular system. In our country, Bama minipigs are used for establishing models of cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial ischemia, patent foramen ovale and so on. Pigs are omnivore-animals and similar to human beings in lipid metabolism, so they can be used in the study of endocrine diseases. Bama minipigs have been used in modeling, genetic susceptibility and complication prevention of diabetes. Bama mini-pigs' digestive system is similar to that of humans, so they can be used as a model of digestive system diseases including chronic pancreatitis, rupture of colon and bilioenteric anastomosis. The aspect that large area of their body surface is covered with white hairs except their head and tail makes them ideal model of skin wound and healing of burns. Bama minipigs can be used for stomatological research for their similarity to human beings in the structure of the teeth and large crack. Bama minipigs have been applied for the research of pulp necrosis and the way of maxillary expansion. They are similar to human beings in anatomy, physiology and pathology, which makes them an appropriate provider for zenotransplantation. In the research of traditional Chinese medicine, Bama minipigs has been used as liver, spleen and femoral arteriovenous fistula hemorrhagic model to study curative effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese preparation.
-
MA Yuanyuan, LIU Chenghai, TAO Yanyan
2018,26(3):398-403, DOI: 10.3969/j. issn. 1005 -4847. 2018. 03. 020
Abstract:
Renal fibrosis is a common pathological pathway of chronic kidney diseases that leads to end?stage renal failure. The pathological changes include glomerulosclerosis and renal interstitial fibrosis. Ideal animal models for the study of pathologic mechanisms and drug development of chronic kidney disease are of great significance. At present, the method of establishment of animal models include drug or toxin induction, surgical models and gene knockout, etc. Different animal models have various characteristics of renal function and pathology, but can not completely simulate human chronic kidney disease, suggesting the complexity of chronic kidney diseases. So the preparation and research of the animal models is important for understanding the pathological mechanisms, prevention and treatment of renal fibrosis.
-
ZHANG Tingting, YANG Manman, WEI Qiang, LI Yanli, LI Lin, WANG Ran, HU Lihua, JIANG Fangfang, LIU Yu, ZHAO Weihua, LI Yong
2020,28(6):779-787, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2020. 06. 007
Abstract:
Objective The high-frequence mutant genotype Condons41 / 42 (-CTTT) of human thalassaemia- related HBB gene ( hHBB) was knocked into genome of the porcine fibroblasts by using CRISPR-Cas9 Site-specific recombination systems. Then the transfected fibroblasts were screened to establish homozygous cell lines with positive genotype. Methods (1) Synthesize the human HBB mutant with Condons41 / 42 (-CTTT) and cloned the left and right homology arm located at the flanking sequence of the pig HBB gene. (2) Then the HBB mutant was inserted between the left and right homology arm using infusion PCR method to building a final homologous recombination vector. ( 3) The sgRNA targeting pig HBB gene were designed using online software and then were verified its activity in pig PK15 cells. (4) Bama pig fetal fibroblasts were co-transfected with CRISPR/ Cas9 vector, sgRNA and pGH-LA-hHBB-RA using by electroporation and then were screened to establish single clone. Results (1) We synthesized full length of the hHBB CDS with a mutant Condons41 / 42 (-CTTT). The left and right homology arm of 1. 062 kb and 1. 024 kb were cloned from Bama pig genome. Then we constructed a final vector pGH-LA-hHBB-RA. ( 2) Two sgRNAs targeted pig HBB gene were validated in PK15 cells and used for further experiments. (3) Finally, we identified 15 single-cell clones of the porcine fibroblast carry the human HBB gene mutant. Conclusions We generated porcine fibroblast carrying the human HBB gene mutant using CRISPR/ Cas9. Our study provides key materials for scientist to generate pig models of human thalassemia.
-
PAN Yong-ming, JIN Ping, XU Jian-qin, LIU Jun-ping, CAI Zhao-wei, XU Mao-sheng, CHEN Min-li
2017,25(4):356-361, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2017.04.003
Abstract:
Objective To observe the morphological structures of WHBE rabbit brain in vivo based on 3.0 T magnetic resonance imaging system (MRI), accumulate the basic biological data of WHBE rabbit brain imaging, and provide a background information to further expand the WHBE rabbit application. Methods Nine healthy adult male WHBE rabbits were intravenously anesthetized with 3% pentobarbital sodium. 3.0 T MRI plus rabbit brain dedicated coil was used to perform routine transverse and sagittal scans, and the size of brain structures were measured. Results MRI scanning can be successfully performed to obtain sagittal and transverse T2WI or T1WI images of WHBE rabbit brain in vivo, and can be clearly observed the basic structures of WHBE rabbit brains in vivo, such as olfactory bulb, cerebrum, cerebellum and pituitary gland. In addition, high signal was found in the hippocampus of the left and right temporal lobes in 4 rabbits with T2WI, but also low signal appeared in the corresponding regions in T1WI, and the others were not abnormal. Meanwhile, the reference data of frontal lobe, hippocampus, cerebrum, lateral ventricles, pituitary gland and other related anatomical structures were also obtained. Conclusions Using the 3.0 T magnetic resonance imaging system and rabbit brain coil,the morphological and anatomical structures of rabbit brain can be clearly observed, and the basic imaging data of WHBE rabbits brain have been established preliminarily.
-
LI Shumin, ZHANG Min, WANG Peng, HONG Fan, WANG Chen, ZHANG Yue, GENG Zhenyang, YANG Xinyu, HE Xiaoxiao, SUN Ying, YANG Fang
2018,26(5):548-553, DOI: 10.3969/j. issn. 1005 - 4847. 2018. 05. 002
Abstract:
Objective To provide a reference for studies of monitoring lung function in mice, this study was aimed to test the indexes of a non?invasive measurement of lung function in mice. Methods Lung function indexes of 460 C57BL/6 mice were detected by whole?body plethysmography. The results were analyzed, and the range of reference values was determined by the percentile method. Results Normal ranges for the following measures were found: inspiration time was 64. 7 (55. 30 -82. 60) ms, expiration time was 83. 4 (71. 70 -109. 20) ms, Rpef was 0. 21 (0. 16 -0. 28) ms, end?inspiratory pause was 2. 19 (1. 96 -3. 76) ms, end?expiratory pause was 1. 67 (0. 12 -9. 15) ms, tidal volume was 0. 44 (0. 25 -0. 58) mL, enhanced pause was 1. 29 (0. 91 -2. 00) ms, pause was 1. 18 (1. 00 -1. 64) ms, expiratory flow?50 was 0. 64 (0. 30 -0. 98) mL/ s, relaxation time was 39. 0 (32. 40 -51. 50) ms, peak inspiratory flow was 9. 74 (5. 33 -12. 83) mL/ s, peak expiratory flow was 9. 86 (5. 12 -13. 47) mL/ s, inspiratory frequency was 412 (331 - 474) BPM, and minute volume was 174. 4 (86. 69 -235. 04) mL. Conclusions The normal reference ranges from non?invasive lung monitoring in C57BL/6 mice can be used as a reference for basic research on respiratory diseases.
-
2020,28(1):100-107, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2020. 01. 015
Abstract:
Objective A hand-made mouse restraint device was designed to establish an immobilization stress model for related stress experiments. Methods A centrifuge tube with a size suitable for the mouse body was used to prepare a mouse restraint device. The mouse restraint device was applied to maternal mice for 3 hours every day for 21 days starting 2 days after delivery to stimulate repeated immobilization stress. The maternal mice were separated from their offspring after delivery. Results In this postpartum mouse immobilization stress model, ghrelin expression was increased in the stomach, hypothalamus and serum, 5-HT2 receptor expression was decreased, and depression-like symptoms, such as decreased exercise and offspring growth retardation, were observed. Conclusions A new device is constructed to establish an immobilization stress model in postpartum mice. Results from repeated experiments show good stability and reproducibility, suggesting that this model can be used to study immobilization stress in mice.
-
MA Chang, GUO Jianmin, XIE Songqiang, YANG Wei
2019,27(2):266-270, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2019. 02. 022
Abstract:
Leukemia is often referred to as a “blood cancer”. The basic characteristic of the disease is thatleukemic cells become malignant and cause unrestricted proliferation in the bone marrow and other hematopoietic tissues.Then, these cells infiltrate all tissues and organs of the body causing various symptoms, and make patients prone to seriousinfections and life-threatening complications such as sepsis, hemorrhage, intestinal failure or hyperuricemia. Therefore,research on the treatment of leukemia using laboratory animal models is of great significance. For the study of leukemia,mice are similar to humans in terms of biology, genetics, and hematopoietic systems, and are, therefore, ideal models forleukemia research. This article reviews the mouse models of leukemia used commonly in studies both in China and abroad in the past 5 years.
-
LIU Yu-ting, GAO Yan-xiang, WANG Shan-shan, REN Wei, SUN Wei-liang, YU Chang-an, ZHENG Jin-gang
2017,25(4):399-403, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2017.04.010
Abstract:
Objective To establish a mouse model of aorta dissection (AD) by β-aminopropionitrile (BAPN) in drinking water + subcutaneously pumped angiotensin Ⅱ (Ang Ⅱ) infusion. Methods Forty 3-week-old C57B1/6J male mice were randomly divided into two groups. All animals received 0.1 g/kg/d BAPN in drinking water for 4 weeks. Then the BAPN drinking + saline infusion group and BAPN drinking + Ang Ⅱ infusion group received continuous saline or Ang Ⅱ (1,000 ng/kg/min) infusion, respectively, via subcutaneous osmotic minipump for 72 hour. The mice were restricted in a noninvasive computerized tail-cuff system and their arterial systolic blood pressure and heart rate were monitored. Autopsy was performed if a mouse died during the experiment. At the end of the experiment, mice were sacrificed by injection with an overdose of sodium pentobarbital and the aortas were harvested. The formation of aortic false lumen was observed by pathology using hematoxylin-eosin staining. Results The overall incidence of AD in the BAPN drinking administration +Ang Ⅱ infusion group was 95%, whereas the incidence of AD in the BAPN drinking administration +saline infusion group was only 5%. The mortality from dissecting aneurysm rupture was 24% in the BAPN drinking administration +Ang Ⅱ infusion group during the experiment. Pathological examination of the aortic cross-sections clearly showed the formation of blood-filled false lumens induced by Ang Ⅱ. Conclusions A mouse model with high incidence of aortic dissection is successfully established.
-
HUANG Shuwu, MIN Fangui, WANG Jing, LUO Yinzhu, HE Lifang, CHEN Meiling, PAN Jinchun
2021,29(6):777-784, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2021. 06. 009
Abstract:
Objective To conduct a comparative study of the intestinal flora in six common strains of mice and rats. Methods In this study, 210 feces or intestinal content samples were collected from 150 SPF mice and rats from three experimental animal production units. PCR amplification of the samples was carried out based on common primers of the bacterial 16S rDNA V3-V4 region, and then the Illumina HiSeq 2500 high-throughput system was used for sequencing. Based on the animal source, breed, gender, age and intestinal segmentation ( duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, colon and rectum) factors, bioinformatics method and cluster analysis of differences were applied to analyze the diversity in the structure of the intestinal flora in rats and mice. Results The intestinal flora of experimental mice or rats with the same source had the highest similarity, whereas the intestinal flora of experimental mice and rats showed certain differences due to the type of species. The intestinal flora from different intestinal segments of experimental mice exhibited certain differences, and stool samples were more similar to the colonic intestinal flora. Under the same breeding and living environment conditions, the species, age and intestinal segment of experimental mice and rats are the main endogenous factors that determine the structure of the intestinal flora, and the effect of strain and gender on their intestinal flora is minimal. Conclusions This study revealed the diversity and differences in the intestinal flora of common mice, explored the influencing factors of the host intestinal flora, and provided more basic data for the relationship between intestinal flora and diseases.
-
LI Yuan, ZHAO Guang-ming, DONG Jian-xun, LU Guang-lin, ZHANG Xu-hui, WANG Le-ping
2014,22(1):63-66, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2014.01.012
Abstract:
Objective To observe the effects of different modeling methods on the wound morphology and healing time of chronic skin ulcers in diabetic rats. Methods SD rats (n=50) were randomly divided into five groups, 10 rats in each group: skin defect group (group QS: dermal deficiency), diabetes group (group DM: STZ injection+skin excision), diabetes plus Staphylococcus aureus group (group DMJJ: STZ injection+skin excision+bacterial infection), diabetes plus hydrocortisone group (group DMJS: STZ injection+skin excision+hydrocortisone intervention) and diabetes plus hydrocortisone and implantation of foreign body group (DMYW group: STZ injection+skin excision+hydrocortisone intervention + foreign body embedded). The rats were measured for body weight and wound healing every day, and blood glucose after stable diabetes once a week. The rats were sacrificed 12 days later and the skin lesions were examined by histopathology.Results The healing rate of the DMYW group was significantly slower than that in the other groups (P<0.01). At 12 days after modeling, the healing rate of the DMYW group was significantly lower than that of the remaining groups (P<0.01), while the healing rates were not significantly different among the remaining groups.Conclusions The modeling method of DMYW group can show skin wounds similar to the clinical characteristics of "Yin syndrome", and the addition of foreign body implantation significantly prolongs the rat skin healing time.
-
2020,28(6):824-830, DOI: 10. 3969 / j.issn.1005-4847. 2020. 06. 013
Abstract:
Objective To explore the protective effect and associated mechanism of action of estrogen on oxidative stress injury of mouse MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts (OB). Methods MC3T3-E1 cells cultured in vitro were divided into a blank control group, H2O2 group (300 μmol / L), H2O2+ 0. 1 μmol / L estrogen group, H2O2+ 1 μmol / L estrogen group, H2O2+ 10 μmol / L estrogen group, and H2O2+ 1 mmol / L NAC group, which were incubated with the corresponding concentrations of the drugs. The proliferative activities of cells in each group were determined by CCK-8. The apoptosis rate and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) were determined by flow cytometry. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were determined using kits. The level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was determined by a fluorescent probe method . The expression of Smad5, Runx2, Bax, Bcl-2, and cleaved Caspase-3 proteins was determined by western blotting. Results Compared with those in the blank control group, the proliferative activities of cells were significantly decreased (P< 0. 05), apoptosis rate and positive rate of JC-1 cells were significantly increased (P< 0. 05), levels of MDA and ROS were significantly increased (P< 0. 05), SOD activity was significantly decreased (P< 0. 05), expression of Smad5, Runx2, and Bcl-2 proteins was significantly decreased ( P < 0. 05), and expression of Bax and cleaved Caspase-3 proteins was significantly increased in the H2O2 group (P< 0. 05). Compared with those in the H2O2 group, proliferative activities of cells were significantly increased (P< 0. 05), apoptosis rate and positive rate of JC-1 cells were significantly decreased (P< 0. 05), levels of MDA and ROS were significantly decreased (P< 0. 05), SOD activity was significantly increased (P< 0. 05), expression of Smad5, Runx2, and Bcl-2 proteins was significantly increased (P< 0. 05), and expression of Bax and cleaved Caspase-3 proteins was significantly decreased in the H2O2+ 1 μmol / L estrogen group, H2O2+ 10 μmol / L estrogen group, and H2O2 + 1 mmol / L NAC group (P< 0. 05). Conclusions Estrogen may reduce the level of ROS in MC3T3-E1 cells damaged by oxidative stress and improve the differentiation ability of cells by activating the expression of the Smad5 / Runx2 signal axis.